To display: Select an object with the Cloth operator already applied to it and click the Cloth tab in the ClothOp property editor.
For more information on cloth in general, see Cloth [ Simulation and Effects].
| Name |
Defines the name of the cloth property associated with the model. |
| Nail |
Only available if you select a cluster on the cloth object and choose Create Note If you use a weight map on the Nail option (click on its connection icon), the results will not be a gradual falloff of the weight map values because the Nail option is an on/off option. This means that 100% of the weight map will be in effect where the weight map value is 50% or more, and 0% where the weight map value is less than 50%. See Using Clusters for Localized Effects [ Simulation and Effects]. |
| Local |
Only available if you select a cluster on the cloth object and choose Create |
| Mass |
Defines the total mass of the cloth. The mass of each vertex of the model is given by that value divided for the number of vertices. |
| Friction |
Defines the friction of the cloth against itself and obstacles. If you want a rotating object to transfer its movement to the cloth, for example, increase this value. |
To help reduce that stretchy, "rubbery" look when a cloth drapes over an obstacle, use high values for all the Stiffness parameters. Low values (no resistance) allow the cloth to deform without resistance.
For more information, see Controlling the Stretch with Spring Nets [ Simulation and Effects].
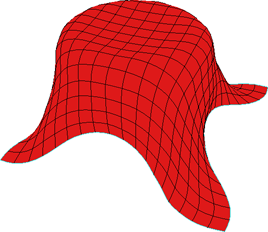
|

|
| Shear Resistance value of 1 on Silk cloth preset. |
Shear Resistance value of 100 on Silk cloth preset. |
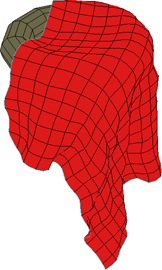
|
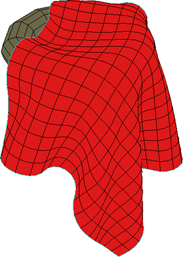
|
| Stretch Resistance value of 1 on Silk cloth preset. |
Stretch Resistance value of 500 on Silk cloth preset. |
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License