Once you have added softness, check to see if there are any grey areas in the key resulting from the setting. If so, there are several techniques to remove the grey areas:
In this section, two methods are shown: using Negative Sampling to refine the softness range, and using the Patch tool to create “selective keys” in the white areas of the matte. To learn other ways to remove unwanted grey areas, see Techniques for Adjusting Softness.
This is probably the simplest method of removing greys from the matte. You sample in the unwanted grey area to subtract those colour values from the softness range.
Try this method first to see if it solves the problem. However, if the colour values in the foreground subject are too similar to those at the edges, you may remove too much of the softness.
If the negative sampling removed too much of the desired softness or brought back graininess, click Undo and try another method.
Patches are another type of sample you can take in the image window. Unlike tolerance and softness, you can specify the colour that a patch sample renders on the matte. Patch samples can be rendered as white, black, or any shade of grey on the matte. You can also set the opacity of a patch.
One use for patches is to remove unwanted grey areas from the matte. Use a patch to isolate a range of colours from those that have been included in the softness range, then set the colour you want the pixels to have on the matte. Sampling a patch to remove grey areas in the key is similar to creating a garbage mask by keying instead of drawing.
You can use up to three different patches in a key.




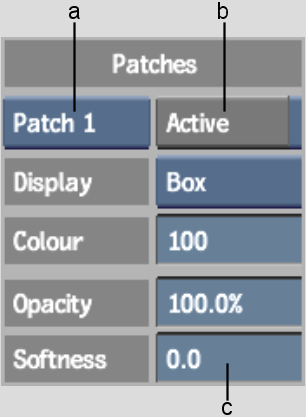
(a) Patches box (b) Active button (c) Patches Softness field
The grey areas of the matte corresponding to the colour values sampled are changed to white.
All the colour values sampled are included in the patch. Notice the patch in the RGB viewer, represented by a white wireframe box. All colour values in the box will be rendered white on the matte.


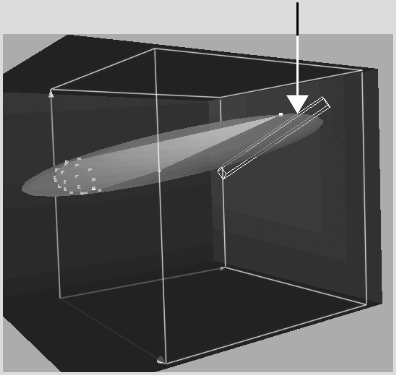
A negative softness value softens the edges of the patch inwards from the edge. A positive value softens the edges outwards beyond the edge, adding softened pixel values to the patch.
The RGB viewer now contains three key elements:
For instructions on completing the key using the basic keying technique, see the sections referred to in 3D Keying Workflow.