mr Proxies are useful when you want to fill a scene with instances of objects that have a high polygon count, such as 3D trees. Proxy objects save you time and free up memory because they do not need to be converted to mental ray format and their source objects do not need to be present during render time.
In this lesson, you convert trees to .mib format so they can be used as mr Proxy objects.
 Zoom and
Zoom and  pan so the tree objects
fill the viewport.
pan so the tree objects
fill the viewport.
 Render the scene.
Render the scene.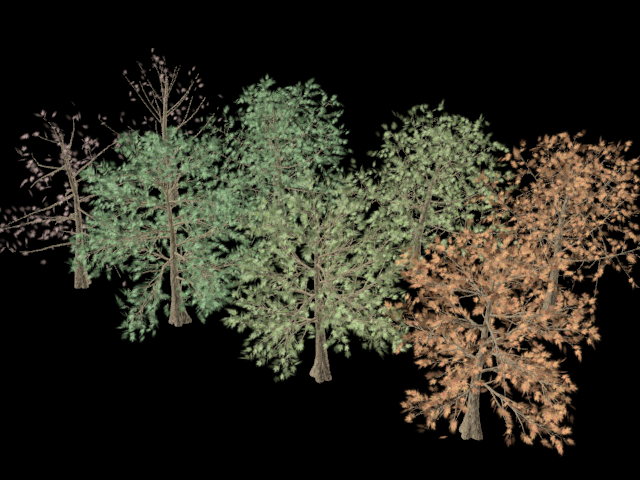
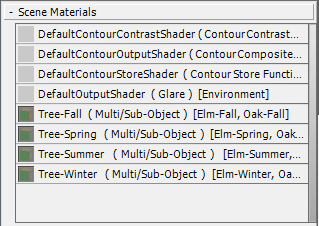
The eight trees in the scene show foliage from four different seasons: winter, spring, summer, and fall. The trees in the front row are oaks, and the trees in the back row are elms.
These trees were created and textured using the methods described in the lesson Creating Billboard Tree Maps. The only difference is that there was no need to center each trees in a viewport and render it: The mr Proxy method works with referenced geometry instead of with rendered bitmaps.
 Close the Rendered Frame
Window.
Close the Rendered Frame
Window.
Save the materials to a library:
The tree materials that you saw in the rendering will need to be reused for the mr Proxy objects. The best way to do this is to save the materials in a library, so you can access them for use in various scenes and situations.
 Open the Slate Material
Editor.
Open the Slate Material
Editor.
 Temporary Library.
Temporary Library.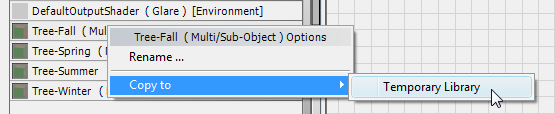
3ds Max creates a Temporary Library group that appears at the bottom of the Browser panel. The Temporary Library has a copy of the Tree-Fall material in it.
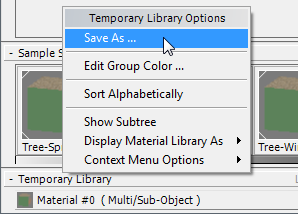
3ds Max opens a file dialog. On the file dialog, navigate if you need to to the \materiallibraries subfolder of your Project Folder, then enter mytrees as the library name (the file name extension for a material library is MAT), and then click Save.
 (Material/Map Browser Options).
This opens a pop-up menu. On the pop-up menu, choose Open Material
Library.
(Material/Map Browser Options).
This opens a pop-up menu. On the pop-up menu, choose Open Material
Library.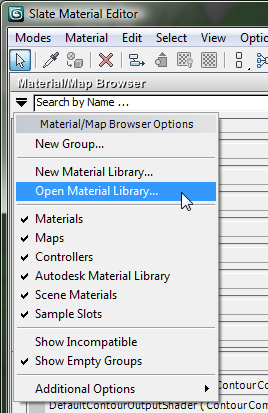
3ds Max opens another file dialog. In the \materiallibraries subfolder, choose the library you just created, mytrees.mat, and then click Open.
3ds Max opens a group for mytrees.mat at the very top of the Browser panel. (The Temporary Library remains visible at the bottom of the panel.)
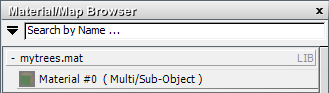
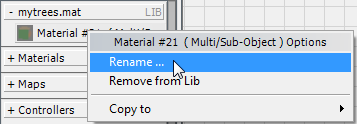
3ds Max opens a Rename dialog. Change the material name back to Tree-Fall, then click OK.
 mytrees.mat.
mytrees.mat.
 Save.
Save. 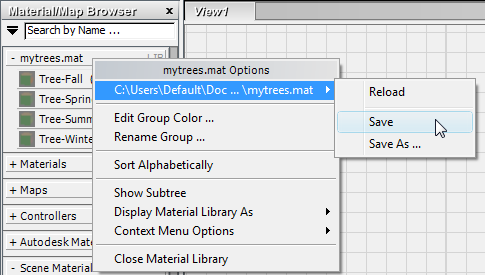
 Close the Slate Material
Editor.
Close the Slate Material
Editor.
Now you have a library of materials to use for the proxy objects. The next task is to create those proxies.
Save source objects in mr Proxy file format:
 Create panel, click
Create panel, click  (Geometry), then open the
Objects drop-down list and choose “mental ray.”
(Geometry), then open the
Objects drop-down list and choose “mental ray.”
 Modify panel. On the Parameters
rollout, in the Source Object group, click the Source Object button
(initially labeled “None”).
Modify panel. On the Parameters
rollout, in the Source Object group, click the Source Object button
(initially labeled “None”).
In the viewport, click the Elm-Winter tree object.
 Source Object group,
click Write Object To File.
Source Object group,
click Write Object To File.
3ds Max opens a file dialog. If you need to, navigate to the \sceneassets\renderassets folder. Name the file My_Elm_Winter (it has a file name extension of MIB), and then click Save.
3ds Max opens an “mr Proxy Creation” dialog. On this dialog, click OK to accept the default values.
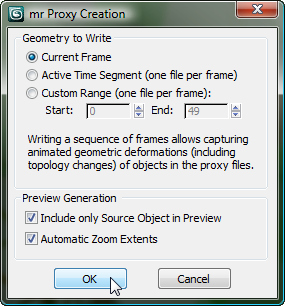
3ds Max briefly displays a small Rendered Frame Window while it renders the proxy geometry.
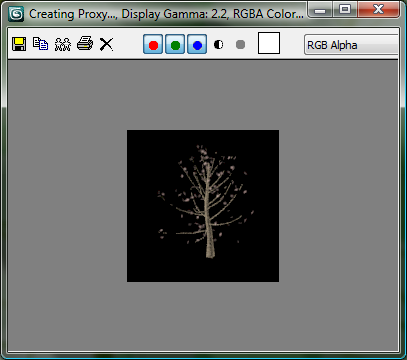
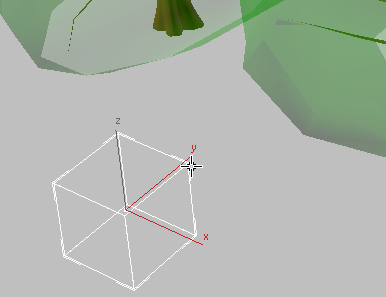
In the viewport, 3ds Max displays the mr Proxy object as a point cloud.
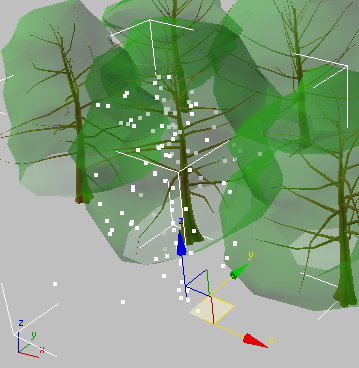
 Display group, change
the Viewport Verts value from 128 to 512, and press Enter.
Display group, change
the Viewport Verts value from 128 to 512, and press Enter. 
The object outline becomes more apparent as more points are displayed, but a denser point cloud can affect viewport performance.
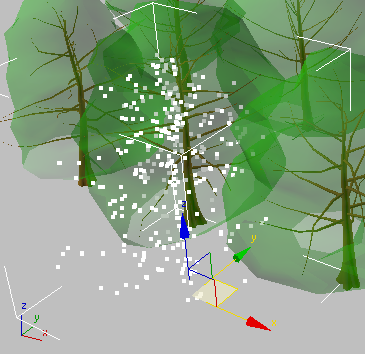

3ds Max displays the proxy surrounded by a complete bounding box.
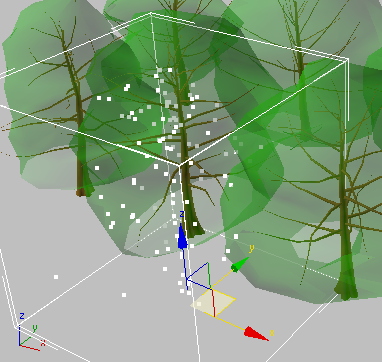
When you’re done, you should have an .mib file for Elm-Spring.
If you were working from scratch, you would repeat the steps for every tree in the scene, but to speed things up a little, we have created .mib files for all the tree types. These are saved in the \sceneassets\renderassets folder. You will use these proxies in the next lesson.
The work you needed to save is contained in the MIB files and their associated bitmaps.