Assembly references (assemblyReference nodes) control which representation of a production asset displays in the scene and let you switch between representations of the asset. Maya scenes can contain multiple assembly reference nodes, letting you add multiple, independent production assets to compose a large scene or layout.
Only objects added to an assemblyDefinition node as an assembly representation can exist in the assembly reference node hierarchy. You cannot add an object directly to an assembly reference node by parenting.
When you create an assembly reference node, it appears in the Outliner, Node Editor, and Hypergraph represented by this icon:  .
.
The following image illustrates a simple assembly reference.
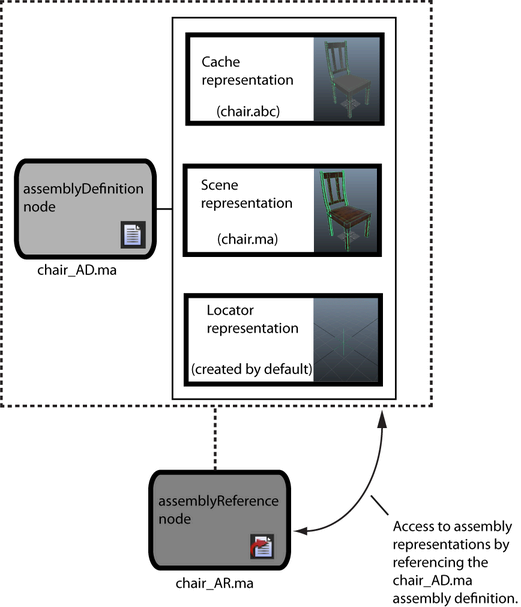
Assembly definitions define the list of assembly representations available for each asset or type of asset. For example, you may have a number of different types of chairs you want to use in a scene or production. This list of chairs is available in the assembly definition, which is a Maya scene file so that you have the convenience of viewing the available representations. While an assembly reference is the principle object for the asset type. You populate scenes with the assembly references and they are the objects you manipulate while assembling a layout or shot.
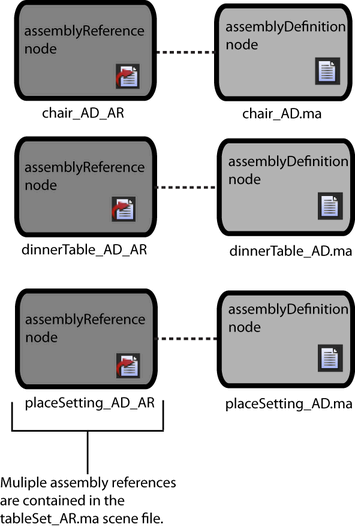
Assembly reference nodes can be nested, letting you expand the structure of the Scene Assembly to include the representation data of multiple assembly definition nodes. A Scene representation can derive from another assembly reference node, letting you access massive data sets and the ability to switch between a large number of production assets within a single Maya scene file.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License