Proxy references let you substitute one or more file references by creating a set of possible substitute references, known as proxies, for a given file reference. Proxy references are files that you create to visually or spatially stand in for an existing file reference. In most cases, proxy references are used to temporarily simplify complex scenes by substituting simpler versions of the objects into the scene. This allows production work to proceed without the overhead of the complex components of the original scene. When a scene is simplified in this manner, Maya’s performance improves.
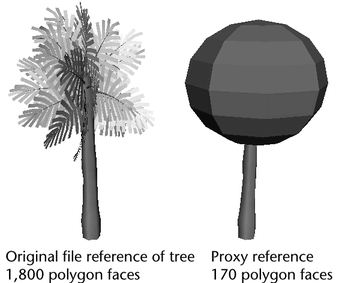
Proxy references reduce the visual clutter in a scene by allowing you to focus on the elements you need to work on while still maintaining a spatial context of the scene’s elements.
For example, you can substitute a scene that contains primitive objects that exist in the same position, size, and scale as a similar scene that contains more complex and detailed versions of furniture for an office. By substituting a simple primitive-based proxy version of the scene, you can obtain better interactive performance when dollying, tumbling, or playing back animation. Because the primitive objects also represent where the more detailed versions of the furniture elements exist spatially in the original file reference, the user can more easily concentrate on animating their character or camera.
To create a proxy reference for a scene you must first create a scene that contains the proxy reference data. This could involve creating a scene that generally matches the contents of a pre-existing scene but contains simplified versions of your characters, props, and assets. The items in this scene should be set up and positioned exactly the same way as your more complex version of the scene, so that a spatial correlation is created between the high and low detail versions of the scenes. Once the high detail version of the scene is referenced, the low detail version can be added as its proxy reference using the Reference Editor.
A proxy reference can only be created for an existing file reference. A proxy cannot exist by itself.
When a proxy reference is first created a proxy set is also created. When the proxy set is created, the original file reference as well as the selected proxy reference are organized under a new proxy manager node. You can then select which file (the original reference or the proxy reference) to load in the scene using the Reference Editor or by right-clicking an object in the scene and making the appropriate selection from the marking menu.
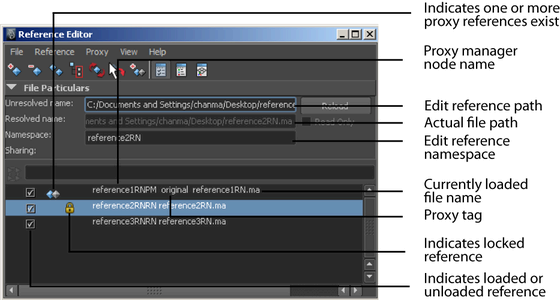
When a proxy reference is added to an existing file reference, the original reference becomes a proxy reference within the new proxy set. In the Reference Editor, an icon is displayed to indicate the existence of one or more proxies for the reference, and the name displayed in the Reference Editor reflects the proxy manager that is created.
By default, any edits on a proxy reference are independent from those on other proxy references in the same set. In order to maintain edits between proxies, you have two options:
If the original reference is created with grouping turned on all subsequent proxy references that get added to the file reference are in the same group. You can use the group to transform/scale/rotate the proxy within the scene, reload a different proxy, and have the transformation/scale/rotation maintained.
For more information, see Proxies with shared edits.
When the second-last proxy reference is removed from the proxy set and only one proxy reference remains, Maya collapses the proxy set. The remaining proxy reference reverts to a file reference and the Reference Editor is updated to reflect this change.
You can differentiate between proxy references for a given file reference by labeling the proxies so they appear with a unique tag in the Reference Editor. This label is called a proxy tag. Proxy tags are useful for managing file references within the Reference Editor because they let you globally load, unload, or switch between proxy files based on their proxy tag.
When a proxy reference is selected for reload, Maya first checks to see if the current proxy is loaded. If it is loaded, Maya unloads it before automatically loading the selected proxy reference. It is not possible to switch between unloaded proxy references, and have the reference remain unloaded. When a proxy tag appears gray in the list, it indicates that it is the currently loaded proxy reference.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License