The Crop tool lets you change the size of an image. When you perform a crop, adjacent rows or columns of pixels next to the edges of the input image are removed. You can crop an image relative to its input size or perform an absolute crop if you want to retain certain portions of the image. To assist in cropping, you can keep a fixed image size regardless of input dimensions.
You can also animate the Crop tool's parameters by setting keyframes or using expressions—see Setting Keys Manually and Validating and Applying the Expression String.
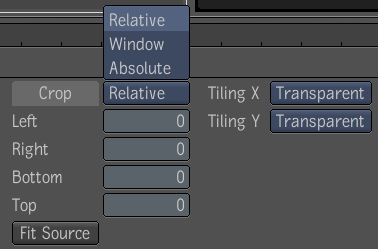
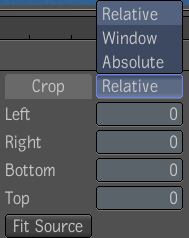
| Use: | To: |
|---|---|
| Relative Crop | Crop an image relative to the size of the input image. The default value for all parameters (left, bottom, right, top) is zero. All parameters have a range of zero to the respective size (width and height) of the image being cropped. Cropping more pixels than an image has results in an invalid image size of zero. |
| Window Crop | Crop an image using absolute values. You can set values for Center X, Center Y, Width, and Height. |
| Absolute Crop | Crop an image using absolute values. You can set values for Left, Right, Bottom, and Top. |
| Tiling | Specify how the input image should be extended outside its region of definition (ROD).The supported tiling modes are Transparent (default), Edge, Repeat, and Mirror. |
Tools that can change the resolution of an image (Garbage Mask, Lens Distort and 2D Transform) have extra controls to manage the crop.
The Auto Crop feature computes a fit-all region where the entire distorted image fits into the output without losing any part of the image. When you set the crop mode to Auto Crop, the output region at each frame will automatically be computed. The region is automatically resized and all crop fields except the mode are disabled.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License