Makes the selected geometry
symmetric, and lets you modify the controls (CVs, edit points, blend
points) on one side, while the corresponding controls on the symmetric
half update automatically to maintain the symmetry.
The symmetry
plane is defined by the default symmetry plane for the layer the
curve or surface belongs to (Y=0 by default). This plane can be
modified by using Layers > Symmetry > Set Plane.
After the curve or surface
has been made symmetric, any transformation tool can be applied
to the controls.
Inputs and selection
- Any type of curve or surface can be selected.
The modified controls can be CVs, edit points, and blend points.
If moving keypoints, the curve loses its keypoint attributes.
- For blend curves, only the position of
the blend points is supported by symmetric modeling (and not other
constraints such as tangent scaling). Blend curves where any blend point
is connected to geometry are not supported.
- Several curves and surfaces can be selected
at once, either before or after entering the tool.
- Symmetry constraints are applied to each
curve or surface individually.
Modification
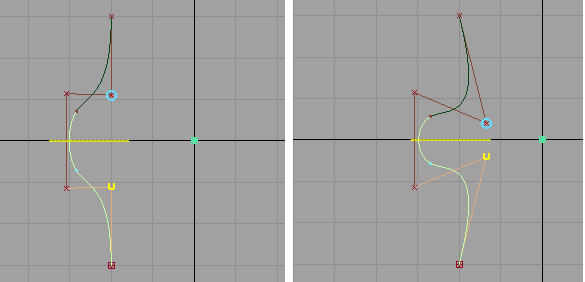
- If the input curve or surface is not
symmetric, the tool modifies the controls of the model to ensure
that it is symmetric. It applies the position of the controls from
the beginning of the curve or surface to the symmetric partners
at the end of the curve or surface. Click the Flip
Master Side button to have it work the other way around.
NoteIf
the curve or surface was already symmetric, the Flip
Master Side button does not appear.
- If a control (CV, edit point, or blend
point) is selected prior to entering the Symmetric Modeling tool,
the side of the object containing the picked control becomes the
master side and is not modified when the object is made symmetric.
- Any transformation tool can be applied
to the controls including Move, Rotate, Scale, Non
Proportional Scale, Move CV (XYZ,
Slide, NUV, Project) or Proportional Modification.
- Once the Symmetric Modeling tool
has been applied to a curve or surface, the controls respond to
any transformation by also modifying their symmetric partner across the
plane of symmetry.
Symmetry plane
- The initial symmetry plane location and
axis direction is defined by the layer symmetry plane. By default
this plane is defined as Y=0 (XZ plane).
- A symmetry plane is assigned and displayed
for each object selected.
- The symmetry plane for a layer can be
modified through Layers > Symmetry > Set Plane.
This does not affect the symmetry plane assigned to any curve or
surface through the Symmetric Modeling tool.
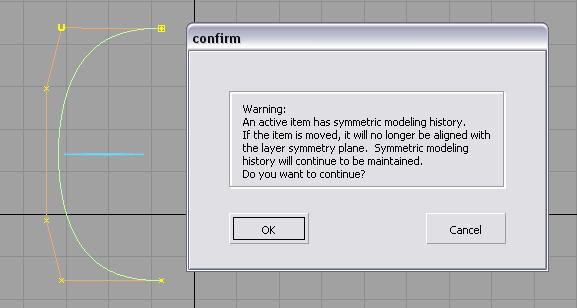
- Once defined, the symmetry plane is unique
to each curve or surface. When a curve or surface is transformed,
its symmetry plane becomes decoupled from the layer symmetry plane,
and follows the object. If the plane doesn’t match the layer symmetry
plane anymore, it is drawn in a different color. A confirm box also
appears in this case.
Undo
- If a curve or surface is modified while
establishing symmetric constraint, you can use Edit
> Undo (
 + Z) to return
it to its original state. Similarly, Undo works
with any symmetric modification to the controls, up to the limit
specified inPreferences > General Preferences.
+ Z) to return
it to its original state. Similarly, Undo works
with any symmetric modification to the controls, up to the limit
specified inPreferences > General Preferences.
- You can return a curve or surface to
its normal state (without symmetric constraint), while maintaining
the modifications to the controls, by removing the construction
history with Delete > Delete Construction History,
or by using the History View window.
 + Z) to return
it to its original state. Similarly, Undo works
with any symmetric modification to the controls, up to the limit
specified inPreferences > General Preferences.
+ Z) to return
it to its original state. Similarly, Undo works
with any symmetric modification to the controls, up to the limit
specified inPreferences > General Preferences.