 |
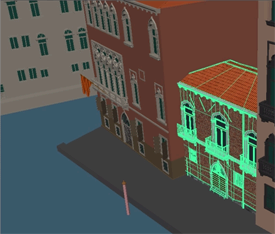
Scene Assembly is a system that lets you build complex Maya scenes without the burden of typical memory overhead. Constructing the scene with Scene Assembly improves viewport interactivity and accelerates file loading, helping to solve common issues when working with large data sets. Scene Assembly consists of two interdependent nodes (assemblyDefinition and assemblyReference) and a system for loading alternative forms of your production assets called representations. The system lets you define these alternate representations and build a complex hierarchy of assets, such as detailed models of entire cities, one object at a time. You can then use representations to manage the scene's complexity at the object level by switching between different versions of each scene object, letting you choose between detailed display and performance as your task requires. |
Convert geometry to bounding boxes
New GPU Cache Configuration preferences let you optimize how your graphics card processes Alembic-based GPU cache files. For example, you can specify video RAM usage for GPU caches, choose from OpenGL selection modes, and more. You can access the GPU Cache Configuration settings from a new GPU Cache section of the Maya Preferences window (Window > Settings/Preferences > Settings > GPU Cache) .
New GPU Cache Import options let you specify the time range and start frame when importing GPU caches into Maya.
Ignore Version global preference
Easily load scene files from any version of Maya by turning on the new global Ignore Version preference.
Composite and the Autodesk Customer Involvement Program
Composite is now part of the Autodesk Customer Involvement Program (CIP) which collects information to help Autodesk learn how you use Composite. Participation is voluntary; select the new Customer Involvement Program option in the Help menu to help us design new features as well as improve existing ones. You have the option to participate anonymously, participate with contact information, or not to participate.