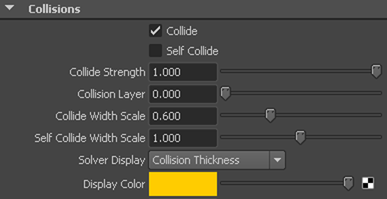
To make it easier to see how the nParticles interact with the pitcher and glass objects, you can turn on the Solver Display attribute to see the nParticle collision volume. Collision volumes are a non-renderable surface offset from each nParticle radius that the nucleus solver uses when calculating collisions between Nucleus objects.
To edit Collide Width Scale and add fluidity
The nParticles occupy the pitcher in distinct layers one on top of the other. In the bottom layer, the nParticles are evenly spaced and level, while in the upper layer, there are gaps between particles. Since the top layer of nParticles represent the surface of the liquid, the gaps between particles create a surface that is uneven and unlike the surface of water.

Increasing Incompressibility decreases the tendency of the particles to be pushed together. This forces the nParticles into a more uniform distribution throughout the volume, which creates a smoother surface for the liquid.

For this tutorial, you leave the following Liquid Simulation attributes at their default values:
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License