For more information about double-sided surfaces, see Double-sided shaded surfaces.
To create a double-sided shaded surface
- In the , create one of each of the following:
- Material (this procedure uses a material).
- A Sampler Info utility. The utility provides access to camera and surface information that you can pipe into your shading networks during rendering.
- A Condition utility. The utility lets you specify which texture is mapped to each side of the surface.
- Checker texture.
- Crater texture.
- Assign the material to the surface.
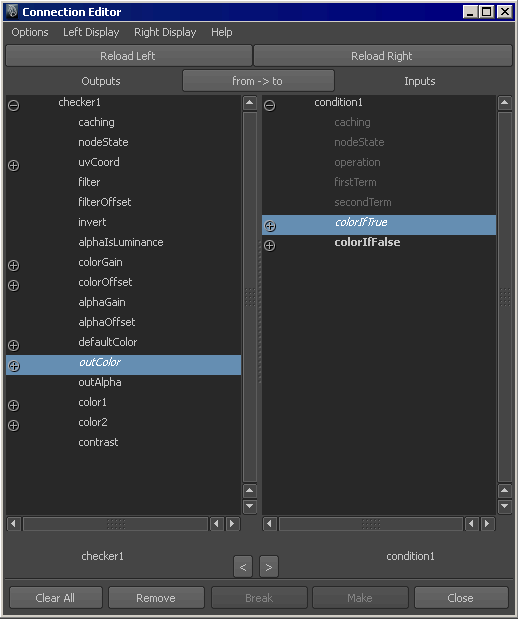
- In the , middle-drag the texture onto the utility to open the .
- In the , connect the ’s attribute to the condition utility’s attribute (click the attribute in the column, then click in the column).
- In the , middle-drag the texture onto the swatch, and in the , connect the ’s to the ’s attribute.
- Middle-drag the swatch over the swatch to open the .
- In the , click the attribute then click the ’s or attribute.
- In the , middle-drag the swatch onto the material swatch and select color to connect it to the ’s attribute.
- Perform a test render.
Maya shades each side of the surface with a different texture.
Note
You must set the to 0 and the to or if you are using the mental ray for Maya renderer.
Swapping the textures on the surfaces
For more information about double-sided surfaces, see Double-sided shaded surfaces.
You can use the utility to specify which texture is applied to the front and back sides of the surface. For more information about the condition
utility, see Condition.
To swap texture mapping for double-sided shading
- Double-click the swatch in to open its .
- In the section, change the attribute to (or if it is set to , change it to ).
- Perform a test render. The following shows the result.
Note
You can apply more than one material to polygonal models at the face level.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License

 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License