You'll add some materials to help visualize your revolving door. You'll add a shiny black finish for the struts and a green glass material for the glazing in the door and the enclosures. You'll also edit the material that already exists on the revolving door, so it matches your own green glass.
 (Open File) and open add_door_materials.max in the \startup folder.
(Open File) and open add_door_materials.max in the \startup folder.
 (Material Editor) from the
Material Editor flyout to open the Compact Material Editor.
(Material Editor) from the
Material Editor flyout to open the Compact Material Editor.
The Material Editor opens as a floating window.
The Compact Material Editor is usually more convenient when you want simply to assign materials that have already been designed. The Slate Material Editor, which takes up more screen space, is more convenient and versatile for designing materials.
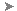 Compact Material Editor.
Compact Material Editor.
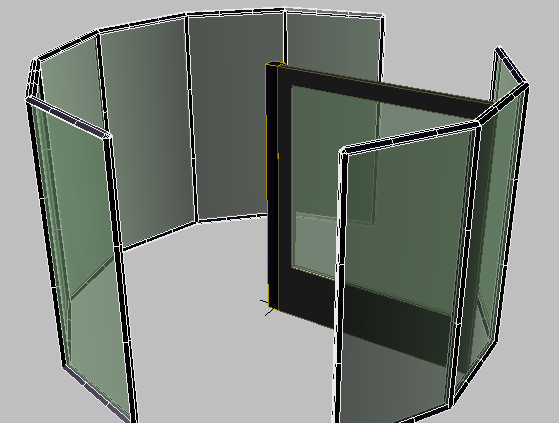
You can choose materials from a material library and apply them to the revolving door so the panel is transparent.
 (Get Material).
(Get Material).
 (Material/Map Browser Options)
(or right-click an empty area of the dialog), and from the pop-up
menu, choose Open Material Library.
(Material/Map Browser Options)
(or right-click an empty area of the dialog), and from the pop-up
menu, choose Open Material Library.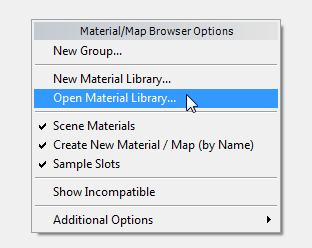
This library is located in the \materiallibraries subfolder of your current Project. If it doesn’t appear in the file dialog when you click Open, browse to this directory, then open the library.
A section for the library now appears in the Browser.
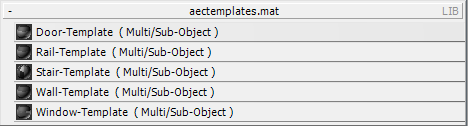
The door material appears in the first sample slot of the Compact Material Editor.

 Close the Material/Map Browser.
Close the Material/Map Browser.
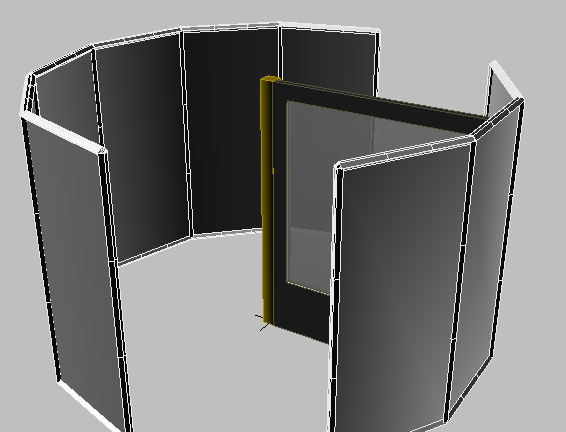
The door now displays with transparent glass. Also, in the Material Editor, the sample sphere is now marked with corners showing that this material has been applied to an object in the scene.
Create and apply a green glass material:
By default, materials in the Material Editor are of the Arch & Design type. You'll change this material to the Standard type.

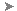 Standard
Standard 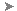 Standard, then double-click
the entry Standard.
Standard, then double-click
the entry Standard.
In the Compact Material Editor, the material type changes from Arch & Design to Standard.
The glass panels of the left enclosure change their appearance in the viewport.

“Blinn,” named after computer-graphics pioneer James Blinn, is the default shader type used by the Standard material. A shader determines how the material interacts with light. And “Diffuse” refers to the basic material color. You'll find more information about these and about materials in general in the User Reference.
Watch in the viewport; each time you click a different color, the material updates in the viewport. When you've decided on a color, click the Close button.
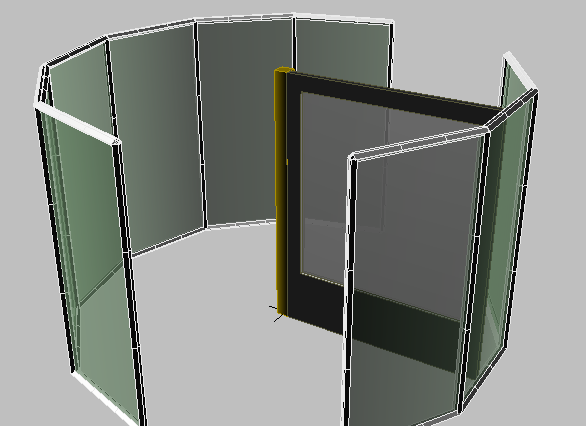
Now the glass on the right enclosure matches the color and transparency of the left enclosure.
“Ambient” refers to the lighting that spreads out within a scene without being cast directly by a light source. Typically it's reflected off surfaces such as walls.
These two settings determine the brightness and size of shiny highlights, respectively.
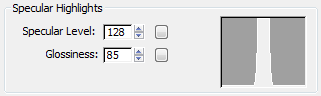
All of these settings combine to produce a black, shiny surface treatment.

 (Assign Material To Selection)
to apply the material to the struts.
(Assign Material To Selection)
to apply the material to the struts.
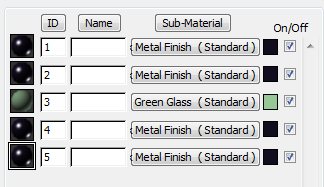
After you created the pivot door, you assigned a Multi/Sub-Object material from a material library to the door. When you have a single object, such as this door, with different, distinct components (such as glazing, frame, and so on), you can use a Multi/Sub-Object material to apply different materials to its various parts.
You will use the eyedropper to get the material from the door into the Material Editor. This will give you a second copy of the material to edit, leaving the original available for use.

 (Pick Material From Object)
to activate it, and then in the viewport click the pivot door.
(Pick Material From Object)
to activate it, and then in the viewport click the pivot door.
The sample sphere is replaced with a sphere that shows five stripes of different materials. This indicates that the selected material is a Multi/Sub-Object material.
On the Multi/Sub-Object Basic Parameters rollout, you can click and access each individual material.
When you copy something using the Instance option, changing one instance changes all of them. For example, if you then made the glass a neutral color, all the instances would reflect that change.
This is the material that is applied to the glazing. The glass on the revolving door turns green in the viewport.
Now make changes to the material and watch them update on the objects in the viewport.
Change the Black Metal Finish to a shiny gold instead. Do the following:
