 Command entry: Render Setup dialog
Command entry: Render Setup dialog  Indirect Illumination panel
Indirect Illumination panel  Caustics and Global Illumination rollout
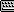
Caustics and Global Illumination rollout
The controls in this rollout are for the effects of caustics and global illumination.
Objects receive caustics by default. If you think this value might have changed for the objects you want to receive caustics, use those objects’ Object Properties dialog to make sure Receive Caustics is turned on. Also, to speed rendering time, you might want to turn off Receive Caustics for those objects that don’t need to show them.
To render with global illumination:
Objects generate and receive global illumination by default. If you think these settings might have changed for any objects in the scene, use the Object Properties dialog to make sure the proper settings are enabled.
 Caustics And Global Illumination rollout
Caustics And Global Illumination rollout  Global Illumination (GI) group and turn on Enable.
Global Illumination (GI) group and turn on Enable.
The settings for generating and receiving caustics are located on the Object Properties dialog  mental ray Panel (Object Properties Dialog).
mental ray Panel (Object Properties Dialog).
When on, the spinner value sets the size of photons. When off, each photon is calculated to be 1/100 of the radius of the full scene. Maximum Sampling Radius default=off; value default=1.0.
In many cases, the default photon size (Radius=off) of 1/100 the scene size gives useful results. In other cases, the default photon size might be too large or too small.
When photon reflections overlap, the mental ray renderer uses sampling to smooth them together. Increasing the number of samples increases the amount of smoothing and can create more natural-looking caustics. When photons have a small radius and don't overlap, the Samples setting has no effect. Low Radius values with a large number of photons result in dotty caustics.
Global Illumination (GI) group
These settings let you control the usage of photons by mental ray for generating global illumination. By default, all objects generate and receive global illumination. The settings for generating and receiving GI are located
on the Object Properties dialog  mental ray Panel (Object Properties Dialog).
mental ray Panel (Object Properties Dialog).
Sets how many photons are used to compute the intensity of the global illumination. Increasing this value makes global illumination less noisy but also more blurry. Decreasing this value makes global illumination more noisy but less blurry. The larger the Samples value, the greater the rendering time. Default=500.
When on, the numeric value sets the size of photons. When off, each photon is calculated to be 1/10 of the radius of the full scene. Default=off, 1.0.
In many cases, the default photon size (Maximum Sampling Radius=off) of one-tenth the scene size gives useful results. In other cases, the default photon size might be too large or too small.
When photons overlap, the mental ray renderer uses sampling to smooth them together. Increasing the number of samples increases the amount of smoothing and can create more natural-looking caustics. When photons have a small radius and don't overlap, the Samples setting has no effect. For global illumination, photons should overlap. To get good results, you might need to turn on Maximum Sampling Radius and increase the photon size.
If turned on before you render the scene, the mental ray renderer computes information to speed up the regathering process. Specifically, each photon stores additional information about how bright its neighbors are. This is particularly useful when combining Final Gather with Global Illumination, in which case the additional information allows Final Gather to quickly determine how many photons exist in a region. The fast lookup computation can take a long time, but it can greatly reduce the total rendering time. Default=off.
The fast lookup computation can be can be stored as additional data inside a photon map (PMAP) file, and then reused in subsequent renderings.
The controls in this group and the ones that follow are for the photon maps used to calculate caustics and global illumination. This group controls volumetric caustics. Volumetric caustics require a material to have a volume shader assign to its Photon Volume component.
When on, the numeric setting determines the size of photons. When off, mental ray calculates each photon to be one-tenth the size of the scene extents. Default: off; value=1.0.
The numeric setting is unavailable when the check box is off.
The Trace Depth controls are similar to those for calculating reflections and refractions, but they refer to the photons used by caustics and global illumination, rather than to rays used in diffuse reflection and refraction.
Limits the combination of reflection and refraction. Reflection and refraction of a photon stop when the total number of both equals the Maximum Depth setting. For example, if Maximum Depth equals 3 and the trace depths each equal 2, a photon can be reflected twice and refracted once, or vice versa, but it can’t be reflected and refracted four times. Default=10.
Controls in this group affect how lights behave when calculating indirect illumination. By default, the energy and photon settings apply to all lights in a scene. Use the mental ray Indirect Illumination rollout for light objects to adjust an individual light either by multiplying the global values, or by setting local values (using multipliers is the recommended method).
Sets the number of photons emitted by each light for use in caustics. This is the number of photons in the photon map used for caustics. Increasing this value increases the accuracy of caustics, but also increases the amount of memory used and the length of render time. Decreasing this value improves memory usage and render time, and can be useful for previewing caustic effects. Default=10000.
Sets the number of photons emitted by each light for use in global illumination. This is the number of photons in the photon map used for global illumination. Increasing this value increases the accuracy of global illumination, but also increases the amount of memory used and the length of render time. Decreasing this value improves memory usage and render time, and can be useful for previewing global-illumination effects. Default=10000.
Specifies how photon energy decays as it moves away from each light source. This value is given by 1/(distance decay ), where distance is the distance between the light source and an object, and decay is the value of this setting. Default=2.0.
In the real world, light decays at an inverse square rate (Decay=2.0), but this gives strictly realistic results only if you provide a realistic value for the energy of the light. Other values of Decay can help you adjust indirect illumination without worrying about physical accuracy.
When on, at rendering time, all objects in the scene can generate and receive caustics and global illumination, regardless of their local object properties settings. When off, an object's local object properties determine whether it generates or receives caustics or global illumination. Turning this on is an easy way to ensure that caustics and global illumination are generated, though it can increase rendering time. Default=off.
This setting does not alter the object's local object properties settings for mental ray. When you turn off All Objects Generate & Receive GI And Caustics, the prior object properties settings are in effect once again.