Activate this option in order to split geometry vertex Normals based on edge continuity.
Do not use this option if you do not require hard edges in MotionBuilder, since this operation duplicates vertex information and converts geometry.
Use this option to preserve whether edges are hard (divided) or not (continuous) when you operate between 3ds Max or Maya and MotionBuilder 2010 and earlier. If you disable this option, all Smoothing Groups in 3ds Max are ignored as well as all hard/soft edge information in Maya.
For example, a 3ds Max-created box that would normally have defined edges would lose them, with all faces visually connected, without visible edges dividing them, in MotionBuilder. This is result is hardly noticeable for organic objects, but is very noticeable on hard surfaces such as tables and cars, and so on.
See the Split per-vertex normals workflow to import FBX files exported from 3ds Max into MotionBuilder with proper edge continuity while retaining the original 3ds Max edge continuity for import back into 3ds Max.
Split per-vertex normals workflow:
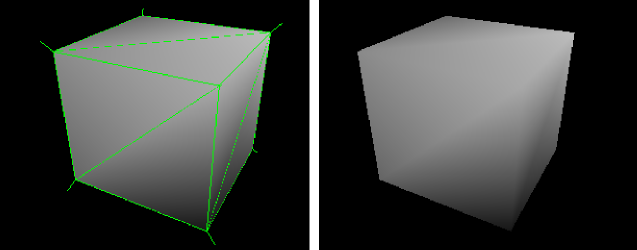
Split per-vertex Normals option disabled on export produces this result in MotionBuilder 2010 and earlier
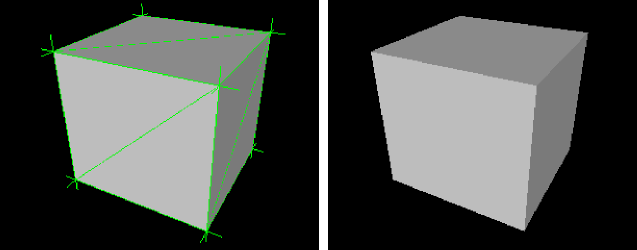
Split per-vertex Normals option activated on export produces this result in MotionBuilder 2010 and earlier