Timelines can contain multiple video and audio tracks. An edit sequence on a track is made of segments and transitions. Video and audio segments appear as a series of rectangles on their associated tracks. Transitions appear as cuts or icons between segments.
Video tracks can be made up of multiple layers. Layers are used to stack video vertically to create composite effects and transitions. If you have more than one layer or track, the positioner's focus point indicates which one is current.
For information on interface elements that apply to stereo tracks, see Stereo Tracks.


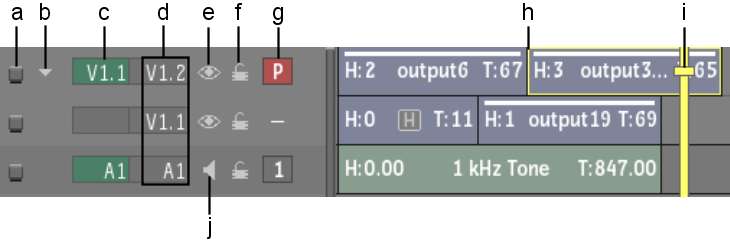
(a) Selector icon (b) Layer collapse arrow (c) Patch identifiers (d) Track identifiers (timeline contains one video track made up of two layers and one audio track) (e) Video Mute icon (f) Lock icon (g) Primary video track indicator (h) Bounding box (i) Positioner (j) Audio Mute icon
Selector iconSelects a layer or track.
Layer collapse arrowCollapses layers into one element. See Collapsing Layers.
Patch and track identifiers and Primary trackIndicate patching for video and audio tracks. See Patching on the Timeline.
Video Mute iconHides the element in the vertical edit. See Muting Layers.
Audio Mute iconMutes or solos the audio. See Audio.
Lock iconPrevents editing operations from being performed on the track. See Locking Tracks.
Bounding boxA yellow bounding box around a timeline segment indicates there is an implicit selection by the positioner. Any editing operations you perform, for example, cuts or soft effects, will occur at the positioner location. If there is no bounding box at the positioner location and you have not explicitly selected the segment, this means there is an explicit selection elsewhere on the timeline. Any editing operations will occur at the explicit selection, not at the positioner location.
Having the visual cue of a bounding box around a segment can help you confirm that you are editing the correct segment. This is especially useful in long- form timelines where you might not see all the segment selections.
PositionerIs the “playhead” for playing the clip. The frame directly beneath the positioner is displayed in the Player or is the current location for an edit such as a dissolve or cut.
Focus pointIndicates the current track. In vertical editing, the positioner's focus point indicates the top layer (focus layer) in the vertical edit.
TrackContains the segments and transitions that you edit together.
LayerUsed for vertical editing and timeline compositing. See Vertical Editing.
ElementRefers to the video segments, audio segments, and transitions that make up an edit sequence. Elements are colour coded to make them easier to identify, as illustrated in the following table. Coloured bars on top of the elements indicate their process and lock status. See Identifying the Status of Soft Effects.
| This interface component: | Is: |
|---|---|

|
A video segment. By default, this segment is pale blue. It represents a video clip in the edit sequence. |

|
A container. By default, this element is dark blue. It represents a container in the edit sequence. |

|
A segment containing a BFX setup. By default, this element is pale magenta. |

|
An audio segment. By default, this segment is pale green. It represents an audio clip in the edit sequence. |

|
An element with unlinked audio. |
| |
A dissolve transition. |
| |
A wipe transition. |