mental ray Paint Shaders
Version 3.8
Version 3.8.0.1
August 17 2009
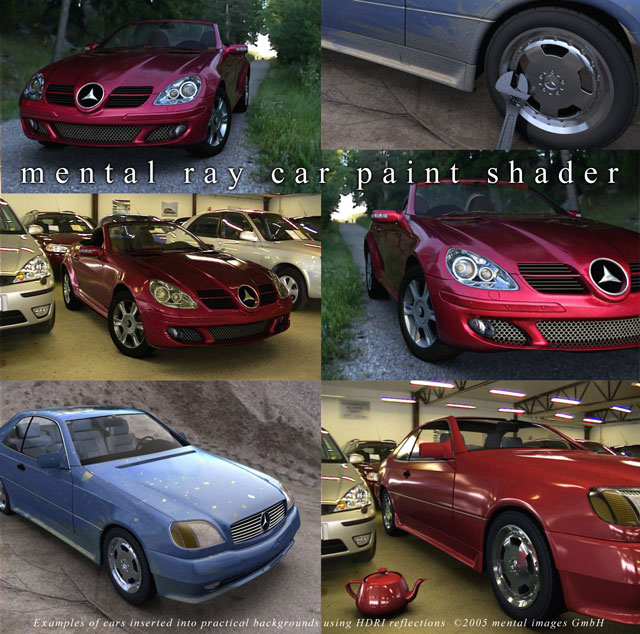 Mental ray car paint shader
Mental ray car paint shaderContents
Paint Shaders
The paint related shaders comes from the paint library.
The declaration of the shaders and Phenomena can be found in the
file paint.mi. To use the shaders, the declaration file must
be inluded and the library linked:
link "paint.so"
$include "paint.mi"
Car paint has several peculiar characteristics. On top of the
cars bodywork is a thin layer of pigment. The properties of this
layer is such that the actual perceived color shifts
depending on the viewing angle as well as the incident angle of the
incoming light.
Within this layer tiny metal flakes are suspended. The flakes
reflect light and can be seen glittering on a sunny day, due to
individual flakes reflecting sunlight directly at the observer.
On top of this is a clearcoat layer, which can be more or less
reflective and more or less glossy, depending on the quality of the
layer and any added wax coating. Most notably, this layer tends to
exhibit a pronounced Fresnel effect, reflecting more light
at glancing angles.
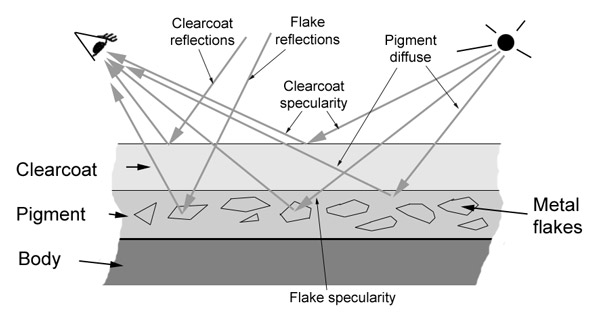 Structure of car paint
Structure of car paintCar paint Phenomenon
The mi_car_paint_phen should be applied as a surface
shader in a material. The shader supports:
- Diffuse reflection in the pigmentation layer, with selectable
color shift due to observer as well as incident light angle.
- Specular highlights from lightsources in the metallic
flakes
- Optional ray traced reflections in the metallic flakes
- Specular highlights from lightsources in the clearcoat (with
optional "glazing" mode)
- Includes a clearcoat layer with selectable mirror or glossy
reflections and specular highlights with an optional "glazing"
mode.
- Includes a lambertian dirt layer, for that "unwashed"
look.
mi_car_paint_phen
declare phenomenon "mi_car_paint_phen"
(
color "ambient",
color "base_color",
color "edge_color",
scalar "edge_color_bias",
color "lit_color",
scalar "lit_color_bias",
scalar "diffuse_weight",
scalar "diffuse_bias",
color "flake_color",
scalar "flake_weight",
scalar "flake_reflect",
scalar "flake_exp",
scalar "flake_density",
scalar "flake_decay",
scalar "flake_strength",
scalar "flake_scale",
color "spec",
scalar "spec_weight",
scalar "spec_exp",
color "spec_sec",
scalar "spec_sec_weight",
scalar "spec_sec_exp",
boolean "spec_glazing",
color "reflection_color",
scalar "edge_factor",
scalar "reflection_edge_weight",
scalar "reflection_base_weight",
integer "samples",
scalar "glossy_spread",
scalar "max_distance",
boolean "single_env_sample",
color "dirt_color",
scalar "dirt_weight",
scalar "irradiance_weight",
scalar "global_weight",
integer "mode",
array light "lights"
)
Diffuse Parameters
- ambient
- is the ambient light component. Note that this parameter is
treated differently to the ambient/ambience parameter pair of many
other base shaders in that it is influenced by the other diffuse
color parameters following, and hence represents incoming light,
rather than the objects "ambient color".
- base_color
- is the base diffuse color of the material.
- edge_color
- is the color seen at glancing angles (i.e. edges) which tend to
appear much darker. For really deep metallic paints seen
on sports cars it tends to be almost black.
- edge_color_bias
- defines the falloff rate of the color towards the edge. The
useful range is 0.0 to approximately 10.0, where the value 0.0
turns the effect off. Higher values makes the edge region narrower,
lower values makes it wider.
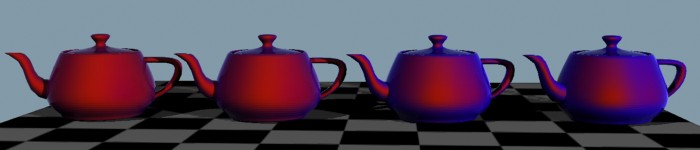 Color shift due to view angle, shifting between a red
base_color and a blue edge_color
Color shift due to view angle, shifting between a red
base_color and a blue edge_color
(atypical colors chosen for demonstration purposes only) with
varying edge_bias
- lit_color
- is the color seen in the area facing the lightsource.
- lit_color_bias
- defines the falloff rate of the color towards the light. The
useful range is 0.0 to approximately 10.0, where the value 0.0
turns the effect off. Higher values makes the colored region facing
the light smaller/narrower, lower values makes it larger/wider.
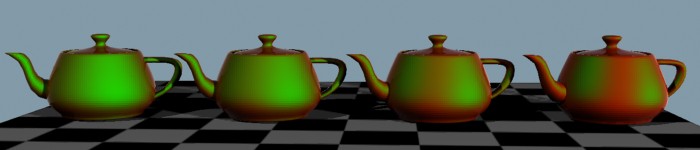 Color shift due to view angle, shifting between a red
base_color and a green lit_color
Color shift due to view angle, shifting between a red
base_color and a green lit_color
(atypical colors chosen for demonstration purposes only) with
varying lit_bias
- diffuse_weight
- controls the overall level of the diffuse parameters.
- diffuse_bias
- modifies the falloff of the diffuse shading. The useful range
is approximately 0.5 to 2.0, where 1.0 represent standard
lambertian shading, higher values pushes the diffuse peak towards
the light source, and lower values flattens the diffuse peak.
- irradiance_weight
- sets the influence of indirect light (photons and final
gathering) on the surface. It is internally divided by PI, i.e. a
value of 1.0 means the standard 1.0/PI weight.
Specular Parameters
- spec
- is the color of the primary specular highlight.
- spec_weight
- is a scalar multiplier.
- spec_exp
- is the Phong exponent.
- spec_sec
- is the color of the secondary specular highlight.
- spec_sec_weight
- is a scalar multiplier.
- spec_sec_exp
- is the Phong exponent.
- spec_glazing
- enables a special mode on the primary specular highlight called
glazing. By threasholding the specular highlight, it makes
the surface appear more polished and shiny. For nice sportscars
with a lot of wax, turn glazing on. For beat up cars in the
junkyard, turn it off.
 Left to right: Flake specularity only, standard specularity,
"glazing" mode enabled, and finally; "glazing" mode specularity
with flakes
Left to right: Flake specularity only, standard specularity,
"glazing" mode enabled, and finally; "glazing" mode specularity
with flakes
Flake Parameters
- flake_color
- is the color (reflectivity) of the flakes, which is generally
white.
- flake_weight
- is a scalar multiplier for the above color.
- flake_reflect
- defines the amount of ray traced reflection in the flakes,
which allows glittery reflections of e.g. an HDRI environment. The
value of 0.0 turns the effect off. The effect should generally be
very subtle and a value of 0.1 is often enough. The final intensity
of reflections also depends on flake_color and
flake_weight.
- flake_exp
- is the Phong specular exponent for the flakes.
- flake_density
- sets the density of the flakes. The useful range is from 0.1 to
approximately 10.0, where lower values indicate less dense flakes
and higher values indicates denser flakes.
- Since flakes are inherently small, they can easily introduce
rendering artifacts if their visual density becomes significantly
smaller than a pixel. If the oversampling of the rendering is set
high, small flakes may also potentially trigger massive
oversampling and hence very long render times needlessly, since the
averaging caused by the oversampling will essentially cancel out
the flake effect. To avoid this the parameter flake_decay
exists.
- flake_decay
- sets a distance at which the influence of flakes fade out. A
value of 0.0 disables fading. Any positive value causes the
flake_weight to be modulated such that is reaches zero at
this distance.
 Flakes at different distances with no flake decay. The furthest
flakes may potentially cause flicker in animations,
Flakes at different distances with no flake decay. The furthest
flakes may potentially cause flicker in animations,
or trigger unnecessary oversampling and long render times (here
rendered with low oversampling for illustrative purposes).
 Using flake decay. The flake strength diminishes by distance.
The same intentionally low oversampling as in the previous image
has been used.
Using flake decay. The flake strength diminishes by distance.
The same intentionally low oversampling as in the previous image
has been used.
- flake_strength
- sets the difference between the orientation of the flakes. The
useful range is 0.0 to 1.0 where 0.0 means that all flakes are
parallel to the surface and higher values means the orientation of
flakes are more and more varied.
- flake_scale
- is the size of the flakes. The procedural texture is calculated
in object space, and will hence follow the object. Keep in mind
that the scale is therefore influenced by any scale transformation
on the object instance.
Reflection Parameters
- reflection_color
- sets the color of the reflections in the clearcoat layer,
generally white.
Clearcoat tends to reflect more at glancing angles (edges).
- edge_factor
- defines the "narrowness" of this edge.
- reflection_edge_weight
- controls the reflective strength at the edge (generally
1.0).
- reflection_base_weight
- defines the reflective strength at facing angles (generally
low, 0.1 - 0.3).
Optionally, clearcoat layers may be glossy.
- samples parameter sets the bumber of glossy reflection
rays traced. The value of 0 disables glossiness.
- glossy_spread
- sets the amount of glossiness. Cars are generally near-mirrors
so this value should be kept small.
The glossy reflections are created with the help of the shader
mib_glossy_reflection.
Therefore, the parameters max_distance (limiting the reach
of reflective rays) and single_env_sample (optimizing lookup
of environment maps) are exposed parameters of that shader. Only a
subset of the parameters are exposed. If more are required, one can
either build a custom shading graph or create ones own variation of
the mi_car_paint_phen Phenomenon.
Dirt Parameters
 Real cars are rarely clean. Here showing the dirt layer (hand
painted dirt placement map), including a bump map applied in the
dirty regions.
Real cars are rarely clean. Here showing the dirt layer (hand
painted dirt placement map), including a bump map applied in the
dirty regions.A simple lambertian dirt layer covers the underlaying paint and
clearcoat layers.
- dirt_color
- is the color of said dirt.
- dirt_weight
- the amount of dirt, which would probably be connected to a
texture shader to get variations in the dirt across the surface. If
dirt_weight is 0.0 no dirt is added.
Advanced Parameters
- irradiance_weight
- sets the influence of indirect light (photons and final
gathering) on the surface. It is internally divided by PI, i.e. a
value of 1.0 means the standard 1.0/PI weight.
- global_weight
- is a global tuning parameter affecting the entire diffuse,
flake and specular subsystems. It does not affect reflections or
dirt.
- mode
- is the light mode.
- lights
- the light list.
The mi_metallic_paint is shader is used to facilitate
the rendering of metallic paint. However, it only takes care of the
pigmentation and the flakes, not the very important clearcoat
reflections. To accomplish the full effect, it needs to be
combined with a reflection shader (i.e. connecting it to the
base_material parameter of mib_glossy_reflection).
It also needs a bump shader for the flakes (generally mi_bump_flakes).
To get all these connections made automatically one can use the
ready-made Phenomenon mi_car_paint_phen,
which also supports a dirt layer. See the above documentation,
which has slightly more detailed documentation of the parameters
with example images.
The shader supports:
- Diffuse reflection in the pigmentation layer, with selectable
color shift due to observer as well as incident light angle.
- Specular highlights from lightsources in the metallic
flakes
- Specular highlights from lightsources in the clearcoat (with
optional "glazing" mode)
- Optional ray traced reflections in the metallic flakes
declare shader
color "mi_metallic_paint" (
color "ambient" default 0 0 0 1,
color "base_color" default 0.8 0.1 0.0 1,
color "edge_color" default 0.0 0.0 0.0,
scalar "edge_color_bias" default 1.0,
color "lit_color" default 0.6 0.0 0.2,
scalar "lit_color_bias" default 8.0,
scalar "diffuse_weight" default 1.0,
scalar "diffuse_bias" default 1.5,
scalar "irradiance_weight" default 1.0,
color "spec" default 1 1 1 1,
scalar "spec_weight" default 0.2,
scalar "spec_exp" default 60.0,
color "spec_sec" default 1 1 1 1,
scalar "spec_sec_weight" default 0.3,
scalar "spec_sec_exp" default 25.0,
boolean "spec_glazing" default on,
color "flake_color" default 1.0 1.0 1.0 1,
scalar "flake_weight" default 1.0,
scalar "flake_reflect" default 0.0,
scalar "flake_exp" default 45.0,
scalar "flake_decay" default 0.0,
shader "flake_bump",
scalar "global_weight" default 1.0,
integer "mode" default 3,
array light "lights"
)
version 2
apply material
end declare
- ambient
- is the ambient light component. Note that this parameter is
treated differently to the ambient/ambience parameter pair of many
other base shaders in that it is influenced by the other diffuse
color parameters following, and hence represents incoming light,
rather than the objects "ambient color".
- base_color
- is the base diffuse color of the material.
- edge_color
- is the color seen at glancing angles (i.e. edges) which tend to
appear much darker. For really deep metallic paints seen
on sports cars it tends to be almost black.
- edge_color_bias
- defines the falloff rate of the color towards the edge. The
useful range is 0.0 to approximately 10.0, where the value 0.0
turns the effect off. Higher values makes the edge region narrower,
lower values makes it wider.
- lit_color
- is the color seen in the area facing the lightsource.
- lit_color_bias
- defines the falloff rate of the color towards the light. The
useful range is 0.0 to approximately 10.0, where the value 0.0
turns the effect off. Higher values makes the colored region facing
the light smaller/narrower, lower values makes it
larger/wider.
- diffuse_weight
- allows to tune the overall level of the diffuse
parameters.
- diffuse_bias
- modifies the falloff of the diffuse shading. The useful range
is approximately 0.5 to 2.0, where 1.0 represent standard
lambertian shading, higher values pushes the diffuse peak towards
the light source, and lower values flattens the diffuse peak.
- irradiance_weight
- sets the influence of indirect light (photons and final
gathering) on the surface. It is internally divided by PI, i.e. a
value of 1.0 means the standard 1.0/PI weight.
- spec
- is the color of the primary specular highlight.
- spec_weight
- is a scalar multiplier.
- spec_exp
- is the Phong exponent.
- spec_sec
- is the color of the secondary specular highlight.
- spec_sec_weight
- is a scalar multiplier.
- spec_sec_exp
- is the Phong exponent.
- spec_glazing
- enables a special mode on the primary specular highlight called
glazing. By threasholding the specular highlight, it makes
the surface appear more polished and shiny. For nice sportscars
with a lot of wax, turn glazing on. For beat up cars in the
junkyard, turn it off.
- flake_color
- is the color (reflectivity) of the flakes, which is generally
white.
- flake_weight
- is a scalar multiplier for the above color.
- flake_reflect
- defines the amount of ray traced reflection in the flakes,
which allows glittery reflections of e.g. an HDRI environment. The
value of 0.0 turns the effect off. The effect should generally be
very subtle and a value of 0.1 is often enough. The final intensity
of reflections also depends on flake_color and
flake_weight.
- flake_exp
- is the Phong specular exponent for the flakes.
- flake_bump
- is the actual flake bump shader used. The shader mi_bump_flakes exists for
this purpose, but any shader that modifies the normal vector (e.g.
mib_passthrough_bump_map)
can be used.
- The shader put in the flake_bump may also return a
color, which will be the color (intensity) of the flake, or it may
leave the color unmodified.
Since flakes are inherently small, they can easily introduce
rendering artifacts if their visual density becomes significantly
smaller than a pixel. To avoid this the parameter
flake_decay exists. It sets a distance at which the
influence of flakes fade out. A value of 0.0 disables fading. Any
positive value causes the flake_weight to be modulated such
that it reaches zero at this distance.
- global_weight
- is a global tuning parameter that is a global multiplier to the
output of the shader.
- mode
- is the light mode.
- lights
- the light list.
Flake Bump Shader
This shader is designed to create a bump map with the appearance
of small individual flakes at slightly different orientations. It
does so by slightly modifying the current normal vector based on a
procedurally generated flake texture. It also returns a color that
indicates the "intensity" for that flake.
mi_bump_flakes
declare shader "mi_bump_flakes" (
scalar "flake_density" default 0.5,
scalar "flake_strength" default 0.8,
scalar "flake_scale" default 0.2,
)
version 1
apply texture
end declare
- flake_density
- only affects the returned color, not the amount of change to
the normal vector. The useful range is from 0.1 to approximately
10.0, where lower values indicate less dense flakes (more flakes
are given low color values near black) and higher values indicates
denser flakes.
- flake_strength
- indicates the amount of normal vector perturbations. Useful
range is 0.0 (which disables the effect) to 1.0. For low values,
flakes are nearly parallell, for higher values, the difference
between each flakes orientation is larger.
- flake_scale
- is the size of the flakes. The procedural texture is calculated
in object space, and will hence follow the object. Keep in mind
that the scale is therefore influenced by any scale transformation
on the object instance.
Copyright (©) 1986-2009 by
mental images GmbH








