There are many shader types which provide various effects and are used for many purposes. There are equally as many ways to categorize them.
Shaders can provide cartoon, reflection, and environmental effects.
While most shaders can make your models look more realistic, cartoon-style shaders give your character a comic book look.
In the following figure, a character has shaders applied which flatten its color depth and outline its form, giving it a two-dimensional cell-animation look to it, even though it is a 3D model.
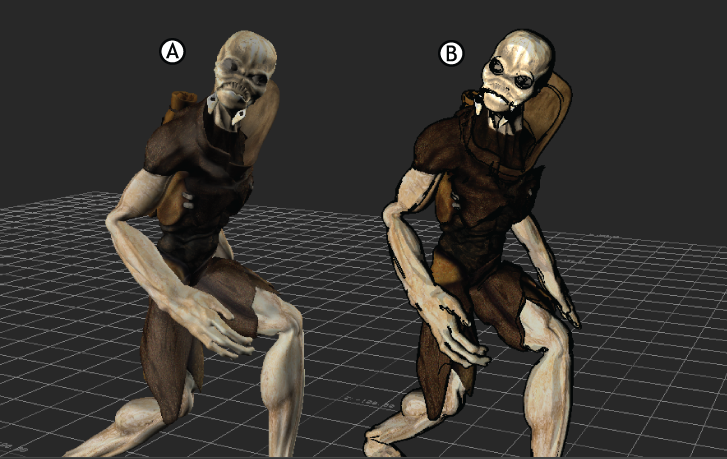

Cartoon Look A. With no shaders B. With Cartoon shading.
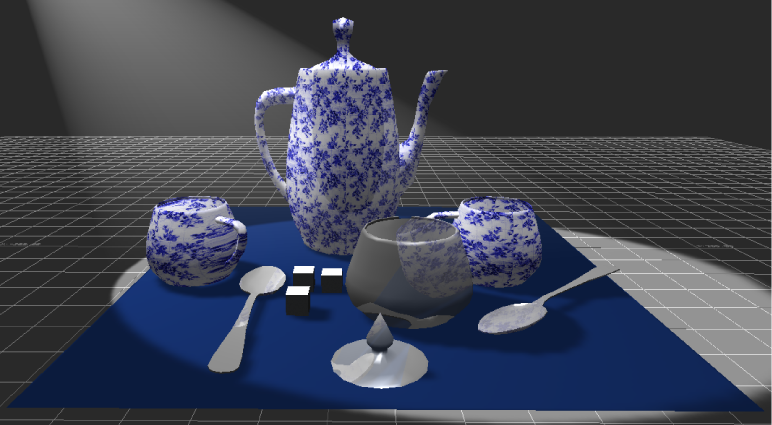
Textures and materials applied to a 3D model cannot give you the sharp reflection effects needed to imply glass, chrome, or mirror. For these effects, you must use reflection shaders.

Reflection shader examples
Reflection shaders make your objects reflect the world around them, but their effects are not limited to creating mirrors. Combine them with transparency to create a shiny glass look, or combine them with a dark material to create a brushed steel look.
You can use live reflections, which will accurately reflect animation in the scene, or a map shader to create a static reflection that does not react to animation around it.
You can use shaders to create environmental effects such as clouds, fire, fog, and rain.
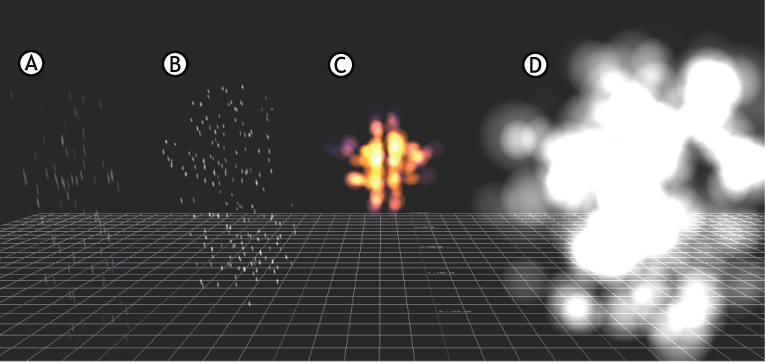
Environmental presets A. Rain B. Snow C. Fireball D. Cloud
Shaders can be applied to objects to create environmental effects like fire, fog, snow, and rain. Because the shader is meant to create an environmental effect, it is applied to a simple object, such as a cube, that defines the area in which the environmental effect occurs. Instead of appending the shader to the object, you replace the object with the shader, so that the model is hidden and only the effect of the shader is visible.
Lighting alone does not convey atmosphere, but how objects react to light does. Use shaders to create realistic shadows and lighting on planes and objects in your scene.
Adjust the shadow intensity to create subtle differences between a ghostly or silhouette effect.
Shadow shader example
You can use shaders to create surface effects on objects that imply that the models have depth and substance, even when the original model was smooth. These effects create further depth and detail.
Some surface effect shaders, such as Faceted and Wireframe, are derived from the model’s construction, while other shaders, such as Bump Map, let you create the appearance of relief over simple geometry.

Surface effects A. Bump map B. Wireframe C. Faceted
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License