You can copy an existing polygon mesh topology into another mesh once using Clone Polygon Mesh, or repeatedly using Create Copies from Polygon Mesh. After that, you can transfer attributes from the source mesh to the new one.
If the source mesh has local materials on polygons, make sure that they are applied as Materials and MaterialID attributes. See Applying Materials in ICE.
If necessary, you can convert cluster-based materials to ICE-based materials. See Converting Cluster-based Materials to ICE.
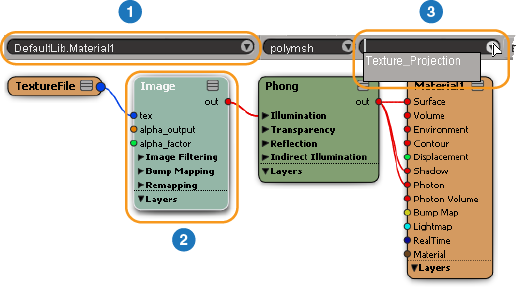
If necessary, make sure that all materials are set to use the New Texture Projection Attribute Name. See Specifying Projections for Materials.
Use the various "Copy [Component] Data from Source" to copy additional attributes, such as weight maps, vertex colors, and additional projections.
Repeating Polygon Mesh Topology
You can create a single polygon mesh object that consists of repeated copies of another mesh's topology. You can specify the offsets of the copies using a transform, a group, or a particle cloud.
If the source mesh has local materials on polygons, make sure that they are applied as Materials and MaterialID attributes. See Applying Materials in ICE.
If necessary, you can convert cluster-based materials to ICE-based materials. See Converting Cluster-based Materials to ICE
If necessary, make sure that all materials are set to use the New Texture Projection Attribute Name. See Specifying Projections for Materials
Use the various "Copy [Component] Data from Source" to copy additional attributes, such as weight maps, vertex colors, and additional projections. Set Source Name to the data to copy, and Target Name to the attribute you want to create to hold the copied data.
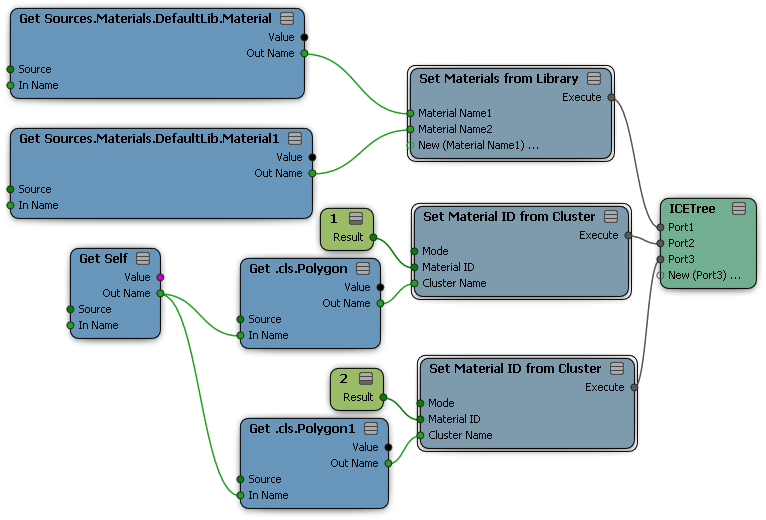
Converting Cluster-based Materials to ICE
To convert local materials applied on clusters so that they can be manipulated and transferred using ICE:
Specifying Projections for Materials
To specify the correct attribute to use for a projection, first select the cloned or copied mesh, open or refresh the render tree, and then do the following: