The degree of a NURBS determines its continuity or smoothness. In Softimage, NURBS can have one of two degrees:
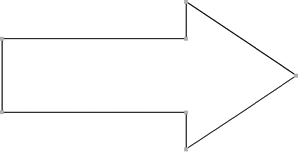
Linear: straight segments joined at the control points. Linear NURBS have positional continuity (also known as C0, degree 0, or zero-order continuity); this means that although it is connected, it is not necessarily smooth. At least two control points are required to define a linear curve.
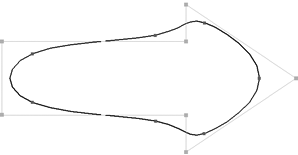
Cubic: smooth NURBS that are interpolated between the control points. Cubic NURBS have curvature continuity (also known as C2, degree 2, or second-order continuity); this means that there are no abrupt changes in the position, tangent, or curvature — in other words, it is very smooth. At least four control points are required to define a cubic curve.
Like curves, surfaces can be either cubic or linear. In addition, they can have different degrees in their U and V directions, so that they can be smooth in one direction and jagged in the other.
You can convert between cubic and linear by fitting — see Fitting Curves onto Curves and Fitting Surfaces.
In addition to linear and cubic, Softimage supports NURBS of other degrees imported from other programs.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License