Using the Node Bin
The node bin contains all of the objects that you can add to your scene. The node bin also contains an image node that displays a proxy of the currently selected media. Click and drag within the node bin rows to scroll through all available nodes.


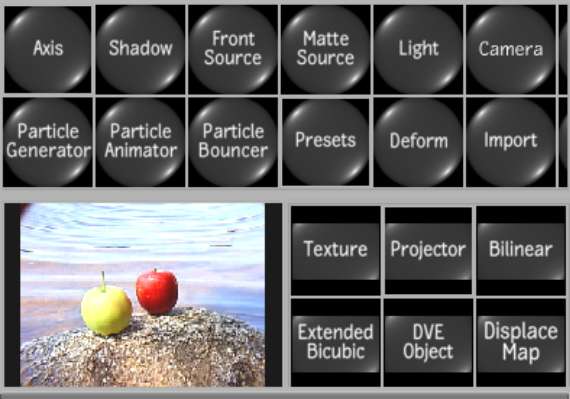
| Select: | To add: |
|---|---|
| Axis | An axis. See Accessing the Axis Menu. |
| Shadow | A shadow to the selected surface. See Adding Shadows. |
| Front Source | A front source node. See Action: Sources. |
| Matte Source | A matte source node. See Action: Sources. |
| Light | A light source. See Adding a Light Source. |
| Camera | Another camera to the scene. See Adding a Camera. |
| 3D Text | 3D text. See Changing 3D Text Properties. |
| Particle Generator | A particle generator. See Generating Particles. |
| Particle Animator | A particle manipulator (referred to as a particle animator in the schematic). See Manipulating Particles. |
| Particle Bouncer | A particle bouncer. See Bouncing Particles. |
| Presets | A preset, by opening the Presets file browser. See Using Particle Presets and Using 3D Text Presets. |
| Deform | A deformation mesh to a selected image or 3D model. See Deforming Models and Surfaces. |
| Import | A 3D model. See Importing 3D Models. |
| Texture | A texture to the selected geometry or particle generator. See Adding Textures. |
| Projector | A projected clip to the scene. See Projecting Textures. |
| Image (proxy) | An image (with axis) to the scene. You can change the surface type of the image. See Changing the Shape of a Surface. |
| Bilinear | A surface with four corners joined using linear interpolation. See Adding Surfaces. |
| Bicubic | A surface with four corners joined using bicubic Bezier interpolation. See Adding Surfaces. |
| Extended Bicubic | A surface with four corners joined using bicubic Bezier interpolation. You can subdivide Extended Bicubic surfaces to obtain additional tangents. See Warping an Extended Bicubic Surface. |
| DVE Object | A DVE Layer Object to emulate the axis and surface structure of DVE clip layers. See Adding a DVE Layer Object. |
| Displace Map | A displace object and parent axis to the scene. See Adding a Displacement Map. |