Create curves-on-surface where an imaginary tube surrounding a surface curve intersects a surface.
This tool takes a curve-on-surface, surface edge, or surface isoparm as input. To create a tube surface from a free curve,
use the Surfaces > Tube Surface tool.
tool.
Create curves-on-surface a certain offset distance from a surface curve
 ❒.
❒.
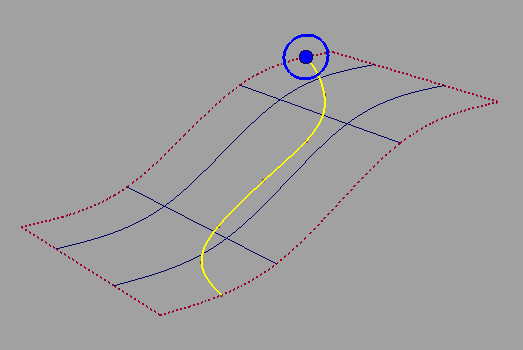
A blue radius manipulator appears at the beginning of the curve.
 (Windows) or
(Windows) or  (Mac).
(Mac).
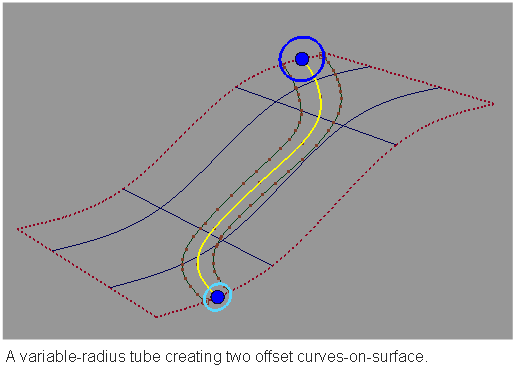
This tool maintains construction history. When you reshape the centerline curves, the offset curves-on-surface are automatically recreated.
This tool will also create a tube surface if the Surface option is set to Tube (closed tube surface) or Groove (half tube surface).
If Surface Type is set to Multiple surfaces, the offset curves-on-surface are segmented to correspond to the multiple tube surface boundaries. (When Bezier Surfaces is off, these also correspond to the input curves-on-surface, or surface edges.) To create the offset curves-on-surface as a single piece (for each surface), you must set Surface Type to Single surface.
Create curves-on-surface offset on more than one surface at once
If two surfaces share an edge, you can build curves-on-surface, grooves, or tubes on both surfaces with the Tubular Offset tool.
The tubular offset is built from the selected edge of the primary surface (first surface you select). The secondary surfaces are trimmed or have curves-on-surface created on them by the tubular offset.
 .
.
The Pick Chooser window appears if the selected edge intersects with other geometry.
The surface turns pink to indicate that it’s selected. The edge of the surface turns yellow showing the path of the tubular offset.
 key to select them through the pick chooser.
key to select them through the pick chooser.
The secondary surfaces turn pink.
The tubular offset is built on all selected surfaces.
The manipulator behaves in exactly the same way as in the previous workflow.