In this final lesson, you will assign a material identification number to each polygon in the model. You can then use these ID numbers to assign materials to specific parts of the model.
Check the default Material ID:
 Select the Tower object,
Select the Tower object,  maximize the Front viewport
and click
maximize the Front viewport
and click  (Zoom Extents Selected).
Make sure the view is in Wireframe mode.
(Zoom Extents Selected).
Make sure the view is in Wireframe mode.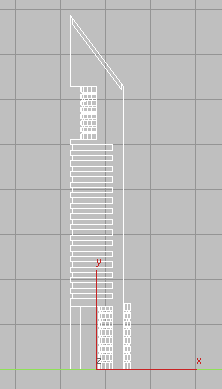
 Modify panel
Modify panel  Selection rollout, turn
on
Selection rollout, turn
on  (Polygon), then press Ctrl+A to select all the polygons
in the Tower object.
(Polygon), then press Ctrl+A to select all the polygons
in the Tower object.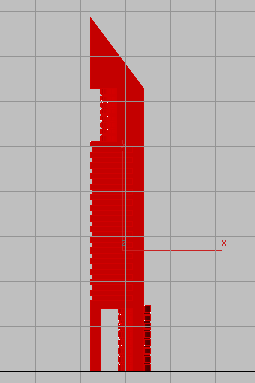
At this point, if you were to assign a material to the Tower object, all its polygons would receive the same material, because they all have the same material ID number.
Assign a new Material ID to the glazing:
 Click anywhere outside the Tower object
to deselect the polygons.
Click anywhere outside the Tower object
to deselect the polygons.
 Zoom in to the upper section
of the tower and begin to
Zoom in to the upper section
of the tower and begin to  Ctrl+click
the polygons that represent the glazing in the cylinder, as shown
in the next illustration.
Ctrl+click
the polygons that represent the glazing in the cylinder, as shown
in the next illustration.
Start your selection by clicking outside the tower and dragging right, across all the glazing polygons. Starting your selection outside the tower ensures that all glazing polygons on the other side of the Tower object are also selected.
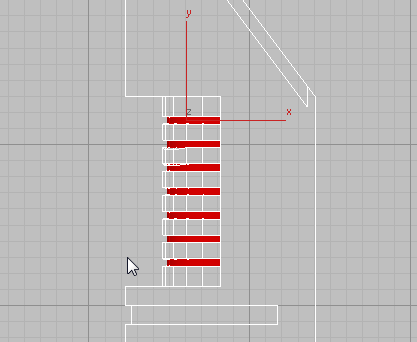
 Zoom out and continue to Ctrl+click all the glazing in the
lower floors, using the same selection technique described in the
previous step. Be sure to include the glazing polygons in the bottom
cylinder. The result is shown in the next illustration.
Zoom out and continue to Ctrl+click all the glazing in the
lower floors, using the same selection technique described in the
previous step. Be sure to include the glazing polygons in the bottom
cylinder. The result is shown in the next illustration.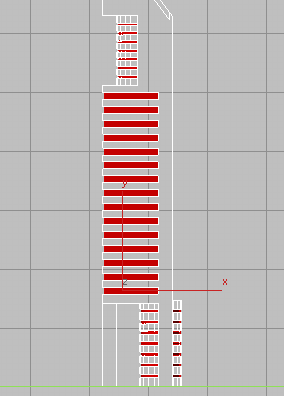
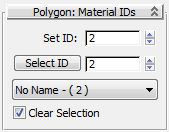
Now you can assign the Tower object two different materials.
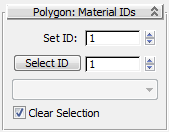
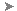 Select ID spinner, type 1,
then click Select ID.
Select ID spinner, type 1,
then click Select ID.
All the material 1 polygons are now selected.
 Compact Material Editor.
Compact Material Editor.
 (Assign Material To Selection).
(Assign Material To Selection). 
3ds Max Design applies the Concrete material to all polygons that have ID 1 assigned to them.
 (Assign Material To Selection).
(Assign Material To Selection).
3ds Max Design applies the Glass material to all polygons that have ID 2 assigned to them.
 Close the Compact Material
Editor.
Close the Compact Material
Editor.
 (Polygon) to exit the Polygon
sub-object level.
(Polygon) to exit the Polygon
sub-object level.
 (Render Production) to view
the result.
(Render Production) to view
the result.
Your rendered image should look something like this:
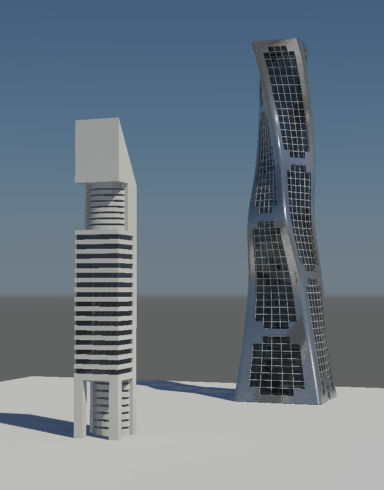
This tutorial introduced you to the concept of Boolean operations and how they can be used to produce complex shapes from simple geometry. You also learned some polygon editing techniques, and how to apply materials to multiple surfaces by assigning material ID numbers to different sets of polygons.