Show in Contents

Add to Favorites

Home: Autodesk Showcase Help

Play a behavior animation

Present the scene

Compare and contrast multiple scenes

Create
an image of an important view
Select File
> Save Image As to create an image
of the current view. To ensure the image is the highest quality,
first make sure the current rendering mode and quality level shows
the desired image on screen.
NoteThe
Save Image function will use the current camera view and rendering
mode (either Hardware rendering or Ray Tracing) for the image creation.
The options presented for creating and saving the image will vary
based on rendering mode.
Ensure the interactive
scene is in the rendering mode desired
Before taking an image,
you should ensure that the current display is showing the rendering
mode, quality and effects that are desired for the image:
- For a Ray Tracing image output, ensure
that the menu item View > Ray Tracing is checked.
For Hardware Rendering output, insure that it Ray Tracing unchecked.
NoteIn
some cases the visual difference between Interactive Ray Tracing
that has progressively improved and Hardware Rendering can be difficult
to determine without altering the view. Check the menu item to avoid
moving the camera or refreshing the on screen image.
- Select Options > Performance
and Quality. The Performance and Quality window appears.
- For Interactive Ray Tracing,
check that the current Quality Range is showing the effects you
expect in your image.
- For Hardware Rendering,
check that the Minimum Anti-aliasing is set to High.
Save Image As...
Create an image file
of the current view
- Enter the rendering mode you wish to
use for creating the image.
- Select File > Save Image As.
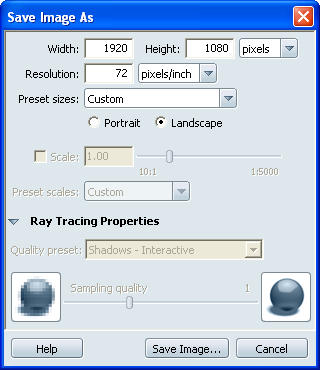
The Save Image As window appears.
NoteThe
available options in the Save Image As dialog are determined by
what rendering mode is active, and whether the view is Orthographic
or Perspective. See
Rendering modes for more
information.
- For a custom output image size, specify
thedimensions and resolution in the units of your choice.
Or, expand the Preset sizes menu
to choose from a list of standard presets. (If you choose a paper
or photo preset, you’ll be able to specify whether you want it to
be saved portrait or landscape.)
NoteYou can create an
image up to 15,000 x 15,000 pixels, depending on the amount of available
memory on your machine, and the specifications of your graphics
card if in Hardware rendering mode.
- Click Save Image....
A browser window appears.
- Browse to the location where you want
to save the image file.
- Select the file format for the image
from the available options for the current rendering mode. (See
the section “Image file formats for saved images” below)
- Type in the name of the file (the file
format extension will be added automatically).
Scale the image accurately
on a page
For orthographic view
renderings, an accurate scale can be used for the image output.
This adjusts the zoom of the image to fit the object dimensions
to the physical size of the output image, based on resolution (the
number of pixels per actual unit).
To save an image to an
accurate scale at a specific resolution:
- View the scene with an orthographic camera
.
- Check the Scale option
in the Save Image As dialog.
- Select a Preset Scale from the dropdown
menu, or move the Scale slider to an appropriate ratio.
The view of the scene
will change on screen to reflect the scale of the objects within
the specified resolution.
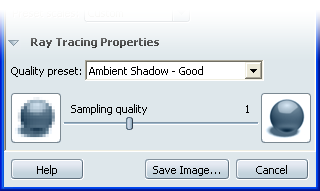
Specify a Quality preset
and sampling for Ray Tracing output
If Ray Tracing is enabled,
the Save Image As... dialog will show the Ray Tracing Properties
for the output. To insure that “what you see” is “what you get”
the current preset used in the Performance and Quality dialog
for Interactive Ray Tracing is chosen, but the Sampling quality
defaults to 1 (or higher if the preset is locked to a higher amount).
NoteSampling
qualities of less than 1 are sub-sampled, meaning they are rendering
the scene smaller than specified and increasing the pixel scale.
If this is desired, the scene can be rendered at a smaller initial
resolution to save time and memory.
To save an image using
specific Ray Tracing settings:
- Enable Ray Tracing using View
> Ray Tracing, or by pressing R.
NoteRay
Tracing can be enabled or disabled for the current Save Image by
pressing the R key while
the Save Image As dialog is open.
- Choose a Quality Range (defines
the overall quality and ray tracing effects used in the rendering)
from the drop-down menu of presets if the current one is not desired.
- Set the Sampling quality slider
(controls the smoothness of the pixels in the final image) to the
desired amount.
- Press Save Image... to
initiate the offline rendering. A browser will appear to set the
filename and image output type, then a progress bar will indicate
the rendering progress.
NoteWhile an offline Ray Tracing rendering is
progressing, the interactive Ray Tracing is disabled. Input for
navigating the scene will be ignored until the rendering is complete.
-
The rendering can be cancelled at any time during
its progress.
Image file formats for
saved images
Images can be saved in
various file formats to make it easier to email or print the images,
or to open the image in an image editor and alter it for presentation
later. The list of file formats is different based on which rendering
mode Showcase is in when the Save Image As... option
is selected.
Hardware rendering
image formats
- JPEG: Joint
Photographic Experts Group format. Common format used for web and
email. Small file size, but can show compression artifacts.
- TIFF: Tagged
Image File Format. Common format used for publishing and archiving.
Larger file size, but without compression.
NoteTIFF images will
include an extra “alpha channel” that is a grayscale mask of the
objects in the scene, with transparency, to separate them from the envronment
or background colors.
- BMP: Bitmap
format. Common Windows image format.
- PSD: Photoshop
Document. File format used by Adobe Photoshop.
NotePSD images will include
two layers. One is the objects in the scene, with transparency,
separate from the envronment or background, and the other is the environment
or background color and shadows without the objects.
Ray Tracing image formats
- JPEG:
Joint Photographic Experts Group format. Common format used for
web and email. Small file size, but can show compression artifacts.
- BMP: Bitmap
format. Common Windows image format.
- HDR: Radiance
RGBE format. Contains greater brightness, contrast and color ranges
than other file formats, but has limited compatibility with most
image editors. Preserves highlights and shadows beyond what is displayed
on screen.
NoteHDR
images may appear to have less contrast or be lighter than the image
viewed interactively on screen. This is due to limitations in the
image editor software. Because the file format contains more dynamic
range than most monitors can show, many image editors display HDR
images without monitor gamma correction or any tonemapping. To acheive
the same visual results, either tonemap the image to an LDR or force
gamma correction on display.
- TIFF HDR: Variant
of TIFF that containsgreater brightness, contrast and color ranges
than other file formats, but has limited compatibility with most
image editors. Preserves highlights and shadows beyond what is displayed
on screen.
- TIFF: Tagged
Image File Format. Common format used for publishing and archiving.
Larger file size, but without compression.
NoteTIFF images (both
regular and HDR) will include an extra “alpha channel” that is a
grayscale mask of the objects in the scene, with transparency, to separate
them from the envronment or background colors.