This section describes the menu items and options for the Reference Editor.
Saves edits that were made within the parent scene for a selected file reference to the corresponding referenced file on disk. The edits get transferred so they no longer reside within the parent scene.
Saving the edits to the referenced file is useful if you want the edits to permanently exist in the referenced file. In this way, the edits are propagated to all users of the reference. Some additional items to consider when saving reference edits:
References the edits from the file you select and applies them to the reference node selected in the Reference Editor. Maya applies edits by matching each nodename.attribute in the edit file to the file its being applied to.
For example, you can export a reference edit for pSphere1.translateX in the scene sphere.ma. This edit is saved in the reference file as <main>:sphere_pSphere1.translateX. You can then apply this edit to the scene ball.ma so that ball:pSphere1.translateX is edited.

When you reference a scene with Use namespaces on, Maya creates a new namespace that contains the referenced data. Turning on Use namespaces ensures that all nodes are uniquely named.
A namespace is a grouping of objects under a given name. Each item in a namespace is identified by its own name along with the namespace it belongs to. See Namespaces.
By default, the basename of the referenced file is added to the beginning of the referenced object names, separated by colons See New Namespace (File Name) below).
For example, if you are referencing a scene named foo.ma that contains an object named ball, after it’s imported the ball is named foo:ball.
The currently set namespace is indicated in the Namespace Options section by the  icon. Namespaces that are parents of the currently set namespace are indicated by an
icon. Namespaces that are parents of the currently set namespace are indicated by an  icon. You can set the current namespace in the Namespace Editor by clicking Set Current. See Namespace Editor Overview and Edit namespaces.
icon. You can set the current namespace in the Namespace Editor by clicking Set Current. See Namespace Editor Overview and Edit namespaces.
Namespaces do not effect selection, the DAG, the Dependency Graph, or any other aspect of Maya.
Lets you perform text substation on the offline edits file as it is applied to the scene. One or more sets of replacement text can be specified and are applied to the file in the order that they appear in the list.
For example, if you wanted to replace all the edits applied to an object named sphere1 and apply them instead to an object named sphere2 , you would type sphere1 in the Search for field and sphere2 in the Replace with field, and click Add.
When you reference a file from Maya 6.5 or earlier, some edits may not be recognized by the conversion process. These unknown edits are listed here. You can refresh this window manually by clicking the Refresh Edit List button or remove specific edits by selecting them and clicking Remove Selected Edits.
Removes all edits from the target reference node.
Using Clean Up Reference should be done only if you are certain that you will no longer require the edits it will remove. Using Clean Up Reference on a loaded reference removes all edits which could not be applied. Using Clean Up Reference on an unloaded reference will remove all edits, whether they could be applied or not, and so should be used with care to avoid unwanted data loss.
Loads or unloads references related to selected objects.
For example, if you want to unload an object and the reference to which it belongs without having to open the Reference Editor and figure out which reference should be unloaded, you can simply  -click the object and choose Unload Related Reference. As well, you can select a locator or annotation, and then load its related references (you must select both the locator/annotation
and the foster parent node for this to work).
-click the object and choose Unload Related Reference. As well, you can select a locator or annotation, and then load its related references (you must select both the locator/annotation
and the foster parent node for this to work).

Adds a proxy reference to the currently selected file reference. When you select Proxy > Add Proxy > you can specify the file type to add and set the Proxy Tag Options within the Proxy Options window that appears.
you can specify the file type to add and set the Proxy Tag Options within the Proxy Options window that appears.
If a proxy reference does not exist for the file reference, a proxy set is created for the proxy references for that file reference. If a proxy reference exists, the new proxy becomes a member of the existing proxy set for that reference.
When a proxy reference is created, the listed file reference updates to display a icon to indicate that one or more proxy references exist for that reference.
For information on how proxy references are tagged, see Proxy Tag options below.
The Proxy Options ( ) window is used to set the following options:
) window is used to set the following options:
Select the file format you want to use as a default for the next time you add a proxy reference. If you have a project set up, when you open a scene, the browser points to the directory containing files of that type. On Windows and Mac OS X, it also sets the filter to display only files of the selected type.
Type the text string for the proxy tag you want applied to the proxy reference or select an existing tag from the list in the drop-down menu. When a proxy tag appears in gray in this list, it indicates that the tag is already in use for this specific file reference. The proxy tag appears in the Reference Editor.
Maya keeps track of, and can distinguish between, the last proxy tag used for a file reference, and the last proxy tag used for a proxy reference. This ability streamlines the tagging process regardless of your preferred workflow.
For example, you may want to tag multiple file references in succession with a tag named hiRes when you first create each one. In this case, you need only type the tag name once and it is automatically assigned to successive file reference tags. If you want to tag multiple proxies for those same references, you only need type in the proxy tag name for the proxy once, and the proxy tag will be remembered for successive proxies.
Alternatively, you may want to create and tag one file reference named hiRes and then immediately create and tag its corresponding proxy reference named loRes. You can then create the next file reference and it will automatically be assigned the tag hiRes, then create its proxy reference, and it will automatically be assigned the tag loRes.
Because Maya can distinguish between the most recent file reference and proxy reference tags specified, this alternating tagging workflow is possible.
If a file reference has not been assigned a unique proxy tag prior to the creation of the first proxy in the scene, the file reference will be assigned a proxy tag named original to differentiate the original file reference from the first proxy. Once a tag has been specified for a file reference, it will continue to be used as the default file reference tag until another is specified. That is, Maya only uses the default original tag if the user has not previously explicitly specified a tag for a file reference.
If a proxy tag is not specified when the first proxy reference is created in the scene, Maya will automatically apply a unique proxy tag based on the name of the reference node. Once a proxy tag has been specified for a proxy reference, it will continue to be the default tag for proxy references until another is specified. That is, Maya only uses a default proxy tag name when the user has not previously specified an explicit tag name for a proxy reference.
Once you create a proxy tag, it will become available for selection within the Proxy Tag Options drop-down menu in both the Proxy Options and Reference Options windows.
Proxy tags must be unique within a given proxy set. That is, a proxy tag will be available for a proxy set provided it is not already in use within the same proxy set. You can create your own tags and reuse them in different proxy sets.
Depending on the File Type you select, various File Type Specific Options are displayed here. See File > Open Scene in the Basics guide for more information.
Removes the proxy reference that is selected from the list of proxy tags that appears within the Remove Proxy submenu. The proxy reference is deleted from the proxy set.
The list of available proxy references is displayed in the menu based on their proxy tags. The list of proxy tags is generated from all of the proxy tags currently in use within the proxy sets selected. When a proxy tag appears in gray, it indicates that it is currently loaded.
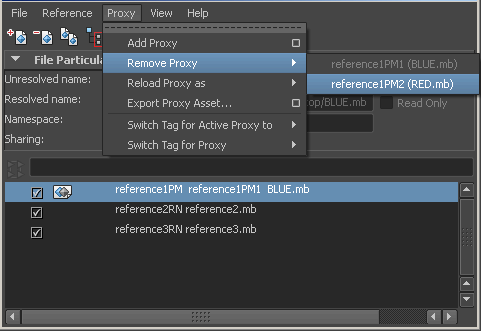
When a proxy reference is removed from a proxy set, and only a single file reference remains, the proxy set is removed and the reference returns to a normal reference state. In the Reference Editor, the icon is removed from the listed file reference, and the listed name of the file reference is updated.
Loads the proxy reference that is selected from the list of proxy tags that appears within the Reload Proxy As submenu. The list of proxy tags is generated from all of the proxy tags currently in use for the proxy sets selected. When a proxy tag appears in gray, it indicates that it is currently loaded.
Reload Proxy As is used to switch between proxy references for a given file reference. The list of available proxy references is displayed in the menu based on their proxy tags. When a proxy tag appears in gray, it indicates that it is currently loaded.
A proxy for a specific proxy set is only reloaded when the selected proxy tag matches one of the available tags for that set. For example, if multiple proxy sets are selected and the high proxy tag is chosen for reload, only those proxy references that have the high tag will be reloaded. Any proxy set that does not include the high tag will remain unchanged.

Exports a proxy asset for the selected asset (referenced or non-referenced). For more information about proxy assets, see Proxy assets.
For proxy asset options, see Assets > Export Proxy Asset.
Displays only the selected references.
Selecting this option also creates a new Reference View Set, which can be found in the View menu. This Reference View Set acts as a bookmark; selecting the created Reference View Set in the future filters the references in the Reference Editor and only displays the references that were selected when the Reference View Set was created.
See Reference View Sets.
The following file information displays when a referenced file is selected in the Reference Editor. You can select to show or hide this information by clicking on the disclosure triangle.
Displays the current namespace for the selected file reference. The namespace for a file reference can be edited within the text field. (This field appears when Use Namespaces is turned on.)