Function curves created in Softimage usually have keys that are located at various frames throughout your animation. Softimage evaluates the fcurve and interpolates between the keys.
Fcurves generated from external sources such as motion capture, however, may have many more keys than necessary (commonly one key per frame) or they may contain "noise" — sharp spikes and jags in the fcurve. You may want to remove some of the keys or reduce the noise to edit the animation.
Conversely, if you keyframe an animation in Softimage and you want to transfer the animation data to an external device that requires frame-by-frame information (for example, a camera), you may want to increase the number of keyframes and preserve the motion as best as possible.
In addition to whole fcurves, you can choose to apply any of the curve processing commands on regions of fcurves that you select with the Region Keys tool (press the Q key). This lets you clean up only certain parts of an fcurve that may need some work.
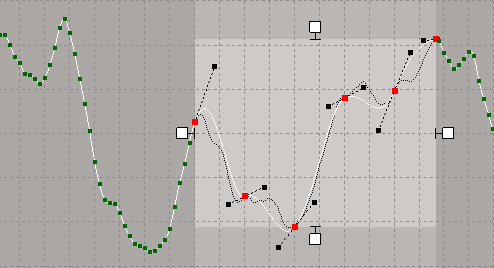
In the image below, fitting has been applied to only the selected region of an fcurve.
Smoothing decreases the variation between consecutive keyframes on the fcurve. It recreates keyframes at a regular time interval along the fcurve. It also modifies each keyframe's value, resetting it closer to the average value of all keyframes so that the result of repeated applications of the Smooth command would be a flat curve!
To reduce noise on an fcurve or region, do either of the following:
Select one or more fcurves, or draw a region over the part of the fcurves, that you want to smooth, then choose Curves  Smooth from the fcurve editor toolbar.
Smooth from the fcurve editor toolbar.
This immediately smooths the fcurves or region using the current options set for smoothing in the Fcurve Editor Preferences editor.
Choose Curves  Curve Processing Options or open the Fcurve Editor Preferences editor.
Curve Processing Options or open the Fcurve Editor Preferences editor.
On the Curve Processing page, choose the Smooth method:
Use Average Filter to apply a moving average where the weights of the averages are uniformly distributed. You can define the number of keys to average at a time using Filter Size. A greater number of keys results in a straighter curve.
Use Gaussian Filter to apply a moving average where the weights of the averages are distributed as a bell curve. Use the Variance setting to control the degree of smoothing. A higher variance results in a smoother curve. The Gaussian filter usually provides better results than the Average filter.
Choose Curves  Smooth from the fcurve editor toolbar using the options you've set.
Smooth from the fcurve editor toolbar using the options you've set.
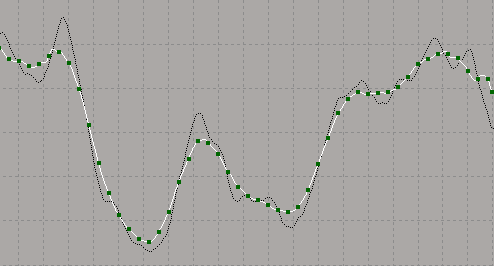
In the image below, a Gaussian filter was used with a Filter Size value of 10 and a Variance value of 5. The original fcurve is displayed as the buffer curve.
You can simplify the curve by reducing the number of keys on it while preserving its original shape, also known as fitting. You can also use the Resample option to reduce (or increase) the number of keys (see below).
To simplify an fcurve or region, do either of the following:
Select one or more fcurves, or draw a region over the part of the fcurves, that you want to fit, then choose Curves  Simplify Curve from the fcurve editor toolbar.
Simplify Curve from the fcurve editor toolbar.
This immediately fits the fcurves or region using the current options set for fitting in the Fcurve Editor Preferences editor.
Select one or more fcurves, or draw a region over the part of the fcurves, that you want to simplify.
Choose Curves  Curve Processing Options or open theFcurve Editor Preferences editor.
Curve Processing Options or open theFcurve Editor Preferences editor.
On the Curve Processing page, define a Simplify  Tolerance value to set the processing accuracy.
Tolerance value to set the processing accuracy.
The higher the value, the more keys are removed, resulting in the curve's shape deviating more from the original fcurve. Smaller values yield a closer fit to the original curve, but retain more keys.
Choose Curves  Simplify Curve from the fcurve editor toolbar.
Simplify Curve from the fcurve editor toolbar.
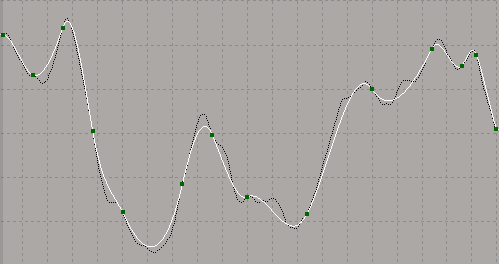
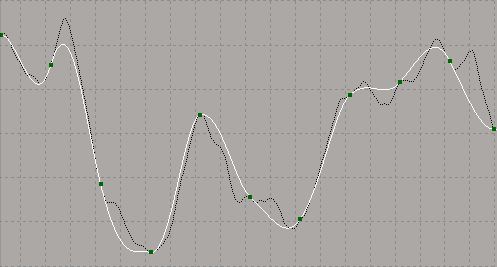
In the image below, the fcurve is fitted with a Tolerance value of 2. The original fcurve is displayed as the buffer curve.
If you are using a low-density fcurve (one with few keys), you may find it useful to resample a curve before simplifying. This way, you can apply a fit using a spline curve to help preserve the smoothness of the resulting fitted curve. If you fit a low-density curve without doing this, the segments between the keys may be more linear than you want.
Resampling adds or removes keyframes at the interval that you specify.
To change the number of keyframes on an fcurve or in a region, do either of the following:
Select one or more fcurves, or draw a region over the part of the fcurves, that you want to resample, then choose Curves  Resample Curve from the fcurve editor toolbar.
Resample Curve from the fcurve editor toolbar.
This immediately resamples the fcurves or region using the current options set for resampling in the Fcurve Editor Preferences editor.
Select one or more fcurves, or draw a region over the part of the fcurves, that you want to resample.
Choose Curves  Curve Processing Options or open the Fcurve Editor Preferences editor.
Curve Processing Options or open the Fcurve Editor Preferences editor.
On the Curve Processing page, set the Resample  Time Step. The time step determines the frequency of the generated keyframes.
Time Step. The time step determines the frequency of the generated keyframes.
For instance, a time step of 2 creates a keyframe on every second frame, or a time step of 5 creates a keyframe at every fifth frame.
You can also choose to keep or discard the original keys on the curve by selecting Keep Existing Keys.
Choose Curves  Resample Curve from the fcurve editor toolbar.
Resample Curve from the fcurve editor toolbar.
In the image below, an fcurve is resampled with a Time Step value of 10 to have one key at every tenth frame. The original fcurve is displayed as the buffer curve.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License