Lets you select polygons based on a user-configured constraint filter.
These are the options for the feature.
Note
The options that display in the option window are dependent on the selection of components in the scene view. That is, you must first select an example of
the component type you wish to filter in order to display the related options within the option window before you can set the filter options.
At the very top of the window in the list, you specify conditions to filter your selection actions in different ways. These options apply to all component modes.
Click the option to make your selection. Which constraints are applied, and to what settings, is determined by the options
you set. There are four different modes:
-
-
When on, no selection constraints are used. This is the default setting.
-
-
When on, the constraints affect only the next selection mode with a technique such as holding the Shift key and clicking the
left mouse button.
-
-
When on, Maya applies the constraint to whatever has already been selected, plus whatever selection you make next.
-
-
When on, Maya applies the constraints to the entire object automatically, plus whatever group you select next.
Constraint options
The following section describes the options you can set for selected components in the properties section of the window.
properties
The following options are applicable to all component types.
Select where the items are constrained.
-
-
If selected, this constraint is not taken into account. The option means the same for every option in the Properties section.
-
-
If on, the selection constrains to only the items on the perimeter of the current objects.
-
-
This is the default setting for Location properties. Maya selects only the items on the inside of the current objects. It
has the reverse effect of .
properties (for edges only)
If you select edges, options are made available. These options do not display for any other component type.
Select the type of edges.
-
-
Click one of these options to constrain the selection to either hard or soft edges.
Constraint for faces
In addition to the properties that all component modes share, when you are in the face component mode, Maya provides numerous
face-specific properties. For example, you can set options to select faces according to order, planarity, and shape— if a
polygon is concave instead of convex—as well as mapping and topology.
These are described next.
Order options are used to set a valid range for the shape of the faces. If the following options are on, Maya constrains the
selection to what you specify.
-
-
Maya only selects faces with three edges.
-
-
Maya only selects faces with four edges.
-
-
Maya only selects faces other than triangles or quads (faces that have more than four edges).
Select eitehr Planar or Non-planar faces.
-
-
selects only planar faces. selects only non-planar faces.
Select polygons based on the angle of their sides.
-
-
selects polygons that have at least one interior angle greater than 180 degrees. selects polygons whose interior angles are all less than or equal to 180 degrees.
Select faces based on whethe they have a hole or not.
-
-
If you select non-holed, only faces that do not have holes are selected. If you select , only faces in which holes have been created (using the Mesh > Make Hole Tool) are selected.
Note
Maya considers faces with holes to be concave.
-
-
Depending on what you choose, only mapped or unmapped faces are selected. Mapped faces are faces with texture (UV) coordinates—unmapped
faces do not have texture (UV) coordinates.
Select from various types of problematic faces.
-
-
A group of faces glued on top of each other are selected. For example, two faces whose normals face each other.
-
-
Lets you select faces that cannot be triangulated. Use this constraint option to select these problem faces, then repair them
using the . See Split polygon faces for details.
options
and values
The and values for most of the options correspond to the units of a polygonal face. The values you set constrain the selection to the size of the face that
corresponds to those units. The default unit size is in centimeters by default. You can change this in the window (Window > Settings/Preferences > Preferences, then click the category).
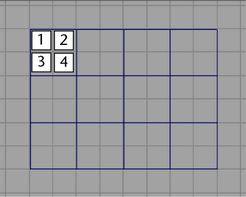
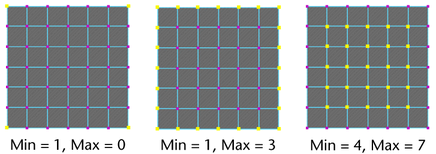
In this example, each face of a polygonal primitive plane is four units. You can determine this by looking at the squares
of the grid within each face.
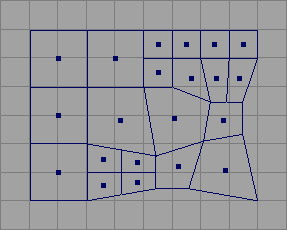
When you scale some of the faces and subdivide others, the topology changes as do the and values you can enter to constrain the selection area.
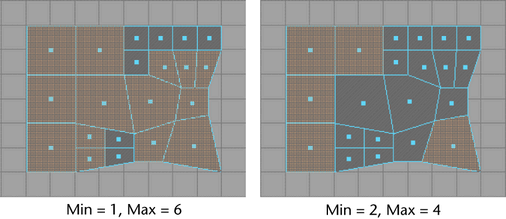
Try setting different and values for the option for faces, for example, to determine which faces fall within the criteria determined by the unit size.
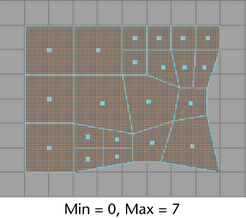
If you set the criteria to a value of 0 and a value of 7, all faces are selected because there are no faces with a unit area less than 0 or greater than 7.
Tip
If you want to constrain the selection for a unit area that is very small, such as the area under the eyes on a polygonal
modeled face, set the Min and values to a small value. The opposite is true if you want to set the constraint area to the cheeks of the face where the
faces cover more unit space.
Options common to all sections ( and )
Each section contains an switch or an option.
- Click (to turn it on) to tell Maya to acknowledge these option settings when making your selections.
- Click (to turn it on) to tell Maya not to acknowledge these option settings when making your selections.
options for faces
Maya selects the faces with an area that is within the range specified in the and boxes. See Min and Max values for details about using these values.
options for vertices and UVs
Maya selects the vertices with no fewer than the number of edges connected to them and no more than the number of edges connected to them.
options for edges
Maya selects the edges whose lengths are within the range specified in the and boxes.
Tip
Use this selection constraint option after collapsing edges () to remove the extra tiny edges sometimes produced as a result of converting a NURBS object.
options for edges, vertices, and UVs
Maya selects edges based on the angle between the two faces sharing the edge. The possible range of angles is set using the
and values.
Maya selects vertices based on the angle between the edges sharing the vertex. The possible range of angles is set using the
and values.
In the case of UVs, Maya selects them according to the range set for the angle between the edges joining the UVs corresponding
to vertices.
Note
This option works only for non-border edges.
options
These options are used to control the area range of components that are flattened out in the window.
-
-
If on, Maya selects all faces whose flattened areas (whether they are positive or negative) are within the minimum and maximum
values you set. Unsigned tells Maya to ignore the direction the face normal is facing.
-
-
If on, Maya selects all faces whose normals are pointing in the same direction and whose flattened areas are within the minimum
and maximum values you set.
- / values
-
You can enter the minimum () and maximum value () for this area which lies in the UV plane. The mapped area of a flattened component can be positive or negative. It is positive
if the face is seen from the front and negative if seen from the back.
options
These options are used to set a reference point and a valid range for the distance between the component, (such as the face
center) and the point you specify.
-
-
The option determines whether Maya acknowledges the distance to the origin you specify (the P, or , , or values).
-
-
The option determines whether Maya acknowledges the distance to the line defined by its origin (P) and its axis (V).
-
-
The option determines whether Maya acknowledges the distance to the plane defined by its origin (P) and its normal (V).
- , ,
-
These values are used to define the location of the point from which you want the selection to extend.
- , , and
-
If is selected, these values define the axis along which the selection is made. If Plane is selected, these values define the
normal vector along which the selection is made.
options for faces, edges, and vertices
-
-
The option determines whether Maya uses the orientation of the component for the selection.
-
-
The option determines whether Maya uses the direction of the component or the selection. Using this option, even two faces facing
opposite each other can be selected.
- , , and
-
These values define the axis along which the selection is made.
options for faces, edges, and vertices
These options are used to set a target point and a focal angle for your selections. Maya selects a component if the target
point can be viewed from the center of a face with its normal as the viewing axis (the , , and values) and the angle as the field of vision.
-
-
This value determines a focal angle for selected components.
- //
-
The value determines the location of the target point in the X axis, the value for the Y axis, and the value for the Z axis.
option
-
-
This value determines how many components to randomly select according to the ratio value you set within the face units. For
example, 0=no faces, 1=all faces, or 0.5=50% of the faces.
options
You can extend your selection using the propagation options at the bottom of the window.
-
-
This option is on by default. That means that no extensions are performed.
-
-
Select Shell to extend the selection up to the border of the individual piece within which the selection has been made. This
option is useful for objects made from a series of individual pieces such as those produced when you use .
-
-
Choose to select the border of the current selection only.
Tip
With set to , select Inside as the and at the bottom of the window, then click a single face to selects all the faces that are inside your object.
, ,
These buttons work the same way as the corresponding menu items.
- Click to increase the number of components you initially selected.
- Click to decrease the number of components you have selected. This button can be useful if you want to shave off one face around
every face in the current selection.
- Click to define the boundary of the current selection region. This is a quick way to select the boundaries of whatever is currently
selected (faces, vertices, edges, or UVs).
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License

 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License