MPxNode Class Reference
[OpenMaya - API module for common classes, Proxy classes]
#include <MPxNode.h>
Detailed Description
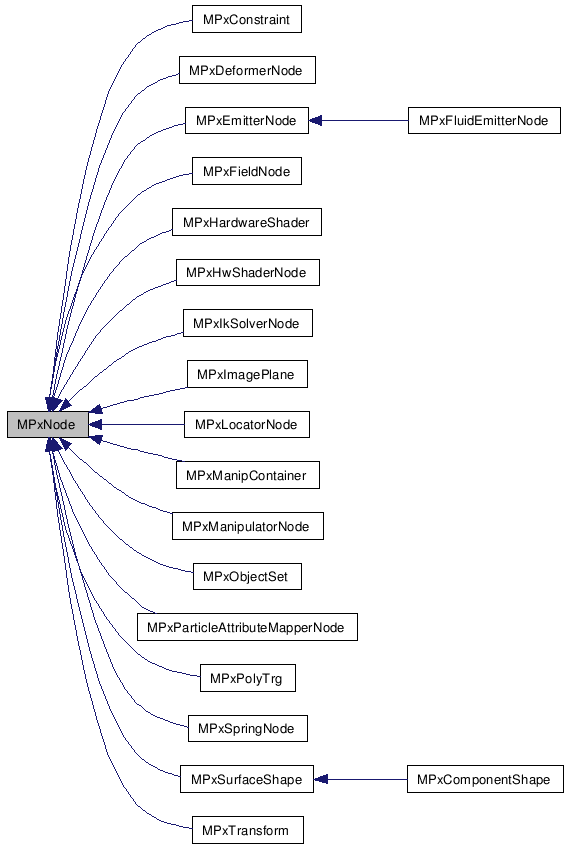
Base class for user defined dependency nodes.MPxNode is the the parent class for user defined dependency nodes. A dependency node is an object that resides in the dependency graph. It computes output attributes based on a set of input attributes. When an input changes, the compute method is called for each dependent output.
The dependency graph is made up of nodes that have connections between their attributes. When an attribute changes, recomputation propagates through the graph until all affected values have been updated.
When writing a dependency node, there is a very basic rule that should be observed. The outputs should be calculated only using the values of the inputs. All information about the world outside the node should come from input attributes. If this rule is not observed, then the results may be unpredictable.
All dependency nodes have four basic attributes. Documentation for them may be found with the documentation for the dependency nodes in Maya. Only one attribute requires special attention by node developers. Developers must decide whether to support the HasNoEffect setting of the state attribute. {HasNoEffect} means that a node should pass through all data without performing computations on it. For example, a deformer node will pass geometry through unmodified when state is set to HasNoEffect. It is up the the plug-in writer to observe the HasNoEffect mode if it is relevant to the type of node.
-
affectsNode.cpp, animCubeNode.cpp, anisotropicShader.cpp, apiMeshCreator.h, arcLenNode.cpp, backfillShader.cpp, blindDataMesh.h, brickShader.cpp, buildRotationNode.cpp, cellShader.cpp, cgfxShaderNode.cpp, cgfxShaderNode.h, cgfxVector.h, checkerShader.cpp, circleNode.cpp, clearcoat.cpp, closestPointOnCurveNode.h, compositingShader.cpp, contrastShader.cpp, cvColorShader.cpp, depthShader.cpp, displacementShader.cpp, exampleMRampAttribute.cpp, flameShader.cpp, fullLoftNode.cpp, gammaShader.cpp, genericAttributeNode.cpp, geomShader.cpp, GLSLShaderNode.cpp, GLSLShaderNode.h, hlslShader.cpp, hlslShader.h, interpShader.cpp, jitterNode.cpp, lambertShader.cpp, latticeNoise.h, lavaShader.cpp, lightShader.cpp, mixtureShader.cpp, multiCurveNode.cpp, noiseShader.cpp, phongShader.cpp, pointOnMeshInfoNode.h, pointOnSubdNode.h, polyModifierNode.h, renderAccessNode.cpp, shadowMatteShader.cpp, shellNode.cpp, shiftNode.cpp, simpleLoftNode.cpp, sineNode.cpp, slopeShaderNode.h, solidCheckerShader.cpp, stringFormatNode.cpp, testNobjectNode.h, testNucleusNode.h, transCircleNode.cpp, volumeShader.cpp, and weightListNode.cpp.
Public Types | |
| enum | Type { kDependNode, kLocatorNode, kDeformerNode, kManipContainer, kSurfaceShape, kFieldNode, kEmitterNode, kSpringNode, kIkSolverNode, kHardwareShader, kHwShaderNode, kTransformNode, kObjectSet, kFluidEmitterNode, kImagePlaneNode, kParticleAttributeMapperNode, kConstraintNode, kManipulatorNode, kLast } |
| Defines the type of node. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| MPxNode () | |
| virtual | ~MPxNode () |
| virtual void | postConstructor () |
| virtual MStatus | compute (const MPlug &plug, MDataBlock &dataBlock) |
| virtual bool | getInternalValueInContext (const MPlug &plug, MDataHandle &dataHandle, MDGContext &ctx) |
| virtual bool | setInternalValueInContext (const MPlug &plug, const MDataHandle &dataHandle, MDGContext &ctx) |
| virtual bool | getInternalValue (const MPlug &plug, MDataHandle &dataHandle) |
| This method is obsolete. | |
| virtual bool | setInternalValue (const MPlug &plug, const MDataHandle &dataHandle) |
| This method is obsolete. | |
| virtual int | internalArrayCount (const MPlug &plug, const MDGContext &ctx) const |
| virtual void | copyInternalData (MPxNode *) |
| virtual MStatus | legalConnection (const MPlug &plug, const MPlug &otherPlug, bool asSrc, bool &isLegal) const |
| virtual MStatus | legalDisconnection (const MPlug &plug, const MPlug &otherPlug, bool asSrc, bool &isLegal) const |
| virtual MStatus | setDependentsDirty (const MPlug &plug, MPlugArray &plugArray) |
| virtual MStatus | connectionMade (const MPlug &plug, const MPlug &otherPlug, bool asSrc) |
| virtual MStatus | connectionBroken (const MPlug &plug, const MPlug &otherPlug, bool asSrc) |
| virtual bool | isPassiveOutput (const MPlug &plug) const |
| virtual MStatus | shouldSave (const MPlug &plug, bool &isSaving) |
| virtual MPlug | passThroughToOne (const MPlug &plug) const |
| virtual bool | passThroughToMany (const MPlug &plug, MPlugArray &plugArray) const |
| MTypeId | typeId () const |
| MString | typeName () const |
| MString | name () const |
| virtual Type | type () const |
| virtual bool | isAbstractClass () const |
| MObject | thisMObject () const |
| MStatus | setExistWithoutInConnections (bool flag) |
| bool | existWithoutInConnections (MStatus *ReturnStatus=NULL) const |
| MStatus | setExistWithoutOutConnections (bool flag) |
| bool | existWithoutOutConnections (MStatus *ReturnStatus=NULL) const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static MStatus | addAttribute (const MObject &attr) |
| static MStatus | inheritAttributesFrom (const MString &parentClassName) |
| static MStatus | attributeAffects (const MObject &whenChanges, const MObject &isAffected) |
Static Public Attributes | |
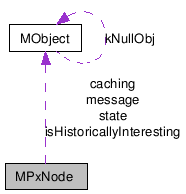
| static MObject | message |
| message attribute | |
| static MObject | isHistoricallyInteresting |
| is historically interesting attribute | |
| static MObject | caching |
| caching attribute | |
| static MObject | state |
| state attribute | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| MDataBlock | forceCache (MDGContext &ctx=MDGContext::fsNormal) |
| USE _forceCache() IN SCRIPT. | |
| void | setMPSafe (bool flag) |
| USE _setMPSafe() IN SCRIPT. | |
| MStatus | setDoNotWrite (bool flag) |
| bool | doNotWrite (MStatus *ReturnStatus=NULL) const |
Member Enumeration Documentation
| enum MPxNode::Type |
Defines the type of node.
- Enumerator:
-
kDependNode Custom node derived from MPxNode. kLocatorNode Custom locator derived from MPxLocatorNode. kDeformerNode Custom deformer derived from MPxDeformerNode. kManipContainer Custom container derived from MPxManipContainer. kSurfaceShape Custom shape derived from MPxSurfaceShape. kFieldNode Custom field derived from MPxFieldNode. kEmitterNode Custom emitter derived from MPxEmitterNode. kSpringNode Custom spring derived from MPxSpringNode. kIkSolverNode Custom IK solver derived from MPxIkSolverNode. kHardwareShader Custom shader derived from MPxHardwareShader. kHwShaderNode Custom shader derived from MPxHwShaderNode. kTransformNode Custom transform derived from MPxTransform. kObjectSet Custom set derived from MPxObjectSet. kFluidEmitterNode Custom fluid emitter derived from MpxFluidEmitterNode. kImagePlaneNode Custom image plane derived from MPxImagePlane. kParticleAttributeMapperNode Custom particle attribute mapper derived from MPxParticleAttributeMapperNode. kConstraintNode Custom constraint derived from MPxConstraint. kManipulatorNode Custom manipulator derived from MPxManipulatorNode. kLast Last value, used for counting.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| MPxNode::MPxNode | ( | ) |
| MPxNode::~MPxNode | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Destructor.
Member Function Documentation
| void MPxNode::postConstructor | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Post constructor.
Internally maya creates two objects when a user defined node is created, the internal MObject and the user derived object. The association between the these two objects is not made until after the MPxNode constructor is called. This implies that no MPxNode member function can be called from the MPxNode constructor. The postConstructor will get called immediately after the constructor when it is safe to call any MPxNode member function.
Reimplemented in MPxPolyTrg, and MPxTransform.
- anisotropicShader.cpp, apiMeshShape.h, backfillShader.cpp, brickShader.cpp, cellShader.cpp, cgfxShaderNode.h, checkerShader.cpp, clearcoat.cpp, compositingShader.cpp, contrastShader.cpp, curvedArrowsNode.cpp, cvColorShader.cpp, depthShader.cpp, displacementShader.cpp, flameShader.cpp, gammaShader.cpp, geometrySurfaceConstraint.h, geomShader.cpp, GLSLShaderNode.h, hlslShader.h, hwAnisotropicShader_NV20.h, hwColorPerVertexShader.cpp, hwDecalBumpShader_NV20.h, hwManagedTextureShader.cpp, hwPhongShader.h, hwReflectBumpShader_NV20.h, hwRefractReflectShader_NV20.h, hwToonShader_NV20.h, hwUnlitShader.h, interpShader.cpp, lambertShader.cpp, lavaShader.cpp, lightShader.cpp, mixtureShader.cpp, noiseShader.cpp, phongShader.cpp, quadricShape.cpp, renderAccessNode.cpp, shadowMatteShader.cpp, slopeShaderNode.h, solidCheckerShader.cpp, squareScaleManipContext.h, and volumeShader.cpp.
| MStatus MPxNode::compute | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| MDataBlock & | block | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
This method should be overridden in user defined nodes.
Recompute the given output based on the nodes inputs. The plug represents the data value that needs to be recomputed, and the data block holds the storage for all of the node's attributes.
The MDataBlock will provide smart handles for reading and writing this node's attribute values. Only these values should be used when performing computations.
When evaluating the dependency graph, Maya will first call the compute method for this node. If the plug that is provided to the compute indicates that that the attribute was defined by the Maya parent node, the compute method should return MS::kUnknownParameter. When this occurs, Maya will call the internal Maya node from which the user-defined node is derived to compute the plug's value.
This means that a user defined node does not need to be concerned with computing inherited output attributes. However, if desired, these can be safely recomputed by this method to change the behaviour of the node.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug plug representing the attribute that needs to be recomputed [in] block data block containing storage for the node's attributes
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Compute was successful
- MS::kFailure Compute failed
Reimplemented in MPxEmitterNode, MPxFieldNode, MPxFluidEmitterNode, MPxParticleAttributeMapperNode, MPxPolyTrg, and MPxTransform.
- affectsNode.cpp, animCubeNode.cpp, anisotropicShader.cpp, apiMeshCreator.h, apiMeshShape.h, arcLenNode.cpp, backfillShader.cpp, blindDataMesh.h, blindDataShader.h, brickShader.cpp, buildRotationNode.cpp, cellShader.cpp, cgfxShaderNode.h, cgfxVector.h, checkerShader.cpp, circleNode.cpp, clearcoat.cpp, closestPointOnCurveNode.h, compositingShader.cpp, contrastShader.cpp, curvedArrowsNode.cpp, cvColorNode.cpp, cvColorShader.cpp, depthShader.cpp, displacementShader.cpp, exampleMRampAttribute.cpp, flameShader.cpp, footPrintManip.cpp, footPrintNode.cpp, fullLoftNode.cpp, gammaShader.cpp, genericAttributeNode.cpp, geometrySurfaceConstraint.h, geomShader.cpp, GLSLShaderNode.h, hwColorPerVertexShader.cpp, hwDecalBumpShader_NV20.h, hwPhongShader.h, hwReflectBumpShader_NV20.h, hwRefractReflectShader_NV20.h, hwToonShader_NV20.h, hwUnlitShader.h, interpShader.cpp, jitterNode.cpp, lambertShader.cpp, latticeNoise.h, lavaShader.cpp, lightShader.cpp, mixtureShader.cpp, multiCurveNode.cpp, noiseShader.cpp, phongShader.cpp, pointOnMeshInfoNode.h, pointOnSubdNode.h, quadricShape.cpp, renderAccessNode.cpp, shadowMatteShader.cpp, shellNode.cpp, shiftNode.cpp, simpleLoftNode.cpp, simpleSpring.h, sineNode.cpp, slopeShaderNode.h, solidCheckerShader.cpp, stringFormatNode.cpp, swissArmyManip.cpp, testNobjectNode.h, testNucleusNode.h, transCircleNode.cpp, volumeShader.cpp, and weightListNode.cpp.
| bool MPxNode::getInternalValueInContext | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| MDataHandle & | dataHandle, | |||
| MDGContext & | ctx | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
This method is overriden by nodes that store attribute data in some internal format.
The internal state of attributes can be set or queried using the setInternal and internal methods of MFnAttribute.
When internal attribute values are queried via getAttr or MPlug::getValue this method is called.
NOTE: the default behaviour of this method is to call MPxNode::getInternalValue( const MPlug&, const MDataHandle& ) if the context is normal.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug the attribute that is being queried [out] dataHandle the dataHandle to store the attribute value [in] ctx the context the method is being evaluated in
- Returns:
- true the attribute was place on the datablock
- false could not handle the specified attribute, pass this request to the default handler
| bool MPxNode::setInternalValueInContext | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| const MDataHandle & | dataHandle, | |||
| MDGContext & | ctx | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
This method is overriden by nodes that store attribute data in some internal format.
The internal state of attributes can be set or queried using the setInternal and internal methods of MFnAttribute.
When internal attribute values are set via setAttr or MPlug::setValue this method is called.
Another use for this method is to impose attribute limits.
NOTE: the default behaviour of this method is to call MPxNode::setInternalValue( const MPlug&, const MDataHandle& ) if the context is normal.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug the attribute that is being set [in] dataHandle the dataHandle containing the value to set [in] ctx the context the method is being evaluated in
- Returns:
- true the attribute was set
- false could not handle the specified attribute, pass this request to the default handler
| bool MPxNode::getInternalValue | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| MDataHandle & | dataHandle | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
This method is obsolete.
- Deprecated:
- Use the method MPxNode::getInternalValueInContext instead.
| bool MPxNode::setInternalValue | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| const MDataHandle & | dataHandle | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
This method is obsolete.
- Deprecated:
- Use the method MPxNode::setInternalValueInContext instead.
| int MPxNode::internalArrayCount | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| const MDGContext & | ctx | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
This method is overriden by nodes that have internal array attributes which are not stored in Maya's datablock. This method is used by Maya to determine the non-sparse count of array elements during file io. If the internal array is stored sparsely, you should return the maximum index of the array plus one. If the internal array is non-sparse then return the length of the array.
This method does not need to be implemented for attributes that are stored in the datablock since Maya will use the datablock size.
If this method is overriden, it should return -1 for attributes which it does not handle. Maya will use the datablock size to determine the array length when -1 is returned.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug the array plug [in] ctx the context
| void MPxNode::copyInternalData | ( | MPxNode * | node | ) | [virtual] |
This method is overriden by nodes that store attribute data in some internal format.
On duplication this method is called on the duplicated node with the node being duplicated passed as the parameter. Overriding this method gives your node a chance to duplicate any internal data you've been storing and manipulating outside of normal attribute data.
- Parameters:
-
[in] node the node that is being duplicated
Reimplemented in MPxTransform.
| MStatus MPxNode::legalConnection | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| const MPlug & | otherPlug, | |||
| bool | asSrc, | |||
| bool & | isLegal | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
This method allows you to check for legal connections being made to attributes of this node.
You should return kUnknownParameter to specify that maya should handle this connection if you are unable to determine if it is legal.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug attribute on this node [in] otherPlug attribute on other node [in] asSrc is this plug a source of the connection [in] isLegal set this to true if the connection is legal, false otherwise
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Operation successful
- MS::kUnknownParameter Unknown attribute
| MStatus MPxNode::legalDisconnection | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| const MPlug & | otherPlug, | |||
| bool | asSrc, | |||
| bool & | isLegal | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
This method allows you to check for legal disconnections being made to attributes of this node.
You should return kUnknownParameter to specify that maya should handle this disconnection if you are unable to determine if it is legal.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug attribute on this node [in] otherPlug attribute on other node [in] asSrc is this plug a source of the connection [out] isLegal set this to true if the disconnection is legal, false otherwise
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Operation successful
- MS::kUnknownParameter Unknown attribute
| MStatus MPxNode::setDependentsDirty | ( | const MPlug & | plugBeingDirtied, | |
| MPlugArray & | affectedPlugs | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
This method can be overridden in user defined nodes to specify which plugs should be set dirty based upon an input plug {plugBeingDirtied} which Maya is marking dirty. The list of plugs for Maya to mark dirty is returned by the plug array {affectedPlugs}. This method handles both dynamic as well as non-dynamic plugs and is useful in the following ways:
- Allows attributeAffects-style relationships to be handled for dynamically-added attributes. Since MPxNode::attributeAffects can only be used with non-dynamic attributes, use of this method allows a way for all attributes of a node to affect one another, both dynamic and non-dynamic.
- Provides more flexible relationships than what is available with MPxNode::attributeAffects. For example, you may wish to not dirty plugs when the current frame is one. However, as the routine is called during dirty propagation, there are restrictions on what can be done within the routine, most importantly you must not cause any dependency graph computation. For details, see the IMPORTANT NOTE below.
The body of a user-implemented setDependentsDirty() implementation might look like the following example, which causes the plug called "B" to be set dirty whever plug "A" is changed, i.e. A affects B.
const MString exampleNode::A( "A" ); // Dynamic attribute "A" MObject exampleNode::attrB; // Non-dynamic attribute "B" MStatus exampleNode::setDependentsDirty( const MPlug &plugBeingDirtied, MPlugArray &affectedPlugs ) { // This example shows a dynamic attribute (A) affecting a // non-dynamic attribute (B). For an example of a dynamic // affecting a dynamic, please the the developer's toolkit // example plug-in, affectsNode.cpp. // if ( plugBeingDirtied.partialName() == A ) { // "A" is being dirtied. We want "A" to affect "B", so we // add "B" to the list of plugs for Maya to dirty. Once again, // please see the IMPORTANT NOTE about what you can and // cannot do within a setDependentsDirty() routine. // MObject thisNode = thisMObject(); MPlug pB( thisNode, exampleNode::attrB ); affectedPlugs.append( pB ); } return( MS::kSuccess ); }
In the above example, whenever plugBeingDirtied is A, we add B to affectedPlugs so that Maya will dirty B and also any plugs which depend upon B.
For cases where multi compound attributes are dirtied, it is the programmer's responsibility to define ALL affects relationships. Dirtying the parent plug of a multi does not imply that all of its children will be marked dirty. Likewise, dirtying a child attribute does not imply the parent of the multi is dirty. This must be explicitly defined using the affected plug array. The following example demonstrates how one would dirty both the element affected and the parent plug.
MObject exampleNode::inputAttr; // Non-dynamic multi-input attribute. MObject exampleNode::outputAttr; // Non-dynamic multi-output attribute. MStatus exampleNode::setDependentsDirty(MPlug const & inPlug, MPlugArray & affectedPlugs) { if ( inPlug.attribute() != inputAttr ) { return MS::kSuccess; } MPlug outArrayPlug(thisMObject(),outputAttr); if (inPlug.isElement()) { // First dirty the output output element first. // Of course, dirty output element itself MPlug elemPlug = outArrayPlug.elementByLogicalIndex( inPlug.logicalIndex()); affectedPlugs.append(elemPlug); // We also need to dirty the parent. // affectedPlugs.append(outArrayPlug); } else { // Mark the parent output plug as dirty. // affectedPlugs.append(outArrayPlug); // Also visit each element. // unsigned int i,n = outArrayPlug.numElements(); for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { MPlug elemPlug = outArrayPlug.elementByPhysicalIndex(i); affectedPlugs.append(elemPlug); } } return MS::kSuccess; }
IMPORTANT NOTE: since the setDependentsDirty() method is called during dirty propagation, you must be careful not to perform any dependency graph computations from within the routine. Instead, if you want to know the value of a plug, use MDataBlock::outputValue() because it will not result in computation (and thus recursion). In general, the majority of {setDependentsDirty()} methods which users will implement should involve only fixed relationships. In the rare occurence where you need to look at plug values, please heed the warning with {MDataBlock::outputValue()} and use plugs which contain values which you know to be up to date prior to the start of dirty propagation.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plugBeingDirtied plug which is being set dirty by Maya [in] affectedPlugs the programmer should add any plugs which they want to set dirty to this list.
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Dirtying was successful
- MS::kFailure Dirtying failed
| MStatus MPxNode::connectionMade | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| const MPlug & | otherPlug, | |||
| bool | asSrc | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
This method gets called when connections are made to attributes of this node.
You should return kUnknownParameter to specify that maya should handle this connection or if you want maya to process the connection as well.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug attribute on this node [in] otherPlug attribute on other node [in] asSrc is this plug a source of the connection
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Operation successful
- MS::kUnknownParameter Unknown attribute
| MStatus MPxNode::connectionBroken | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| const MPlug & | otherPlug, | |||
| bool | asSrc | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
This method gets called when connections are broken with attributes of this node.
You should return kUnknownParameter to specify that maya should handle this connection or if you want maya to process the connection as well.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug attribute on this node [in] otherPlug attribute on other node [in] asSrc is this plug a source of the connection
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Operation successful
- MS::kUnknownParameter Unknown attribute
| bool MPxNode::isPassiveOutput | ( | const MPlug & | plug | ) | const [virtual] |
This method may be overridden by the user defined node if it wants to provide output attributes which do not prevent value modifications to the destination attribute. For example, output plugs on animation curve nodes are passive. This allows the attributes driven by the animation curves to be set to new values by the user.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug plug representing output in question
- Returns:
- true indicates passive
This method may be overridden by the user defined node. It should only be required to override this on rare occasions.
This method determines whether a specific attribute of this node should be written out during a file save. The default behavior is to only write the value if it differs from the default and is not being supplied by a connection. This behavior should be sufficient in most cases. This method is not called for ramp attributes since they should always be written.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug plug representing the attribute to be saved [in] isSaving boolean telling whether to save or not
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Operation successful
- MS::kUnknownParameter Unknown attribute
This method may be overriden by nodes that have a one-to-one relationship between an input attribute and a corresponding output attribute. This method is used by Maya to perform the following capabilities:
- When this node is deleted, the delete command will rewire the source of the input attribute to the destination of the output attribute if the source and destination are connected to nodes that are not deleted.
- History traversal algorithms such as the bakePartialHistory command use this method to direct its traversal through a shape's construction history.
- The base class Maya implementation of passThroughToAll will call this method if passThroughToAll returns false.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug the plug
- Returns:
- The corresponding plug, or an empty plug if no corresponding plug exists
| bool MPxNode::passThroughToMany | ( | const MPlug & | plug, | |
| MPlugArray & | plugArray | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
This method is overriden by nodes that want to control the traversal behavior of some Maya search algorithms which traverse the history/future of shape nodes looking for directly related nodes. In particular, the Artisan paint code uses this method when searching for paintable nodes, and the disk cache code uses this method when searching for upstream cacheFile nodes.
If this method is not implemented or returns false, the base class Maya implementation of this method calls passThroughToOne and returns the results of that call.
- Parameters:
-
[in] plug the plug [in] plugArray the corresponding plugs
- Returns:
- true if plug was handled, false to invoke base class implementation
| MTypeId MPxNode::typeId | ( | ) | const |
Returns the TYPEID of this node. The TYPEID is a four byte identifier that uniquely identifies this type of node to the binary file format.
It is not necessary to override this method.
- Returns:
- Type id of the node
| MString MPxNode::typeName | ( | ) | const |
Returns the type name of this node. The type name identifies the node type to the ASCII file format. It may also be used with the MEL command "createNode" to create a new node of this type.
It is not necessary to override this method.
- Returns:
- Type name of the node
| MString MPxNode::name | ( | ) | const |
Returns the name of this particular instance of this class. Each object in the dependency graph has a name. This name will be used by the UI and by MEL.
It is not necessary to override this method.
- Returns:
- Type id of the node
| MPxNode::Type MPxNode::type | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Returns the type of node that this is. This is used to differentiate user defined nodes that are derived off different MPx base classes.
It is not necessary to override this method.
- Returns:
- Type of the node
Reimplemented in MPxDeformerNode, MPxEmitterNode, MPxFieldNode, MPxFluidEmitterNode, MPxHardwareShader, MPxHwShaderNode, MPxIkSolverNode, MPxImagePlane, MPxLocatorNode, MPxManipContainer, MPxObjectSet, MPxParticleAttributeMapperNode, MPxSpringNode, MPxSurfaceShape, and MPxTransform.
| bool MPxNode::isAbstractClass | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Override this class to return true if this node is an abstract node. An abstract node can only be used as a base class. It cannot be created using the 'createNode' command.
It is not necessary to override this method.
- Returns:
- true if the node is abstract.
Reimplemented in MPxPolyTrg.
| MObject MPxNode::thisMObject | ( | ) | const |
Returns the MObject associated with this user defined node. This makes it possible to use MFnDependencyNode or to construct plugs to this node's attributes.
It is not necessary to override this method.
- Returns:
- MObject handle for this node
This method adds a new attribute to a user defined node type during the type's initialization.
This method will only work during the static initialization method of the user defined node class. The initialization method is the one that is passed into MFnPlugin::registerNode. The attributes must first be created using one of the MFnAttribute classes, and can then be added using this method.
For compound attributes, the proper way to use this method is by calling it with the parent attribute. If a compound attribute is passed, this method will add all of its children. NOTE: A failure will occur if you attempt to call addAttribute() on the children of a compound attribute.
- Parameters:
-
[in] attr new attribute to add
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Operation successful
- MS::kInvalidParameter Attribute is invalid or already added or child of a compound attribute is being added before the parent
- MS::kFailure Method was not called during the node's initialize routine
This method allows a class of plugin node to inherit all of the attributes of a second class of plugin node.
This method will only work during the static initialization method of the user defined node class. The initialization method is the one that is passed into MFnPlugin::registerNode.
- Parameters:
-
[in] parentClassName class of node to inherit attributes from
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Operation successful
- MS::kInvalidParameter Class name is invalid
- MS::kFailure Method was not called during the node's initialize routine
| MStatus MPxNode::attributeAffects | ( | const MObject & | whenChanges, | |
| const MObject & | isAffected | |||
| ) | [static] |
This method specifies that a particular input attribute affects a specific output attribute. This is required to make evaluation efficient. When an input changes, only the affected outputs will be computed. Output attributes cannot be keyable - if they are keyable, this method will fail.
This method must be called for every attribute dependency when initializing the node's attributes. The attributes must first be added using the MPxNode::addAttribute method. Failing to call this method will cause the node not to update when its inputs change. If there are no calls to this method in a node's initialization, then the compute method will never be called.
This method will only work during the static initialization method of the user defined node class. The initialization method is the one that is passed into MFnPlugin::registerNode. As a result, it does not work with dynamic attributes. For an alternate solution which handles dynamic as well as non-dynamic attributes refer to MPxNode::setDependentsDirty.
- Parameters:
-
[in] whenChanges input attribute - MObject that points to an input attribute that has already been added [in] isAffected affected output attribute - MObject that points to an output attribute that has already been added
- Returns:
- Status code
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess Operation successful
- MS::kInvalidParameter At least one of the attributes is invalid or has not been added to this node using the addAttribute routine
- MS::kFailure Method was not called during the node's initialize routine
| MStatus MPxNode::setExistWithoutInConnections | ( | bool | flag | ) |
This method specifies whether or not the node can exist without input connections.
If a node connected to this node is deleted resulting in no more input connections and if this flag is false, then this node will be deleted.
- Parameters:
-
[in] flag true if this node can exist without input connections, false otherwise
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess operation successful
- MS::kFailure this MPxNode has not been initialized properly. Make sure this method is not being called from the constructor.
| bool MPxNode::existWithoutInConnections | ( | MStatus * | ReturnStatus = NULL |
) | const |
Determines whether or not this node can exist without input connections.
If a node connected to this node is deleted resulting in no more input connections and if this flag is false, then this node will be deleted.
- Returns:
- true is this node can exist without input connections, false otherwise
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess operation successful
- MS::kFailure this MPxNode has not been initialized properly. Make sure this method is not being called from the constructor.
| MStatus MPxNode::setExistWithoutOutConnections | ( | bool | flag | ) |
This method specifies whether or not the node can exist without output connections.
If a node connected to this node is deleted resulting in no more output connections and if this flag is false, then this node will be deleted.
- Parameters:
-
[in] flag true if this node can exist without output connections, false otherwise
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess operation successful
- MS::kFailure this MPxNode has not been initialized properly. Make sure this method is not being called from the constructor.
| bool MPxNode::existWithoutOutConnections | ( | MStatus * | ReturnStatus = NULL |
) | const |
Determines whether or not this node can exist without output connections.
If a node connected to this node is deleted resulting in no more output connections and if this flag is false, then this node will be deleted.
- Returns:
- true is this node can exist without output connections, false otherwise
- Status Codes:
- MS::kSuccess operation successful
- MS::kFailure this MPxNode has not been initialized properly. Make sure this method is not being called from the constructor.
| MDataBlock MPxNode::forceCache | ( | MDGContext & | context = MDGContext::fsNormal |
) | [protected] |
USE _forceCache() IN SCRIPT.
Get the datablock for this node. If there is no datablock then one will be created. NOTE: This should be used only in places where fast access to the datablock outside of a compute is critical such as the transformUsing method of MPxSurfaceShape.
- Parameters:
-
[in] context The context in which the node will evaluate.
- Returns:
- The datablock
| void MPxNode::setMPSafe | ( | bool | flag | ) | [protected] |
USE _setMPSafe() IN SCRIPT.
Set a flag to specify if a user defined shading node is safe for multi-processor rendering. For a shading node to be MP safe, it cannot access any shared global data and should only use attributes in the datablock to get input data and store output data.
NOTE: This should be called from the postConstructor() method for shading node plug-ins only. If a shading node is non-safe, then it will only be useful during single processor rendering.
- Parameters:
-
[in] flag True if user node is safe, false if non-safe.
| MStatus MPxNode::setDoNotWrite | ( | bool | flag | ) | [protected] |
Use this method to mark the "do not write" state of this proxy node. If set, this node will not be saved when the Maya model is written out.
NOTES: 1. This should be called from the postConstructor() method only. 2. Plug-in "requires" information will be written out with the model when saved. But a subsequent reload and resave of the file will cause these to go away. 3. If this node is a DAG and has a parent or children, the "do not write" flag of the parent or children will not be set. It is the developerís responsibility to ensure that the resulting scene file is capable of being read in without errors due to unwritten nodes.
- Parameters:
-
[in] flag True if the user node should not be saved.
| bool MPxNode::doNotWrite | ( | MStatus * | ReturnStatus = NULL |
) | const [protected] |
Use this method to query the "do not write" state of this proxy node. True is returned if this node will not be saved when the Maya model is written out.
- Parameters:
-
[out] ReturnStatus