In Schematic view, a node exists for each object in the scene. For example, the camera, axes, shadows, and lights are represented by circles. Surfaces and textures are represented by rectangles. Each node displays the name of the object it represents.


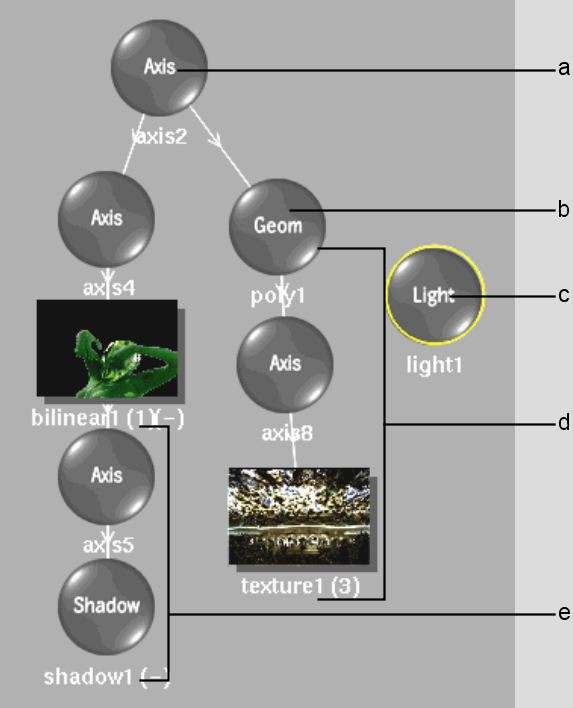
(a) Axis object is the parent of axis 4 and poly1 (b) 3D model (c) Light source (d) Texture applied to the 3D model (e) Drop shadow of bilinear1
Here are some hints when working in the schematic with some of the various node types.
Surface Nodes(Bilinear, Bicubic, and Extended Bicubic) When you add one of these surface nodes to the schematic, the node name is shown with two numbers in parentheses. These numbers indicate the media applied to the surface and the media used as a displacement source. For example, a bicubic object labeled (2)(1) shows that the bicubic uses the clips from Media 2 and is displaced using the clips from Media 1.


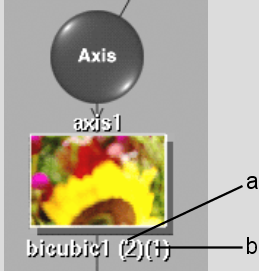
(a) Media 2 is used by the bicubic surface. (b) Media 1 is used for displacement.
For more information on the relationship between media and surfaces, see Adding Surfaces. For more information on displacement, see Adding a Displacement Map.
DVE Layer Object NodeA DVE Layer Object node is a special node designed to simplify working in the Action schematic. A DVE Layer Object node is a grouped node of all axes and surfaces that DVE users are accustomed to using. See Adding a DVE Layer Object.
Camera NodeThe camera node appears in Schematic view by default and you can link it to any image. Use the camera node to rotate the camera about its own axis, and parent other nodes including shadow, texture, and geometry nodes.
Shadow and Texture NodesShadow and texture nodes each have a single number in parentheses that indicates the media used for the shadow or texture. For example, a shadow labeled (2) shows that the shadow uses the matte from Media 2.
Source NodesSource nodes are used as part of an advanced schematic structure that separates the media's matte and front so that each clip can be animated individually. You can also use sources to create complex compositing effects such as nesting. See Action: Sources.