Shape keys have two parts: sources and clips.
A shape source is a shape that you have stored and are usually referred to as shape keys. By storing several shape keys for an object, you can build up a library of sources.
Shape sources are stored only in the model's Mixer  Sources
Sources  Shape folder; that is, they are not also stored at the scene (application) level as action sources are.
Shape folder; that is, they are not also stored at the scene (application) level as action sources are.
A shape clip is an instance of a shape key (source) at a particular position along a track in the animation mixer. You can create multiple clips of the same source, thereby returning to the same shape several times in the same animation.
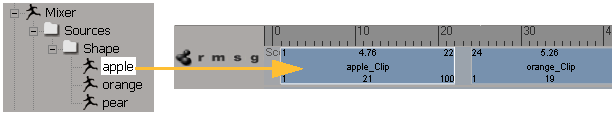
On the left, the shape source, also called a shape key, stores the current pose of an object's cluster.
On the right, a shape clip in the animation mixer is an instance of that source. The clip always refers to the source.
Shape sources and clips are stored in the Mixer node of the current model. For more information, see The Mixer Node [Nonlinear Animation in the Animation Mixer].
Deleting a shape key removes it as an available shape for the animation. It also removes all shape clips in the mixer created
(instantiated) from that shape key. You can delete a shape key from its Mixer  Sources
Sources  Shape folder in the explorer.
Shape folder in the explorer.
Shape animation is stored for clusters, which means that you can have several clusters on the same object that all have shape animation. In the animation mixer, a compound clip that contains all shape keys set is created for each shape-animated cluster.
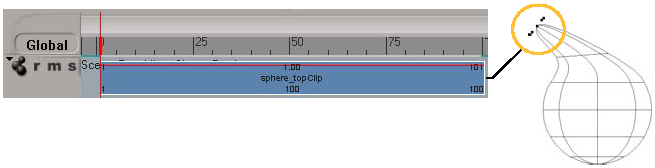
To weight the compound clips against each other, see Weighting with Compound Clips.
If clusters overlap — that is, if certain points belong to more than one cluster — you can control the relative weight of each cluster's animation on the shared points — see Mixing between Clusters.
For information on creating compound clips, see Combining Clips into Compound Clips [Nonlinear Animation in the Animation Mixer].
See Setting an Infinite Length for Clips [Nonlinear Animation in the Animation Mixer] for more information.
The Cluster Shape Combiner is an operator under the shape-animated object's geometry that lets you control how much each point in a shape-animated cluster is influenced by each deformation that is applied to it. For more information, see Mixing between Clusters.
This operator is created as soon as a shape clip is created in the mixer, such as if you store and apply a shape key, or bring it into the mixer to create a shape clip.
The operator appears in the object's Shape Modeling region of its construction history and its order is important. As a basic rule, shape animation is done on everything that's below the Cluster Shape Combiner; the operators that are above the Combiner (in the Animation region) are used to create the relative shapes.
For more information on the Cluster Shape Combiner's position in the construction history, see Creating Shape Keys in Shape Modeling Mode.
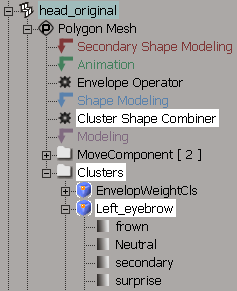
While you are working with shapes, you'll find that the explorer is a valuable tool in helping you find things in your scene. There are two main nodes to keep track of when working with shapes: the model's Mixer node and the shape-animated object's Geometry node.
The Mixer node is found in every model for which some object in it has some type of source created for it. For more information on this node's contents, see The Mixer Node [Nonlinear Animation in the Animation Mixer].
The Geometry node (such as the Polygon Mesh node) of the shape-animated object contains information about its clusters and the Cluster Shape Combiner.

The Cluster Shape Combiner is an operator in the Shape Modeling region that lets you set the weight of different clusters, including overlapping clusters, as described in The Cluster Shape Combiner.
The Clusters folder contains all clusters on the object, whether they have shape keys on them or not.
If a cluster has shape keys, you'll see them listed below it. For example, as shown above, the shape keys for the cluster called left_eyebrow are frown, neutral, secondary, and surprise.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License