Show in Contents

Add to Favorites

Home: Autodesk Maya Online Help

Convert a texture or shading network to a File Texture
Map and position textures

Creating normal maps for use with hardware shaders
Create texture maps with the Transfer
Maps editor
Use
the Transfer Maps editor to create
various types of texture maps. For more information, see
Transfer Maps.
Note
- All Transfer
Maps editor target objects must have clean, non-overlapping UVs.
- NURBS
and Subdivision Surfaces are not supported as source or target meshes.
The Transfer Maps editor can only
generate texture maps for polygonal geometry.
- By
default, if multiple target objects are loaded in the Transfer
Maps editor, then a single map is generated for all the
targets. However, if you want to create separate maps for each of
your target objects, then you need to perform the Transfer
Maps bake operation for each target separately.
- You
can use display layers or quick select sets to separate and keep
track of your source and target meshes.
- You
can use file referencing to bring high resolution geometry into
your scene to be used as source meshes.
For a description of the Transfer
Maps editor options, see
Lighting/Shading > Transfer Maps.
To
create a map of one object’s mesh attributes and then bake that
map onto another object
- Select
Lighting/Shading > Transfer Maps.
The Transfer Maps window
appears.
- In
the scene view, select the object you want as your target.
This is the object to which you want to bake the texture map.
- In
the Target Meshes section of the Transfer
Maps editor, click the Add Selected button.
The object you selected in the scene view is
now the current target for your object transfer map operation.
- In
the scene view, select the object that you want as your source.
This is the object that has the mesh attributes for which you want
to create a texture map.
- In
the Source Meshes section of the Transfer
Maps editor, click Add Selected.
The object you selected in the scene view is
now the source mesh for your transfer map operation. By default,
all the unselected meshes in your scene are loaded as the source
meshes.
TipA shortcut to this procedure is to first
select the object that you want as your target and then select
Lighting/Shading > Transfer Maps.
This way, the object that you selected is automatically listed in
the
Target Meshes section of the
Transfer
Maps editor. All other unselected meshes in your scene
are also automatically loaded as the source meshes.
- From
the list of icons, select the types of output map you
want to generate when you create your texture map and click on the
appropriate icon.
See
Output maps.
- Set
the output options for each of your texture maps.
If you plan to create several maps with the
same width and height, you can reuse your settings by entering them
in the
Maya Common Output section
(or mental ray Common Output section)
of the Transfer Maps window.
Otherwise, if you uncheck the Use
Maya common settings option (or Use mental
ray common settings option) for your texture map, the Map
width and Map height attributes appear
in the texture map section that you are currently working on.
See
Maya Common Output.
- Select
one of the following:
- Click Bake
and Close if you want to generate the texture maps and
then close the Transfer Maps editor.
- Click Bake to
generate a texture map and leave the Transfer Maps window open.
- Click Close to
disregard any changes to the Transfer Maps editor
settings.
To
create a normal map using the Transfer Maps editor’s
default settings
- Load
your source and target meshes into a new Maya scene.
- Make
sure that your source and target meshes are positioned on top of each
other in the scene view.
- Select
your target mesh in the scene view.
- Select
Lighting/Shading > Transfer Maps.
The mesh you selected is automatically loaded
as a Target and all other meshes in your scene are loaded as Sources.
- In
the Output Maps section, click
on Normal from the list of icons
to create a Normal map.
- Set
the following attributes in the Normal map
section:
- File
name (Normal map field)
This determines the name of the texture map
file as well as where the map will be saved.
This determines the file format of the normal
map you generate.
NoteIf you want to render your normal map in
mental ray for Maya, you must save the normal map as one of the
supported formats: EXR, Maya IFF, JPEG, MI, PNG, YUV, RLA, SGI,
PIC, TIM, TGA, and BMP. You must also turn on the
Maya
derivatives option in the
Render Settings: mental ray tabs,
Options tab,
Translation section,
Performance sub-section.
For more information, see
Render Settings: mental ray tabs in
the
Rendering guide.
Select Tangent Space.
- Check
the Use Maya common settings option
so that you can share and reuse your settings when you create more
than one map with the same width and height.
- Scroll
to the Maya Common Output section
and expand the section to set your common map attributes. Set the
following options:
This specifies the resolution for the texture
map.
NoteThe Maya scene view only supports tangent
space maps and they are only visible in the scene view when in High
Quality Rendering mode.
- Select
a medium Sampling Quality.
- Select World
Space in Transfer in.
- Keep
the rest of the options at their default settings.
- Scroll
to the Connect Output Maps section
to specify how the texture map you are going to create will be linked
to the target mesh. To view the results of the texture map within
Maya, enable Connect maps to: New shader /Connect
maps to: Assigned shader.
- Bake
the normal map.
Tip
- You
can use display layers or quick select sets to separate and keep
track of your source and target meshes.
- You
can use file referencing to bring high resolution geometry into
your scene to be used as source meshes.
To
create a left-handed tangent space normal map
- In
order to create a left-handed tangent space normal map, you must
do the following:
- Open
the Attribute Editor for the target
meshes’ shape node.
- Expand
the Tangent Space section and select Left
Handed under Coordinate System.
For more information regarding the left handed
tangent space, see
Tangent Space of
the Polygonal Modeling guide.
Advanced normal map generation
To
create a custom search envelope
- Select
Lighting/Shading > Transfer Maps.
The Transfer Maps editor
appears in the scene view.
- In
your scene view, select the polygonal mesh that you want to define
as your custom search envelope.
- In
the Target Meshes section, click Add
Selected.
The selected mesh is loaded into the Transfer
Maps editor as a target mesh.
 -click
on the mesh’s name In the Target Meshes section
and select Use Selection as Envelope from
the context-sensitive menu that appears.
-click
on the mesh’s name In the Target Meshes section
and select Use Selection as Envelope from
the context-sensitive menu that appears.
The polygon mesh you selected is now the search
envelope for your Transfer Maps operation.
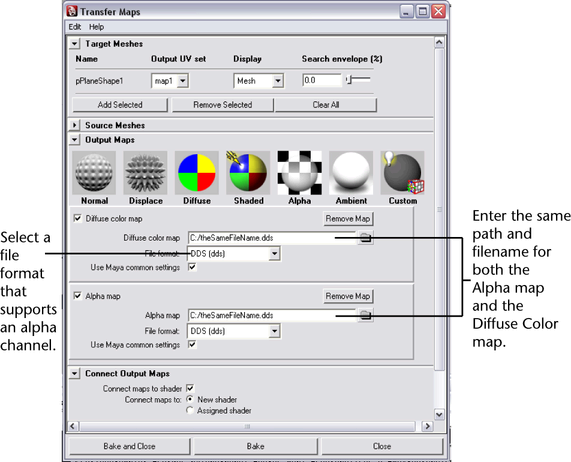
To
create a texture map with an alpha channel
- Transfer
maps allow you to pack any scalar output (for example, alpha or displacement)
into the alpha channel of the texture map being used for a vector
output (for example, color or normal). Therefore, you can create, for
example, a color map with alpha, or a normal map with displacement, or
a color map with displacement, and so forth.
- Select
a file format that supports an alpha channel (for example, .dds, .exr, .tif).
- Enter
the same path and file name into the two output you want to combine
into a single texture map. The path and file names are case sensitive.
- Bake
the map.
NoteIf the Connect maps to shader option
is enabled, Maya attempts to connect the combined map to the shader.
However, many of the combinations that are generated using this
method require a custom (hardware) shader for correct display in
the scene view.

 -click
on the mesh’s name In the Target Meshes section
and select Use Selection as Envelope from
the context-sensitive menu that appears.
-click
on the mesh’s name In the Target Meshes section
and select Use Selection as Envelope from
the context-sensitive menu that appears.