The Ink 'n Paint material creates cartoon effects. Rather than the three-dimensional, realistic effect most other materials provide, Ink 'n Paint provides flat shading with “inked” borders.

Snake rendered with ink 'n paint
Because Ink 'n Paint is a material, you can create a scene that combines 3D-shaded objects with flat-shaded cartoon objects.
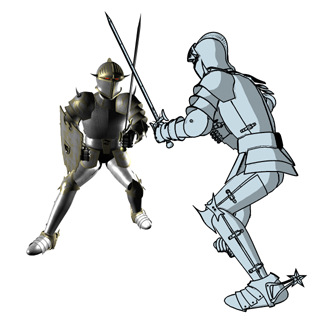
Rendering that combines realistic shading with cartoon shading
In the Ink 'n Paint material, ink and paint are two separate components, with customizable settings.
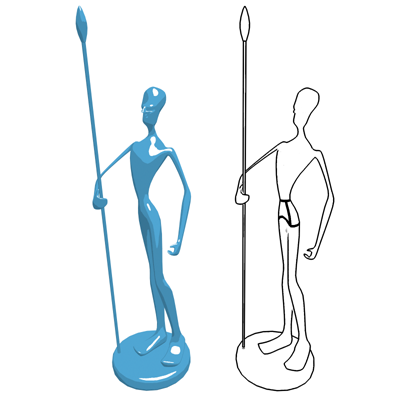
Left: The paint component only
Right: The ink component only
You can use Ink 'n Paint on multiple objects, but in general, it tends to work best if you do the following:
Typically, you would do this at the Element sub-object level, although you can certainly apply different material IDs to faces and polygons as well.
Here are some commonly encountered problems, and potential solutions:
The Overlap bias is probably too high. Decrease it. If Underlap is on, this might also have too high a bias.
Another possible reason is that you have a self-intersecting object, or an object built by attaching smaller objects, thus creating intersecting faces. In this case, set up the objects to use the Mat ID or SmGroup ink components. If elements already have differing material IDs, try turning off Only Adjacent Faces.
The Overlap or Underlap bias might be too low. Try increasing it.
Find out which ink component is the sloppy one and adjust its bias control.
Turn on Clamp. You can also try to see if reducing the lighting level helps. Or, you can try turning off Variable Width, then assigning a Falloff map to the Ink Width component.
Basic Material Extensions rollout

Makes the material 2-sided. Applies the material to both sides of selected faces.
Applies the material to the faces of the geometry. If the material uses maps, it requires no mapping coordinates. The maps are applied automatically to each facet of the object.
When on, enables the Bump map. Use the numeric setting to control the bump amount and the map button to assign a Bump map.
When on, enables the Displacement map. Use the numeric setting to control the displacement amount and the map button to assign a Displacement map.
Paint is the main color of the material, and has three components. This section describes the components first and then their common controls.

The first numeric setting is the percent of the Lighted color that appears on the unlighted side of objects. Default=70.0.
Turning off this component displays a color swatch, which you can use to assign a distinct color to shaded areas. Default=on.
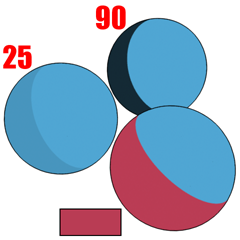
Increasing the value of Shaded increases the saturation of the shaded area. You can also use Shaded to assign a distinct color for shading.
The color of the specular highlight. Default=white.
When this component is off, there is no specular highlight. Default=off.

Left: No highlights
Right: Highlight on
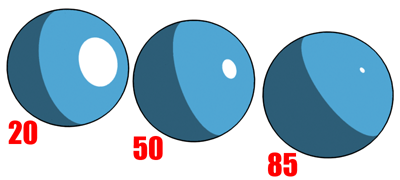
Increasing glossiness decreases the size of the highlight.
These are the controls that are duplicated for each of the paint components. Each has an on/off toggle, a main control, and then on the right, a set of map controls.


Mapping the Lighted component
Right rear: The original, unmapped material
Left: Lighted component with a Falloff map applied
Right front: Lighted component with a Bitmap map applied
While a map is assigned and enabled, at 100 percent it completely overrides the main color component. At lower percentages, the map is blended with the color.
Ink is the linework, the outlines, in the material.
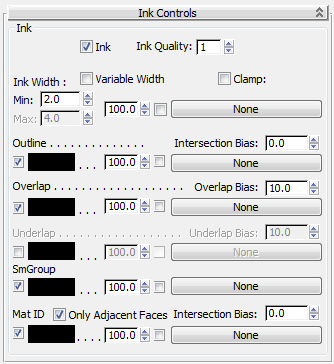
Except for Ink Width, each of the ink components has an on/off toggle and a color swatch. Click the color swatch to display a Color Selector and change the ink component's color. Each ink component, Ink Width included, also has a set of map controls.
Affects the shape of the brush and the number of samples it uses. When Quality equals 1, the brush is a “+” shape, and samples are taken over an area of 5 pixels. When Quality equals 2, the brush is octagonal and the samples are taken over an area of 9 to 15 pixels. When Quality equals 3, the brush is nearly circular, and samples are taken over an area of 30 pixels. Range=1 to 3. Default=1.
The width of the ink, in pixels. This is specified by the spinner labeled Min (minimum) unless Variable Width is on. When Variable Width is on, the Max (maximum) spinner is also enabled, and the ink width can vary between the minimum and maximum values. Default: Min=2.0, Max=4.0.

Left: One-pixel ink width
Middle: Five-pixel ink width
Right: Ink width varies from one to five pixels.
The ink where the outer edges of the object appear against the background or in front of a different object. Default=on.

Left: Rendering the outline only
Right: Rendering only the overlap and underlap
The ink used when a portion of an object overlaps itself. Default=on.
Similar to Overlap, but applies ink to the farther surface rather than the nearer one. Default=off.
The ink drawn between the boundaries of smoothing groups. In other words, it inks the edges of the object that have not been smoothed. Default=on.
The ink drawn between different material ID values. Default=on.
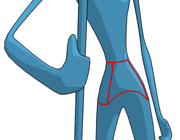
Inking the edges between sub-materials
