Actions have two parts: sources and clips. First you animate objects in a model and store the animation as an action source, then you instantiate that source as action clips on tracks in the animation mixer.
Action sources and clips are stored in the Mixer node of the current model. For information, see The Mixer Node and Models and the Mixer.
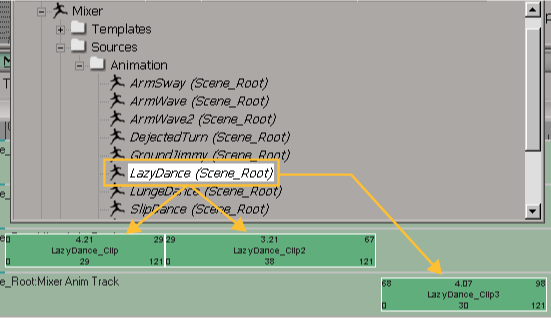
You can create multiple action clips that all come from, and stay linked to, the same action source.
Think of sources as the "mother ship" container for stored animation. Action sources contain one or more animation items. Each animation item contains a parameter name and its animation data (function curve, expression, constraint, or linked parameters).
To successfully create sources, you need to know the type of animation you want to store. See Choosing What to Store in an Action to help you decide which commands are appropriate for the animation you want to store. Then when you're ready to create an action source, see Storing Animation in Action Sources.
When you create an action source, the original is stored within the Sources  model folder for your scene, as you can see in the explorer below. Having sources stored at the scene level makes it easy to see
the sources available for any model in that scene. As well, you can easily copy sources from one model to another at this
level (simply drag and drop the sources).
model folder for your scene, as you can see in the explorer below. Having sources stored at the scene level makes it easy to see
the sources available for any model in that scene. As well, you can easily copy sources from one model to another at this
level (simply drag and drop the sources).
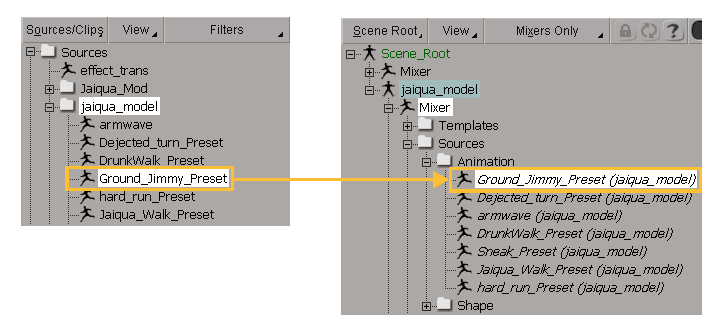
The original action source is stored at the scene level and a reference copy of it is stored under the model's Mixer node for convenience sake. The latter is shown in italics so that you know it's referenced from the original source's location.
You can modify the original animation data stored in a source as described in Modifying Action Sources. Modifying the original animation updates it in all clips (except expressions and constraints) that refer to that source.
As well, you can return to the original stored animation, such as the original function curves, at any time by applying an action source. See Restoring (Applying) the Animation in Action Sources to an Object for more information.
After you create an action source, you can create an instance of it called an action clip. Action clips allow you to use action sources in the animation mixer. You can create any number of clips from each source.
There are two ways in which you can create clips:
You can create a clip automatically when you create an action source — see Creating Action Sources.
You can drag a source from an explorer to a track in the mixer to create a clip from it — see Creating Action Clips in the Mixer.
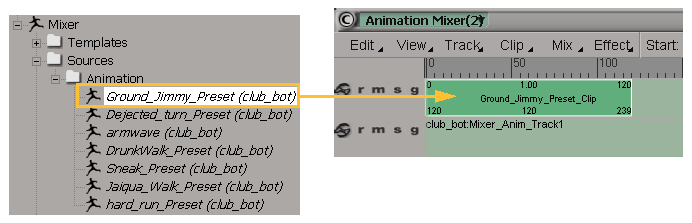
The action clip doesn't actually contain any animation itself: it simply references the animation stored in the source. Basically, a clip wraps the animation data in an action source with timing information. The timing information describes how the animation in the source is "pulled." The clip establishes the connections between the source's animation data and the driven objects in the model using a connection template and connection mapping information.
For function curves, the clip simply makes a reference to the animation in the action source — all clips share the function curves of their source. However, if you want to add animation to a clip without affecting the source, you can use clip effects as described next.
For expressions and constraints, each clip maintains its own local data that is independent of the source. This means that you can edit the data in each clip without affecting the source (see Modifying Action Clip Values).
To create higher-level clips, you can combine several action clips together into a compound clip — see Combining Clips into Compound Clips for information.
Clip effects let you adjust the animation in a clip without affecting the action source. This applies only to clips that are created from function curve sources. Clip effects add values to a clip, such as by adding noise, offsets, and other higher-level operations, without touching the original animation. They are displayed as a yellow bar on top of an action clip.
For more information on clip effects, see Modifying Action Clips with Clip Effects.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License