You can adjust the softness gradient of a mask to smoothen its edges. You can smoothen the gradient towards the inside edge, the outside edge, as well as the area where the inside and outside adjustments have an effect. You can create a uniform gradient around the edge of the mask, or use an advanced gradient to control the shape of the gradient at different parts of the mask.
To create a uniform gradient, you define how far you want the gradient to be offset from the edge of the mask and then set its transparency. To vary the shape of the gradient, you move vertices on inner and outer softness splines. The gradient will be based on how far each vertex point is offset from the mask.


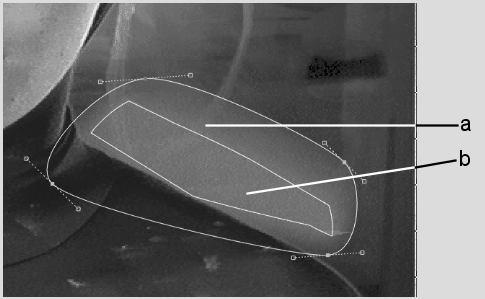
(a) Alpha region (b) Inner offset
Advanced gradient provides a versatile method for setting the softness of the mask edge. It applies a gradient according to the distance of the softness borders from the garbage mask spline. It allows you to customize the softness gradient at different parts of the mask. The advanced gradient has two softness borders, one inside and one outside the mask border. It also includes inner and outer softness vertices for each regular mask vertex.


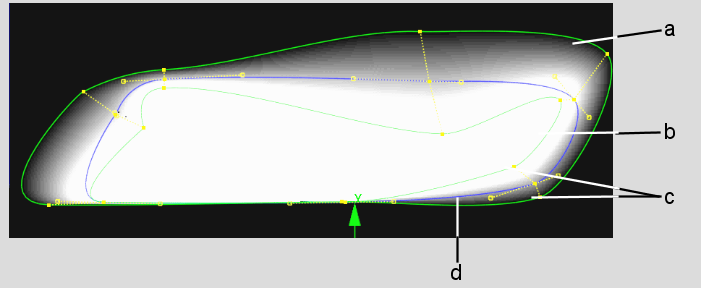
(a) Outer Softness border (b) Inner Softness border (c) Softness vertices (d) Mask border
Some potential uses for the advanced gradient are:
When using the Tracer in the GMask node in Batch, you can work in two modes: advanced gradient and pickers. Individual vertices can be set to either of these modes.
You can change the default mode of the Tracer from advanced gradient to pickers, a system of localized keys. Tracer analyses the colour information both inside and outside the mask, then compares the values and uses a keying algorithm to derive a key for the mask edge. This system allows you to key images with a lot of detail at the edges.
To control softness and advanced gradients, use the Garbage Mask Shape controls.


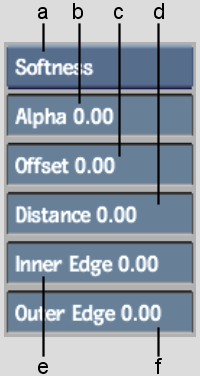
(a) Edge Softness box (b) Alpha field (c) Offset field (d) Distance field (e) Inner Edge field (f) Outer Edge field