| Long name (short name) | [argument types] | Properties |
|---|
-device
(-d)
| string | 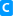 |
|
Specifies the device into which the take data is read. This is a
required argument.
|
|
-angle
(-a)
| string |  |
|
Sets the angular unit used in the take. Valid strings are
"deg", "degree", "rad", and "radian".
C: The default is the current user angular unit.
|
|
-linear
(-l)
| string |  |
|
Sets the linear unit used in the take. Valid strings are
"mm", "millimeter", "cm", "centimeter", "m", "meter", "km",
"kilometer", "in", "inch", "ft", "foot", "yd", "yard", "mi",
and "mile".
C: The default is the current user linear unit.
|
|
-take
(-t)
| string |  |
|
Reads the specified take file. It is safest to pass the full
path to the flag.
|
|
-noTime
(-nt)
| |  |
|
Specifies if the take (.mov) file contains time stamps.
C: The default is to assume time stamps are part of the take file.
|
|
-frequency
(-f)
| float |  |
|
The timestamp is ignored and the specified frequency is used. If
timeStamp data is not in the .mov file, the -noTimestamp flag
should also be used. This flag resample, instead
the data is assumed to be at the specified frequency.
C: If the take file does not use time stamps, the default frequency
is 60Hz.
|
|