Functions for Shaders
mental ray makes a range
of functions available to shaders that can be used to access data,
cast rays, looking up images, and perform standard mathematical
computations. The functions are grouped by the module that supplies
them. The shader writer may also use C library functions, but it is
mandatory to include
<</i>stdio.h> and
<</i>math.h> if printing functions such as fprintf (use
mi_info or similar for
console debugging messages) or math functions such as sin
are used. Not including these headers may abort rendering at
runtime, even though the compiler did not complain. All shaders
must include the standard mental ray header file,
shader.h.
Here is a summary of functions provided by mental ray. Section
functype shows which functions
can be used in which shaders.
Shader Calls
| type |
name |
arguments |
| miBoolean |
mi_call_shader |
*result, type, *state, tag |
| miBoolean |
mi_call_shader_x |
*result, type, *state, tag, *arg |
| miBoolean |
mi_call_material |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_call_photon_material |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_call_shadow_material |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_call_environment_material |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_call_volume_material |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_call_photonvol_material |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_call_contour_material3.4 |
*result, *void, *void, *state |
| void * |
mi_eval |
*state, *param |
| miBoolean * |
mi_eval_boolean |
*param |
| miInteger * |
mi_eval_integer |
*param |
| miScalar * |
mi_eval_scalar |
*param |
| miVector * |
mi_eval_vector |
*param |
| miScalar * |
mi_eval_transform |
*param |
| miColor * |
mi_eval_color |
*param |
| miTag * |
mi_eval_tag |
*param |
| void |
mi_flush_cache |
*state |
DB
| type |
name |
arguments |
| int |
mi_db_type |
tag |
| int |
mi_db_size |
tag |
| void * |
mi_db_access |
tag |
| void |
mi_db_unpin |
tag |
| void |
mi_db_flush |
tag |
RC Functions
| type |
name |
arguments |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_eye |
*result, *state, *org, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_reflection |
*result, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_refraction |
*result, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_transparent |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_environment |
*result, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_probe |
*state, *dir, *org |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_transparent |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_continue |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_light |
*result, *dir, *nl, *st, i |
| miBoolean |
mi_sample_light |
*result, *dir, *nl, *st,i,*s |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_shadow |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_trace_shadow_seg |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_continue_shadow_seg3.4 |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_ray_offset |
*state, *offset |
| miBoolean |
mi_ray_falloff |
*state, *start, *stop |
| miBoolean |
mi_inclusive_lightlist |
*n, **lights, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_exclusive_lightlist |
*n, **lights, *state |
| miScalar |
mi_lightprofile_value3.1 |
*prof, phi, theta, *pos, rel |
| miScalar |
mi_lightprofile_sample3.1 |
*state, proftag, rel |
| miBoolean |
mi_compute_irradiance |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_compute_irradiance_backside |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_compute_avg_radiance |
*result, *state, face, irrad_options |
| miBoolean |
mi_compute_volume_irradiance |
*result, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_compute_directional_irradiance |
*result, *state, r, g1, g2 |
| miBoolean |
mi_finalgather_store |
*result, *state, mode |
| miBoolean |
mi_sample |
*sample, *i, *state, dim, *n |
RC Photon Functions
| type |
name |
arguments |
| miBoolean |
mi_photon_light |
*energy, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_photon_reflection_specular |
*energy, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_photon_reflection_glossy |
*energy, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_photon_reflection_diffuse |
*energy, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_photon_transmission_specular |
*energy, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_photon_transmission_glossy |
*energy, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_photon_transmission_diffuse |
*energy, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_photon_transparent |
*energy, *state |
| miBoolean |
mi_photon_volume_scattering |
*energy, *state, *dir |
| void |
mi_store_photon |
*energy, *state |
| void |
mi_store_volume_photon |
*energy, *state |
RC Direction Functions
| type |
name |
arguments |
| void |
mi_reflection_dir |
dir, state |
| void |
mi_reflection_dir_specular |
*dir, *state |
| void |
mi_reflection_dir_glossy |
*dir, *state, shiny |
| void |
mi_reflection_dir_glossy_x3.4 |
*dir, *state, shiny, *sample |
| void |
mi_reflection_dir_anisglossy |
*dir, *state, u, v, shiny_u, shiny_v |
| void |
mi_reflection_dir_anisglossy_x3.4 |
*dir, *state, u, v, shiny_u, shiny_v, *sample |
| void |
mi_reflection_dir_diffuse |
*dir, *state |
| void |
mi_reflection_dir_diffuse_x3.4 |
*dir, *state, *sample |
| miBoolean |
mi_refraction_dir |
dir, state, ior_in, ior_out |
| miBoolean |
mi_transmission_dir_specular |
*dir, *state, *in, *out |
| miBoolean |
mi_transmission_dir_glossy |
*dir, *state, *in, *out, shiny |
| miBoolean |
mi_transmission_dir_glossy_x3.4 |
*dir, *state, *in, *out, shiny, *sample |
| miBoolean |
mi_transmission_dir_anisglossy |
*dir, *state, *in, *out, u, v, shiny_u, shiny_v |
| miBoolean |
mi_transmission_dir_anisglossy_x3.4 |
*dir, *state, *in, *out, u, v, shiny_u, shiny_v, *sample |
| void |
mi_transmission_dir_diffuse |
*dir, *state |
| void |
mi_transmission_dir_diffuse_x3.4 |
*dir, *state, *sample |
| void |
mi_scattering_dir_diffuse |
*dir, *state |
| void |
mi_scattering_dir_directional |
*dir, *state, directionality |
| miScalar |
mi_scattering_pathlength |
*state, density |
Vector and Matrix Math Functions
| type |
name |
arguments |
| void |
mi_vector_neg |
*r |
| void |
mi_vector_add |
*r, *a, *b |
| void |
mi_vector_sub |
*r, *a, *b |
| void |
mi_vector_mul |
*r, f |
| void |
mi_vector_div |
*r, f |
| void |
mi_vector_prod |
*r, *a, *b |
| miScalar |
mi_vector_dot |
*a, *b |
| miScalar |
mi_vector_norm |
*a |
| void |
mi_vector_normalize |
*r |
| void |
mi_vector_min |
*r, *a, *b |
| void |
mi_vector_max |
*r, *a, *b |
| miScalar |
mi_vector_det |
*a, *b, *c |
| miScalar |
mi_vector_dist |
*a, *b |
| void |
mi_matrix_null |
r |
| void |
mi_matrix_ident |
r |
| miBoolean |
mi_matrix_isident |
a |
| void |
mi_matrix_copy |
r, a |
| miBoolean |
mi_matrix_invert |
r, a |
| void |
mi_matrix_prod |
r, a, b |
| void |
mi_matrix_rot_det |
a |
| void |
mi_matrix_rotate |
a, x, y, z |
| void |
mi_matrix_rotate_axis |
a, *v, r |
| void |
mi_matrix_solve |
*x, a, *b, c |
Transformation Math Functions
| type |
name |
arguments |
| void |
mi_point_transform |
*r, *v, m |
| void |
mi_vector_transform |
*r, *v, m |
| void |
mi_vector_transform_T |
*r, *v, m |
| void |
mi_point_to_world |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_point_to_camera |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_point_to_object |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_point_to_light |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_point_to_raster |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_point_from_world |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_point_from_camera |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_point_from_object |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_point_from_light |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_vector_to_world |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_vector_to_camera |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_vector_to_object |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_vector_to_light |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_vector_from_world |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_vector_from_camera |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_vector_from_object |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_vector_from_light |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_normal_to_world |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_normal_to_camera |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_normal_to_object |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_normal_to_light |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_normal_from_world |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_normal_from_camera |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_normal_from_object |
*state, *r, *v |
| void |
mi_normal_from_light |
*state, *r, *v |
Noise Functions
| type |
name |
arguments |
| miScalar |
mi_random |
|
| miScalar |
mi_srandom |
seed |
| miScalar |
mi_erandom |
seed[3] |
| double |
mi_par_random |
*state |
| miScalar |
mi_spline |
t, n, *ctl |
| miScalar |
mi_noise_1d |
p |
| miScalar |
mi_noise_2d |
u, v |
| miScalar |
mi_noise_3d |
*p |
| miScalar |
mi_noise_1d_grad |
p, *g |
| miScalar |
mi_noise_2d_grad |
u, v, *gu, *gv |
| miScalar |
mi_noise_3d_grad |
*p, *g |
| miScalar |
mi_unoise_1d |
p |
| miScalar |
mi_unoise_2d |
u, v |
| miScalar |
mi_unoise_3d |
*p |
| miScalar |
mi_unoise_1d_grad |
p, *g |
| miScalar |
mi_unoise_2d_grad |
u, v, *gu, *gv |
| miScalar |
mi_unoise_3d_grad |
*p, *g |
IMG Functions
| type |
name |
arguments |
| void |
mi_img_put_color |
*image, *color, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_get_color |
*image, *color, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_put_scalar |
*image, scalar, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_get_scalar |
*image, *scalar, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_put_vector |
*image, *vector, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_get_vector |
*image, *vector, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_put_depth |
*image, depth, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_get_depth |
*image, *depth, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_put_normal |
*image, *normal, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_get_normal |
*image, *normal, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_put_label |
*image, label, x, y |
| void |
mi_img_get_label |
*image, *label, x, y |
| miBoolean |
mi_img_tonemap |
*outimage, *inimage, *paras |
Color Profile Functions
| type |
name |
arguments |
| miUint1 |
mi_colorprofile_renderspace_id |
|
| miUint1 |
mi_colorprofile_internalspace_id |
|
| miUint1 |
mi_colorprofile_ciexyz_id |
|
| miBoolean |
mi_colorprofile_internal_to_render |
*color |
| miBoolean |
mi_colorprofile_internal_to_ciexyz |
*color |
| miBoolean |
mi_colorprofile_render_to_internal |
*color |
| miBoolean |
mi_colorprofile_render_to_ciexyz |
*color |
| miBoolean |
mi_colorprofile_ciexyz_to_render |
*color |
| miBoolean |
mi_colorprofile_ciexyz_to_internal |
*color |
Shading Models
| type |
name |
arguments |
| miScalar |
mi_fresnel |
n1, n2, t1, t2 |
| miScalar |
mi_fresnel_reflection |
*state, *i, *o |
| miScalar |
mi_phong_specular |
spec, *state, *dir |
| void |
mi_fresnel_specular |
*ns, *ks, s, *st, |
|
|
*dir, *in, *out |
| miScalar |
mi_blinn_specular |
spec, *state, *dir |
| miScalar |
mi_blong_specular |
spec, *state, *dir |
| miBoolean |
mi_cooktorr_specular |
*result, *di, *dr, *n, roughness, *ior |
| miScalar |
mi_ward_glossy |
*di, *dr, *n, shiny |
| miScalar |
mi_ward_anisglossy |
*di, *dr, *n, *u, *v, shiny_u, shiny_v |
| miScalar |
mi_schlick_scatter |
*di, *dr, directionality |
| miRay_type |
mi_choose_scatter_type |
*state, transp, *specular, *glossy, *diffuse |
| miRay_type |
mi_choose_simple_scatter_type |
*state, *rdiff, *rspec, *tdiff, *tspec |
| miInteger |
mi_choose_lobe |
*state, r |
Auxiliary Functions
| type |
name |
arguments |
| miBoolean |
mi_lookup_color_texture |
*col, *state, tag, *v |
| miBoolean |
mi_lookup_scalar_texture |
*scal, *state, tag, *v |
| miBoolean |
mi_lookup_vector_texture |
*vec, *state, tag, *v |
| miBoolean |
mi_lookup_filter_color_texture |
*col, *state, tag, *paras, ST |
| miBoolean |
mi_texture_filter_project |
p[3], t[3], *state, disc_r, space |
| miBoolean |
mi_texture_filter_transform |
ST, p[3], t[3] |
| miScalar |
mi_luminance |
*state, color |
| miBoolean |
mi_tri_vectors |
*state, wh, nt, **a, **b, **c |
| miBoolean |
mi_texture_interpolate3.4 |
*state, space, *result |
| miBoolean |
mi_raster_unit |
*state, *x, *y |
| miBoolean |
mi_query |
query, *state, tag, *result, ... |
| miBoolean |
mi_shaderstate_enumerate |
*state, *cb, *arg |
| miBoolean |
mi_shaderstate_set |
*state, *key, ks, *val, vs, t |
| void * |
mi_shaderstate_get |
*state, *key, ks, *vs |
| miBoolean |
mi_fb_put |
*state, fb, *data |
| miBoolean |
mi_fb_get |
*state, fb, *data |
| miImg_image * mi_output_image_open3.4 |
*state, idx |
| void |
mi_output_image_close3.4 |
*state, idx |
| miBoolean |
mi_geoshader_add_result |
query, *state, tag, *result, ... |
| miBoolean |
mi_geoshader_tesselate |
*state, *leaves, source |
| miBoolean |
mi_geoshader_tesselate_end |
leaves |
| miBoolean |
mi_geoshader_echo_tag |
*fp, tag, *eopt |
| char * |
mi_string_substitute |
*new, *old, size |
| miInteger |
mi_volume_num_shaders |
*state |
| miInteger |
mi_volume_cur_shader |
*state |
| miColor * |
mi_volume_tags |
*state |
| miTag * |
mi_volume_user_color |
*state |
| void |
mi_opacity_set |
*state, *color |
| miBoolean |
mi_opacity_get |
*state, *color |
Multipass Rendering Functions
These functions are available only to pass merge (access) or pass
preprocessing (get, put, flush, black) shaders.
| type |
name |
arguments |
| void * |
mi_renderpass_access3.1 |
*state, pass, db |
| miBoolean |
mi_renderpass_sample_get3.1 |
*result, sz, *state, fb, x, y |
| miBoolean |
mi_renderpass_sample_put3.1 |
*result, sz, *state, fb, x, y |
| miBoolean |
mi_renderpass_samplerect_flush3.1 |
*result, *state, x, y |
| miBoolean |
mi_renderpass_samplerect_black |
*result, *state, x, y |
Obsolete Auxiliary Functions
These functions are obsolete; use mi_query for future
implementations.
| type |
name |
arguments |
| void |
mi_light_info |
tag, *org, *dir, **paras |
| int |
mi_global_lights_info |
**tag |
| void |
mi_texture_info |
tag, *xres, *yres, **paras |
| void * |
mi_shader_info |
*state |
| int |
mi_instance_info |
*state, **paras, **p1, **p2, **p3 |
Contour Functions
| miBoolean |
mi_get_contour_line |
*p1, *p2 |
| void |
mi_add_contour_lines |
p1[], p2[], n |
Light Mapping Functions
| miImg_image* |
mi_lightmap_edit |
**handle, tag |
| void |
mi_lightmap_edit_end |
*handle |
Memory Allocation
| type |
name |
arguments |
| void * |
mi_mem_allocate |
size |
| void * |
mi_mem_test_allocate |
size |
| void * |
mi_mem_reallocate |
mem, size |
| void * |
mi_mem_test_reallocate |
mem, size |
| void |
mi_mem_release |
mem |
| void |
mi_mem_check |
|
| void |
mi_mem_dump |
mod |
| char * |
mi_mem_strdup |
*text |
Thread Parallelism and Locks
| type |
name |
arguments |
| void |
mi_init_lock |
*lock |
| void |
mi_delete_lock |
*lock |
| void |
mi_lock |
lock |
| void |
mi_unlock |
lock |
| int |
mi_par_localvpu2.1 |
|
| int |
mi_par_nthreads2.1 |
|
| int |
mi_par_aborted |
|
Messages and Errors
| type |
name |
arguments |
| void |
mi_fatal |
*message, ... |
| void |
mi_error |
*message, ... |
| void |
mi_warning |
*message, ... |
| void |
mi_info |
*message, ... |
| void |
mi_progress |
*message, ... |
| void |
mi_debug |
*message, ... |
| void |
mi_vdebug |
*message, ... |
Shader Calls
Shaders can be called either explicitly, or implicitly by
evaluating a shader parameter that may be assigned to the output of
another shader.
miBoolean mi_call_shader(
miColor * const result,
miShader_type type,
miState * const state,
miTag shader)
miBoolean mi_call_shader_x(
miColor * const result,
miShader_type type,
miState * const state,
miTag shader,
void *arg)
These functions call the shader specified by the tag
shader. The extended version passes the arg parameter
as a fourth argument to the shader. The other version passes a null
pointer as fourth argument to the shader. mi_call_shader_x is slightly more
efficient than mi_call_shader.
The tag is normally a texture
shader or light shader or
some other type of shader found in the calling shader's parameter
list. The caller must pass its own state and the shader type, which
must be one of miSHADER_LENS, miSHADER_MATERIAL,
miSHADER_LIGHT, miSHADER_SHADOW
miSHADER_ENVIRONMENT miSHADER_VOLUME, and
miSHADER_TEXTURE. The sequence of operations is:
- shader is written into
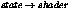 .
.
- If the called shader is dynamically loaded and has an init
shader that has not been called yet, it is called now, with
state as its only argument.
- The shader referenced by shader is called with three
arguments: the result pointer, the given state, and
the shader parameters retrieved
from shader.
- After the shader returns,
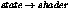 is
restored to its old value.
is
restored to its old value.
The return value of the shader is returned. If the shader
expects a result argument of a type other than miColor,
the pointer must be cast to miColor when passed to
mi_call_shader. Note
that the shader tag references an entire function call
including shader parameters as
defined in the .mi file with a texture, light, or
some other statement combining shading function and shader
parameters; shader is not just a simple pointer or
reference to a C function.
miBoolean mi_call_material(
miColor *result,
miState *state);
Call the material shader in
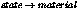 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials.
miBoolean mi_call_photon_material(
miColor *result,
miState *state);
Call the photon shader in
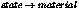 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the photon shader of a
material Phenomenon.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the photon shader of a
material Phenomenon.
miBoolean mi_call_shadow_material(
miColor *result,
miState *state);
Call the shadow shader in
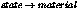 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the shadow shader of a
material Phenomenon.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the shadow shader of a
material Phenomenon.
miBoolean mi_call_environment_material(
miColor *result,
miState *state);
Call the environment shader
in 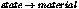 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the environment shader
of a material Phenomenon.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the environment shader
of a material Phenomenon.
miBoolean mi_call_volume_material(
miColor *result,
miState *state);
Call the volume shader in
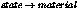 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the volume shader of a
material Phenomenon.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the volume shader of a
material Phenomenon.
miBoolean mi_call_photonvol_material(
miColor *result,
miState *state);
Call the photonvol shader in 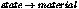 . This
works both for standard materials and Phenomenon materials. It
calls the photonvol shader of a material Phenomenon.
. This
works both for standard materials and Phenomenon materials. It
calls the photonvol shader of a material Phenomenon.
miBoolean mi_call_contour_material(
miContour_endpoint *result,
void *info_near,
void *info_far,
miState *state);
3.4 Call the contour
shader in 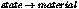 . This works both for
standard materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the contour
shader of a material Phenomenon. mi_call_contour_material may only
be called in contour mode, with a contour shader as parent of a
shade tree. info_near and info_far must be passed
from a parent contour shader. The contour contrast shader, the
contour storage shader, and the contour shader itself must use
matching info_near and info_far values. The info
structures must have the same size and layout.
. This works both for
standard materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the contour
shader of a material Phenomenon. mi_call_contour_material may only
be called in contour mode, with a contour shader as parent of a
shade tree. info_near and info_far must be passed
from a parent contour shader. The contour contrast shader, the
contour storage shader, and the contour shader itself must use
matching info_near and info_far values. The info
structures must have the same size and layout.
void *mi_eval(
miState *state,
void *param)
miBoolean *mi_eval_boolean(
miBoolean *param)
miInteger *mi_eval_integer(
miInteger *param)
miScalar *mi_eval_scalar(
miScalar *param)
miVector *mi_eval_vector(
miVector *param)
miScalar *mi_eval_transform(
miScalar *param)
miColor *mi_eval_color(
miColor *param)
miTag *mi_eval_tag(
miTag *param)
Return the value of a shader parameter. If the shader
parameter value is a constant, mi_eval returns its argument. If
the parameter is assigned to another shader, call that shader and
return a pointer to its return value (or the cached return value if
it has been called recently). If the parameter is assigned to a
Phenomenon interface, return a pointer to the value in the
interface. The latter two cases let shaders operate in the contexts
of shader assignments and phenomena without needing knowledge of
the context, which is automatically handled. The pointer remains
valid until the shader returns, which avoids the need to copy a
large returned data structure such as a color or array to temporary
variables. Shaders should always access their parameters with
mi_eval. If parameters
are accessed without mi_eval and the parameter is
assigned to another shader or an interface, the shader will see
garbage.
The typed variants of mi_eval are implemented as macros
for the convenience of shader writers. They cast their argument to
a void pointer, call mi_eval, and recast the returned
pointer to the appropriate type. They all make the assumption that
the shader has a local variable state of type miState
* in scope. Experience has shown that the typed variants make
source code look much cleaner.
Note that there is only one macro mi_eval_tag that can be used for
parameters of type shader, color texture, vector texture, scalar
texture, light, material, and geometry. All typed variants have
been designed to return the same type they accept as an
argument.
Always use the correct simple type. For example, if the
parameter has type color, it must be evaluated as a single color
(probably using mi_eval_color). It is not possible to use
four scalar evaluations to access the R, G, B, and A components
separately. Also, by convention, arrays should be evaluated as a
unit, evaluating two integers for the i_ index, the
n_ member count, and the array itself. However, structures
are not evaluated as a unit; a separate evaluation is necessary for
every simple member it contains.
void mi_flush_cache(
miState *state)
Prevents the cache from being used by future calls to
mi_eval. If mi_eval calls another shader, the
result is stored in a special cache in that other shader, which is
normally flushed only when the entire shader graph returns. This
means that the other shader will only ever be called once during
the evaluation of a shader graph, and all mi_evals are satisfied from the
cache. Notice that flushing applies to the entire sub-graph of
shaders evaluated by this and future mi_evals; there is no way to flush
the cache of a single shader because that would leave its
sub-shaders in a funny state. The result cache is still active for
shaders which call mi_flush_cache.
This is useful if the code calls a another shader more than
once, such as a texture shader to sample a texture at three
different locations to compute bump
mapping gradients. Although the shader, if called with
mi_call_shader or
mi_lookup_color_texture,
will get called each time, its sub-shaders inside the same
Phenomenon will not if these subshaders are called as the result of
mi_eval. (Remember that
mi_eval results are
cached.) However, if mi_flush_cache is used before the
second and every subsequent shader call, the called shader's
mi_eval calls will cause
a fresh subshader call.
Copyright © 1986-2006 by mental images GmbH
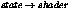 .
.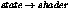 is
restored to its old value.
is
restored to its old value.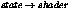 .
.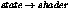 is
restored to its old value.
is
restored to its old value.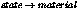 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials.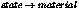 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the photon shader of a
material Phenomenon.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the photon shader of a
material Phenomenon.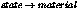 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the shadow shader of a
material Phenomenon.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the shadow shader of a
material Phenomenon.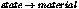 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the environment shader
of a material Phenomenon.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the environment shader
of a material Phenomenon.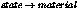 . This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the volume shader of a
material Phenomenon.
. This works both for standard
materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the volume shader of a
material Phenomenon.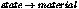 . This
works both for standard materials and Phenomenon materials. It
calls the photonvol shader of a material Phenomenon.
. This
works both for standard materials and Phenomenon materials. It
calls the photonvol shader of a material Phenomenon.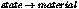 . This works both for
standard materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the contour
shader of a material Phenomenon. mi_call_contour_material may only
be called in contour mode, with a contour shader as parent of a
shade tree. info_near and info_far must be passed
from a parent contour shader. The contour contrast shader, the
contour storage shader, and the contour shader itself must use
matching info_near and info_far values. The info
structures must have the same size and layout.
. This works both for
standard materials and Phenomenon materials. It calls the contour
shader of a material Phenomenon. mi_call_contour_material may only
be called in contour mode, with a contour shader as parent of a
shade tree. info_near and info_far must be passed
from a parent contour shader. The contour contrast shader, the
contour storage shader, and the contour shader itself must use
matching info_near and info_far values. The info
structures must have the same size and layout.