
You can transform, scale, and deform models and components of models using tools in the Pose Tools tray.
For example, you can use the posing tools to place a character model in various positions and stances, to deform components, or change component proportions. You can deform and shape non-character models just as easily by moving, bending, or twisting their components.
You can import and pose models with skeletons rigged in other applications (such as Maya, 3ds Max, and Softimage) using the FBX file format. For example, to perform range of motion tests and determine whether the proportions of the arms allow the fingers to reach a character’s face, and so on.
You pose or deform your models in Mudbox using joints. Placing joints on a model lets you rotate, transform (and otherwise deform) related components that you define (such as the arm, foot, leg, and so on).
Joints define the points at which the model can deform when you use the Pose tool. Much like a human knee joint rotates to move the associated parts of the lower leg (shin, foot, and toes), the joints you place on a model define how it can be articulated into a desired pose. The individual vertices associated with a joint (with their associated faces) can move as one unit.
Joints are critical for deforming and posing your models into a variety of positions, and they also let you change your model’s proportions and scale in ways that would otherwise be difficult using the sculpt tools alone.
You can use single joints on a model to create simple poses, or create multiple joints and joint hierarchies to transform a model into more complex poses.
Using the Create Joint tool, you click-drag to interactively create a joint and define its initial area of influence, all in one operation.
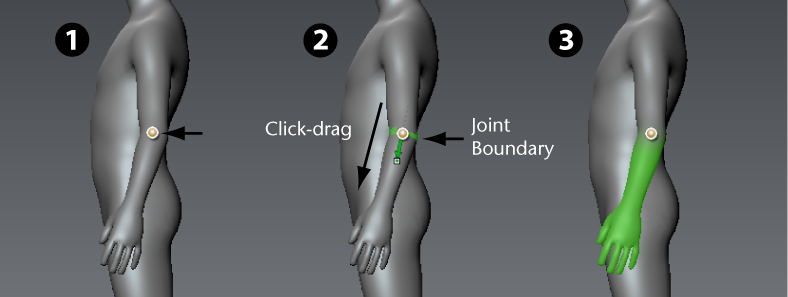
As you create a joint and specify its region of influence (weighting), you determine how much of the surrounding vertices are affected when the associated model component is rotated or transformed about the joint.
See Create joints.
You can pose joints created in Mudbox or joints imported with an imported model. All posing operations are performed in relation to the current camera position.
Select the Pose tool and drag a highlighted area to pose it. This rotates the selected region in relation to a rotation axis that is normal to the current camera view.
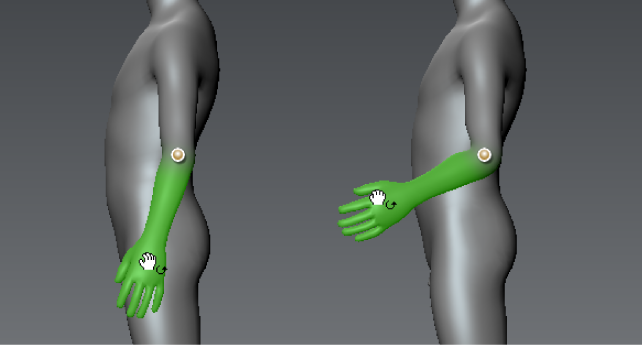
Middle-dragging a highlighted region moves the region within the camera viewing plane.
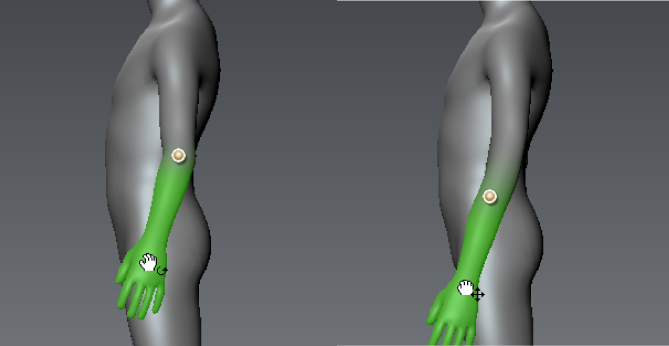
Click-dragging directly on a joint rotates the component about vertical and horizontal axes that lie planar in relation to the current camera view.
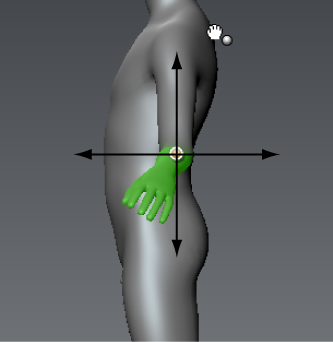
Middle-dragging the joint scales the selected region non-proportionally, or proportionally when you press the Shift key.
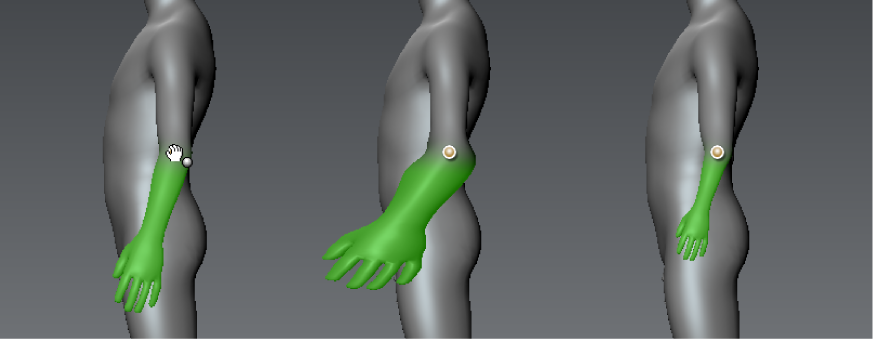
To pose all of the model except the weighted region, press the Ctrl key while posing.