 Command entry:
Command entry:Rendering menu

Effects

Environment and Effects dialog

Effects panel

Add

Add Effect dialog

Lens Effects
Lens Effects create real-life effects commonly associated with a camera. Lens effects include Glow, Ring, Ray, Auto Secondary, Manual Secondary, Star, and Streak.
Procedures
To add an effect:
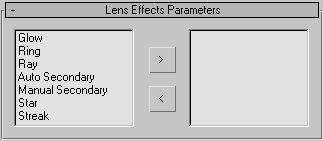
- Select the desired effect from the list on the left side of the Lens Effects Parameters rollout.
- Click the (>) arrow button to move it into the column on the right.
To delete an applied effect:
- Select the effect from the list on the right side of the Lens Effects Parameters rollout.
- Click the (<) arrow button to remove it from the list.
Interface
Lens Effects Parameters rollout
The Lens Effects system allows you to apply effects to your rendered image by choosing a particular effect from the list on
the left and adding it to the list on the right. Each effect has its own rollout of parameters, but all effects share two
panels of global parameters.
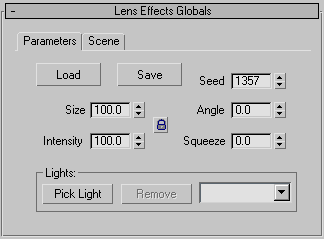
Lens Effects Globals rollout, Parameters panel
- Load
-
Displays the Load Lens Effects file dialog that enables you to open an LZV file. The LZV file format contains information
saved from a previous configuration of Lens Effects. This allows you to load and use Lens Effects that have been saved from
previous sessions of 3ds Max.
- Save
-
Displays the Save Lens Effects file dialog that enables you to save an LZV file. The LZV file format contains information
saved from a previous configuration of Lens Effects. This allows you to save several types of Lens Effects and use them in
multiple 3ds Max scenes.
NoteSaving an effect as an LZV file will only save the attributes of the effect on the frame that it is saved at. The LZV file
format doesn’t save the animation keys of an animated parameter.
- Size
-
Affects the size of the overall Lens Effect. This value is a percentage of the size of the rendered frame.
- Intensity
-
Controls the overall brightness and opacity of the Lens Effect. Higher values produce a bright, more opaque effect, and lower
values produces a dim, transparent effect.
- Seed
-
Gives the random number generator in Lens Effects a different starting point, which creates a slightly different Lens Effect
without changing any settings. Using Seed guarantees a different Lens Effect, even if the differences are very small. For
example, if you set up a Ray effect, you will get slightly different rays in the lens flare if you adjust the seed value.
- Angle
-
Affects the amount that the Lens Effect rotates from its default position, as the position of the effect changes relative
to the camera.
- Squeeze
-
Squeezes the size of the overall Lens Effect, either horizontally or vertically to compensate for different frame aspect ratios.
Positive values stretch the effect horizontally, and negative values stretch it vertically. The value is a percentage of the
size of the flare. Range=100 to -100.
Lights group
Allows you to choose lights to apply Lens Effects to.
- Pick Light
-
Enables you to select a light directly through the viewports. You can also select a light by pressing H to open the Pick Object dialog.
- Remove Light
-
Removes a selected light.
- Drop-down list
-
Provides quick access to lights that you have added to the Lens Effect.
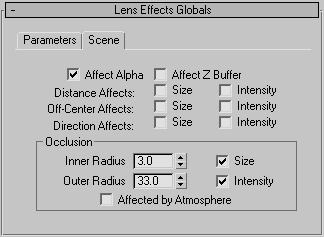
Lens Effects Globals rollout, Scene panel
- Affect Alpha
-
Specifies whether or not the Lens Effect affects the alpha channel of an image when the image is rendered in a 32-bit file
format. The alpha channel is an extra 8 bits of color (256 colors) that indicate transparency in an image. Alpha channels
are used to composite one image seamlessly over the top of another. If you want to composite a Lens Effect, or an image that
contains a Lens Effect, over the top of another image, enable this option. If you are not rendering to a 32-bit file, do not
enable this option.
- Affect Z Buffer
-
Stores an object's distance from the camera. The Z-Buffer is useful for optical effects. When this option is enabled, the
linear distance of the Lens Effect is recorded, and can be used in special effects that make use of the Z-Buffer.
- Distance Affects
-
Allows distance from the camera or viewport to affect the size and/or the intensity of the effect.
The Auto Secondary, Manual Secondary, and Star effects do not support Distance Affects  Size, and the Auto Secondary effect does not support Distance Affects
Size, and the Auto Secondary effect does not support Distance Affects  Intensity, either.
Intensity, either.
- Off-Center Affects
-
Allows an effect that is off-center from the camera or viewport to affect the size and/or the intensity of the effect.
- Direction Affects
-
Allows direction of spot lights with respect to the camera or viewport to affect the size and/or the intensity of the effect.
The size and intensity of the effect are at a maximum when the light is pointed at the camera (or viewport).
Occlusion group
Occlusion is used to determine when a Lens Effect will be affected by an object that comes between the effect and the camera.
By using two spinners to determine occlusion you can have scene objects realistically affect the look of your effect. The
outer radius will determine when another scene object will begin to occlude and the inner radius will determine when the scene
object will cause the effect to reach maximum occlusion.
- Inner Radius
-
Sets the inner radius around the effect that another scene object must intersect in order to completely occlude the effect.
- Outer Radius
-
Sets the outer radius around the effect that another scene object must intersect in order to begin to occlude the effect.
- Size
-
Decreases the size of the effect when being occluded.
- Intensity
-
Decreases the intensity of the effect when being occluded.
- Affected by Atmosphere
-
Allows Atmospheric Effects to occlude Lens Effects.
- Glow Lens Effect
Glow lets you add a glowing aura around any assigned object. For example, for an exploding particle system, adding a glow
to the particles makes them seem as though they are brighter and hotter.
- Ring Lens Effect
The ring is a circular color band that surrounds the center of the source object.
- Ray Lens Effect
Rays are bright lines that radiate from the center of the source object, providing the illusion of extreme brightness for
the object. Rays let you emulate scratches in the lens elements of a camera.
- Auto Secondary Lens Effect
Secondary flares are the small circles you would normally see coming out from the source of the lens flare along an axis relative
to the camera position. These are caused by light refracting off the different lens elements in the camera. As the camera
position changes relative to the source object, the secondary flares move.
- Manual Secondary Lens Effect
Manual secondary flares are additional secondary flares that are individually added to the lens flare. These can be used in
addition to, or in place of auto secondary flares.
- Star Lens Effect
A Star is larger than a Ray effect and is composed of 0 to 30 spokes, instead of hundreds like a ray.
- Streak Lens Effect
A streak is a wide band that runs through the center of the source object. In real camera work, it is produced when using
anamorphic lenses to film a scene.
- Lens Effects Dialogs
The topics in this section describe support dialogs that are common to the various lens effects.