These additional Linux user notes provide special information for configuring Maya to run on Linux, describe differences between Maya for Linux and other versions of Maya, and provides other information specific to using Maya on the Linux operating system. For complete information on limitations and possible workarounds, also refer to the Maya 2009 Release Notes.
Compiling plug-ins and standalone programs
To compile plug-ins and standalone applications for Maya 2009 on Linux, use the released gcc 4.1.2 compiler. Maya has been compiled with this compiler under RHEL 4 WS. As well, some libraries and symbolic links are installed in the /lib directory under your Maya directory, and should not interfere with the normal operation of your Linux system.
For more information, see Compiler Requirements, Linux environments (64-bit), and Linux compiler requirement in the API Guide.
When installed on a Linux system, Maya works in much the same way as when installed on Windows.
Using the MayaScheme file to set fonts, font sizes, and colors
Fonts, font sizes, and colors can be configured using the MayaScheme file. This file lets you specify X Resources that Maya uses for configurable text. The default file is found in /usr/autodesk/maya2009-x64/app-defaults/MayaScheme. Copy this file to your home directory’s $HOME/app-defaults directory so that it can be edited.
Refer to the Maya 2009 Release Notes for any known limitations.
To use Maya on Linux, certain default keyboard and mouse bindings must be changed from the factory settings. These default bindings prevent commands from being received by Maya, such as the ones that let you tumble or pan a view in a panel.
Different Linux window managers have different key bindings and different procedures for setting them. Linux systems are highly customizable, and many combinations of Linux system components are possible for use with Maya—more than can be described (or tested) by Autodesk.
The following instructions give the procedures necessary for changing the most common configurations.
KDE and Gnome desktop configuration
For Maya to work properly with KDE and Gnome, some modifications should be made to the mouse control. The default bindings of the Alt key and mouse buttons do not work well with Maya. We recommend turning off the Alt+mouse buttons. Since Maya uses the Alt+mouse buttons for scene view tumbling, you need to ensure the bindings don’t conflict.
Different versions of KDE and Gnome may have different methods of selecting the key bindings. See the KDE and Gnome documentation for instructions if the following steps don’t work for your particular window manager.
For modifier key Meta, set all mouse action combinations to Nothing.
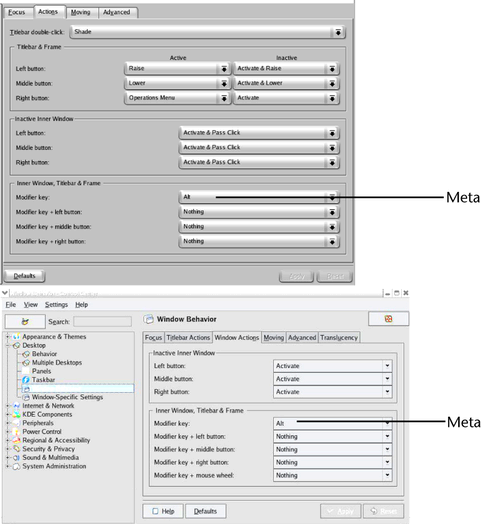
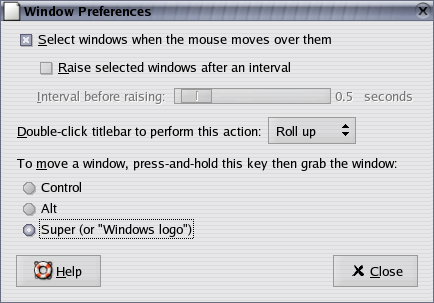
(Setting either Control or Alt here may cause problems when using Maya.)