You can set the following preferences in the sub-category below the category in the window. (There are also preferences under the category. See Animation (Display) preferences.)
See also Edit animation preferences.
-
-
Specifies whether Maya will automatically set keys on a previously animated object’s attributes when you change the values
of those attributes. This preference has the same effect as the Controls’ button 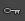 (next to the button
(next to the button  in the Animation controls). This option is off by default.
in the Animation controls). This option is off by default.
These options are available only when is on.
For more information, see What are character sets?.
-
-
Sets keys only for attributes that have been modified.
-
-
Sets keys for all attributes, whether they have been modified or not.
To set the rotation interpolation options, see Set rotation interpolation for curves.
-
-
Specifies the type of rotation interpolation used when creating curves. These options are the same as those available in the
Change Rotation Interp menu item in the . For more information on rotation interpolation, see Animated rotation in Maya.
-
-
Calculates the rotation using three separate angles representing rotations about the X, Y, and Z axes, and an order or rotation. In this mode, the curves that define the rotation for a given node are represented in Euler-angles, interpolation
is performed on each curve independently in Euler space, and keyframes may occur at your discretion—they are not synchronized
with the other sibling rotation curves at the node. You can also animate a single rotation ordinate. This is the default setting.
-
-
Creates curves that have keyframes on sibling curves locked together but with interpolation between keyframes performed in
Euler-space.
It’s useful to keep rotation keyframes synchronized because rotation is a composition of the three separate rotate values.
Deleting just one key on a curve can have a dramatic and unexpected effect on the interpolation.
-
-
Interpolation is calculated using spherical linear interpolation and does not depend on the tangents of the input curves.
-
-
Interpolation is calculated using quaternion cubic interpolation (Squad) and does not depend on the tangents of the input
curves.
-
-
Interpolation is calculated using quaternion interpolation based on the input curve tangents. For example, if the tangents
are linear, Maya uses spherical linear interpolation (Slerp), and if the tangents are clamped, Maya uses cubic interpolation
(Squad).
-
-
Let you set the default rotation interpolation type for new HIK curves. This drop-down list contains the same set of rotation
interpolation options as the preference (listed above). The default for HIK curves is .
Tangents determine the status of curve segments when they enter and exit from a key.
-
-
Weighted tangents represent the amount of influence a tangent has on an animation curve segment. When on, all new tangents
are automatically weighted. Weighted Tangents is off by default. See Edit tangents.
-
-
Specifies the default in tangent type. The In Tangent setting controls the shape of the animation segment before a key.
Options include:
-
-
(Default) An Auto In Tangent compares the current keyframe value to the previous keyframe value, and flattens the curve segment
if it travels above or below those keyframe values. (See also Auto tangents in the menu.)
-
-
A spline tangent rounds the animation curve smoothly before the key. If the key’s Out Tangent is also a spline, the tangents
of the curve are then co-linear (both at the same angle). This ensures that the animation curve smoothly enters and exits
the key.
-
-
A linear tangent creates an animation curve as a straight line before the key.
-
-
The clamped tangent smoothly rounds the animation curve (like the Spline selection) before a key unless the next key is very
close. If so, the In Tangent and the previous key’s Out Tangent are both straight (like the Linear selection), making the
animation curve between the keys straight.
-
-
A flat tangent type sets the tangents before the key to be horizontal with a slope of 0 degrees (flat).
-
-
A plateau tangent type eases animation curves in and out of their keyframes, flattens curve segments that occur between equal-valued
keyframes, flattens keyframes at the points in their curves where hills and valleys occur, and flattens the first and last
keyframes on their curves.
-
-
Specifies the default out tangent type. The setting controls the shape of the animation curve right after a key.
Options include:
-
-
(Default) An Auto out tangent compares the current keyframe value to the next keyframe value, and flattens the curve segment
if it travels above or below those keyframe values. (See also Auto tangents in the menu.)
-
-
A spline out tangent rounds the animation curve smoothly after the key. If the key’s In Tangent is also a spline, the tangents
of the curve are then co-linear (both at the same angle). This ensures that the animation curve smoothly enters and exits
a key.
-
-
A linear tangent creates an animation curve as a straight line after a key.
-
-
Specifies the animation curve is smoothly rounded (like the Spline selection) after a key unless the next key is very close.
If so, the Out tangent and the previous key’s In tangent are both straight (like the Linear selection), making the animation
curve between the keys straight.
-
-
A flat tangent type sets the tangents after the key to be horizontal with a slope of 0 degrees (flat).
-
-
A stepped tangent type forces the animation curve to hold its value from the one key to the next key.
-
-
A plateau tangent type eases animation curves in and out of their keyframes, flattens curve segments that occur between equal-valued
keyframes, flattens keyframes at the points in their curves where hills and valleys occur, and flattens the first and last
keyframes on their curves.
The preferences let you specify the types of blends that can occur between object connections. For example, when you turn on
, you can then both animate and constrain a single object.
When this preference is on:
- You can move or key objects that have existing connections such as animation and constraints.
- When you key or constrain an object, Maya inserts a pairBlend node between the object’s existing connections and the new keys or constraints.
- The attribute is off by default for all new constraints.
is on by default.
When this preference is on:
- You can only key objects that are not constrained.
- When you key an object, Maya inserts pairBlend nodes between the object’s existing connections and the new keys.
- Objects with connections cannot be constrained.
- The attribute is on by default for all new constraints.
When this preference is on:
- You can only key objects that have no existing connections.
- Maya does not insert pairBlend nodes to blend object connections.
- The attribute is on by default for all new constraints.
preferences
-
-
When on (default), neighboring keys with similar values automatically align as you edit curves in the . Enable this preference if you want similar, adjacent keys to snap to identical values.
-
-
When on (default), you can drag to move selected keyframes in the graph view area with a single click. When off, clicking
selected keyframes has no effect in the graph view area, and you must select the Move tool and middle-drag to adjust keyframes.
Enabling this option may be preferable if you are familiar with keyframe editing workflows in other Autodesk applications,
such as MotionBuilder.
preferences
This preference lets you set what you want to occur when you double-click a camera shot in the .
-
-
Set the frame range in the to match the Maya start frame and Maya end frame of the selected shot. (See Camera shot overview.)
-
-
Select the camera assigned to the selected shot.
-
-
Frame the selected shot in the shot view area.
-
-
Turn on the Solo option for the track containing the selected shot.
-
-
Select to keep the Sequence Time indicator at the current time, regardless of where you double-click.
-
-
Select to have the Sequence Time indicator jump to where you double-click.
-
-
Select to have the Sequence Time indicator jump to the start of the selected shot.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
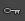 (next to the Animation Preferences button
(next to the Animation Preferences button  in the Animation controls). This option is off by default.
in the Animation controls). This option is off by default.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License