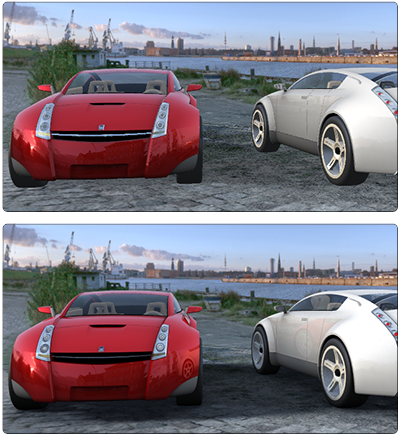
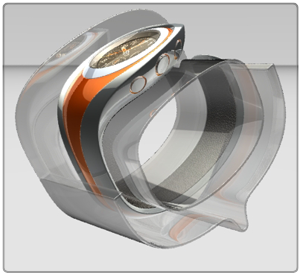
Showcase is capable of
displaying a scene either in Hardware rendering (top
image above) or Ray Trace rendering mode. Each
rendering mode has distinct properties and advantages, while all
workflows and tools for data preparation, presentation, and output
remain the same, regardless of which mode is used. Switching between
Hardware and Ray Trace rendering modes is easy, and the appearance
of the scene is maintained to the limits of each mode.
NoteHardware
rendering is the default method of display for all scenes. To enable
or disable Ray Tracing, select View > Ray Tracing or
press R at
any time.
Advantages of each rendering mode
Hardware rendering
mode
- Uses the GPU (video card) to calculate
and display the scene.
- Very fast response time (frames per second)
on qualified hardware.
- Easy to manipulate objects, materials,
textures and cameras due to response time.
- Very fast image and movie output at large
resolutions.
Ray Trace rendering
mode
- Uses the CPU (computer processors) to
calculate and display the scene.
- Very high quality visuals, with realistic
shadows, transparency and reflections.
- Enhances environments, lights and materials
with new properties and capabilities.
- Can be optimized for interactivity or
final output quality.
NoteThe
interactivity of each rendering mode is dependant on different computer
specifications and the scene that is loaded. For Hardware rendering,
the type and memory size of the video card will influence performance,
while for Ray Trace rendering the number and speed of processors
and cores will greatly effect performance.
What is ray tracing?
Ray tracing is a rendering
method that produces highly realistic visuals by tracing “rays”
from each rendered pixel into the 3D scene, which then bounce, bend
and create visual effects similar to real light. In Showcase, ray
tracing will be visually similar to hardware rendering, but adds
many new effects.
- Ray tracing in Showcase can be both interactive
(the scene can be manipulated while the ray tracing updates), and
offline for output (the scene can be rendered at any size or quality
level and written to disk immediately).
- Interactive Ray Tracing can progressively
improve in quality whenever the scene is static.
- Advanced ray tracing effects can be selectively
added and controlled using presets in the Performance and Quality dialog.
- All tools, controls and manipulators
appear the same in Hardware rendering and in Ray Tracing, with the
exception of wireframe display and some image output formats.
Types of Ray Tracing effects
In addition to displaying
what is seen in Hardware rendering, Ray Tracing creates visual effects
that add to the quality of the image. Some of these effects are
based on the materials in the scene, others require a particular
Ray Tracing Quality preset to be used to see the effect. Some of
the effects are listed below, in order or their appearance within
presets.
- Ray traced reflections
and transparency: objects can reflect themselves, the
environment, and other objects in the scene. The effect is controlled
by material properties, and the Reflection and Transparency Max
Limit in the Performance and Quality dialog
sets the number of reflections seen at once.
- Refraction: objects
seen through transparent materials will appear distorted based on
the Index of Refraction for that material, similar to lenses and
transparent media in the real world. The effect is controlled in
material properties.
- Absorbance: transparency
of materials can be colored and depth-limited by simulating the
absorbance of light based on thickness. The effect is controlled
in material properties.
- Ray traced shadows: objects
can cast accurate shadows on themselves, other objects in the scene,
or on the environment. Lights in the scene also cast shadows in
Ray Tracing mode, and all shadows can have varied softness based
on distance and light size. The effect is controlled by light properties and
enabled in Ray Tracing Quality presets.
- Ray traced ambient shadows: all
objects can have ambient shadows (shading from light surrounding
the scene) calculated by the ray tracer. Unlike Create
ambient shadows, this effect does not require pre-calculation
and is not visible in Hardware rendering. The effect is enabled
in Ray Tracing Quality presets.
- Global Illumination: all
objects can have simulated “bounce light” from other objects and
the environment cast upon their surfaces. This will visibly lighten
the scene in areas where strong lighting is present. The effect
is enabled in Ray Tracing Quality presets.