Shading node plug-ins rely on the usage of Compound Attributes and Simple Attributes. The mapping of data between rendering samplers and shading networks is by attribute name. This approach is straightforward and easy to learn and remember, and general enough to work with both the present rendering requirements and future enhancements.
All rendering attributes for which a plug-in is interested has been pre-computed for the current sample being considered. The “datablock” argument that is passed into the plug-in’s compute() method contains the rendering attribute information the node has requested. When the plug-in is evaluated by the dependency graph it also passes in a “plug” argument for the specific attribute it wants to evaluate. To optimize evaluations, you need to check for only the output attributes you defined in your plug-in.
This example plug-in node has 20 attributes (aside from its id attribute).
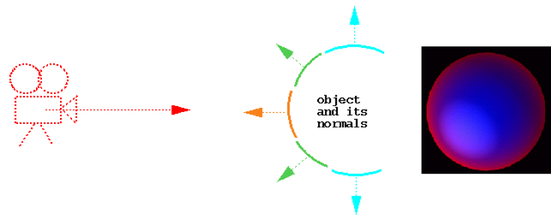
The node interpolates between two colors based on the direction of the surface normal it gets from the datablock, and uses the compute() method in that class to derive a result color that is placed into the output color attribute.
class InterpNode : public MPxNode
{public:
InterpNode();
virtual ~InterpNode();
virtual MStatus compute( const MPlug&, MDataBlock& );
static void * creator();
static MStatus initialize();
static MTypeId id;
protected:
static MObject InputValue;
static MObject color1R,color1G,color1B,color1;
static MObject color2R,color2G,color2B,color2;
static MObject aNormalCameraX, aNormalCameraY,
aNormalCameraZ, aNormalCamera;
static MObject aPointCameraX, aPointCameraY,
aPointCameraZ, aPointCamera;
static MObject aOutColorR, aOutColorG, aOutColorB,
aOutColor;
};
MObject InterpNode::InputValue;
MObject InterpNode::color1R;
MObject InterpNode::color1G;
MObject InterpNode::color1B;
MObject InterpNode::color1;
MObject InterpNode::color2R;
MObject InterpNode::color2G;
MObject InterpNode::color2B;
MObject InterpNode::color2;
MObject InterpNode::aNormalCameraX;
MObject InterpNode::aNormalCameraY;
MObject InterpNode::aNormalCameraZ;
MObject InterpNode::aNormalCamera;
MObject InterpNode::aPointCameraX;
MObject InterpNode::aPointCameraY;
MObject InterpNode::aPointCameraZ;
MObject InterpNode::aPointCamera;
MObject InterpNode::aOutColorR;
MObject InterpNode::aOutColorG;
MObject InterpNode::aOutColorB;
MObject InterpNode::aOutColor;
initializePlugin/uninitializePlugin
MStatus initializePlugin( MObject obj )
{const MString UserClassify( “utility/general” );
MFnPlugin plugin( obj, “Autodesk”, “1.0”,
“Any”);
plugin.registerNode( “Interp”, InterpNode::id,
InterpNode::creator,
InterpNode::initialize,
MPxNode::kDependNode, &UserClassify);
return MS::kSuccess;
}
MStatus uninitializePlugin( MObject obj)
{MFnPlugin plugin( obj );
plugin.deregisterNode( InterpNode::id );
return MS::kSuccess;
}
MStatus InterpNode::initialize()
{MFnNumericAttribute nAttr;
// Inputs and Attributes
//
// User defined attributes require a long-name and short-
// name that are required to be unique within the node.
// (See the compound attribute color1 named “Sides”.)
//
// Rendering attributes that your node wants to get from
// the sampler require them to be defined given the pre-
// defined unique long-name.(See the compound attribute
// aNormalCamera named “normalCamera”.)
//
// User defined Attributes are generally something that you
// want to store in the Maya file. The setStorable(true)
// method enables an attribute to be stored into the Maya
// scene file.
//
// Rendering attributes are primarily data that is
// generated per sample and not something that you want to
// store in a file. To disable an attribute from being
// recorded to the Maya scene file use the
// setStorable(false) method.
//
// Simple attributes that represent a range of values can
// enable a slider on the Attribute Editor by using the
// methods setMin() and setMax().
// (See the simple attribute InputValue named “Power”.)
//
// Compound attributes that represent a vector of 3 floats
// can enable a color swatch on the Attribute Editor that
// will launch a color picker tool by using the method
// setUsedAsColor(true).
// (See the compound attribute color1 name “Sides”.)
//
// Both Simple and Compound attributes can be initialized
// with a default value using the method setDefault().
//
// Attributes by default show up in the Attribute Editor
// and in the Connection Editor unless they are specified
// as being hidden by using the method setHidden(true).
//
// Attributes by default have both read/write access in the
// dependency graph. To change an attributes behaviour you
// can use the methods setReadable() and setWritable(). The
// method setReadable(true) indicates that the attribute
// can be used as the source in a dependency graph
// connection. The method setWritable(true) indicates that
// the attribute can be used as the destination in a
// dependency graph connection.
// (See the compound attribute aOutColor named “outColor”
// below. It has been marked as a read-only attribute since
// it is the computed result of the node, it is not stored
// in the Maya file since it is always computed, and it is
// marked as hidden to prevent it from being displayed in
// the user interface.)
//
//
// User defined input value
InputValue = nAttr.create( “Power”, “pow”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
nAttr.setDefault(1.0f);
nAttr.setMin(0.0f);
nAttr.setMax(3.0f);
nAttr.setStorable(true);
// User defined color attribute
color1R = nAttr.create( “color1R”, “c1r”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
color1G = nAttr.create( “color1G”, “c1g”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
color1B = nAttr.create( “color1B”, “c1b”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
color1 = nAttr.create( “Sides”, “c1”, color1R, color1G,
color1B);
nAttr.setStorable(true);
nAttr.setUsedAsColor(true);
nAttr.setDefault(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
color2R = nAttr.create( “color2R”, “c2r”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
color2G = nAttr.create( “color2G”, “c2g”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
color2B = nAttr.create( “color2B”, “c2b”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
color2 = nAttr.create( “Facing”, “c2”, color2R,
color2G, color2B);
nAttr.setStorable(true);
nAttr.setUsedAsColor(true);
nAttr.setDefault(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// Surface Normal supplied by the render sampler
aNormalCameraX = nAttr.create( “normalCameraX”, “nx”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
nAttr.setStorable(false);
nAttr.setDefault(1.0f);
aNormalCameraY = nAttr.create( “normalCameraY”, “ny”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
nAttr.setStorable(false);
nAttr.setDefault(1.0f);
aNormalCameraZ = nAttr.create( “normalCameraZ”, “nz”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
nAttr.setStorable(false);
nAttr.setDefault(1.0f);
aNormalCamera = nAttr.create( “normalCamera”,”n”,
aNormalCameraX,
aNormalCameraY, aNormalCameraZ);
nAttr.setStorable(false);
nAttr.setHidden(true);
// Point on surface in camera space, will be used to compute view vector
aPointCameraX = nAttr.create( “pointCameraX”, “px”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
nAttr.setStorable(false);
nAttr.setDefault(1.0f);
aPointCameraY = nAttr.create( “pointCameraY”, “py”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
nAttr.setStorable(false);
nAttr.setDefault(1.0f);
aPointCameraZ = nAttr.create( “pointCameraZ”, “pz”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
nAttr.setStorable(false);
nAttr.setDefault(1.0f);
aPointCamera = nAttr.create( “pointCamera”,”p”,
aPointCameraX,
aPointCameraY, aPointCameraZ);
nAttr.setStorable(false);
nAttr.setHidden(true);
// Outputs
aOutColorR = nAttr.create( “outColorR”, “ocr”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
aOutColorG = nAttr.create( “outColorG”, “ocg”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
aOutColorB = nAttr.create( “outColorB”, “ocb”,
MFnNumericData::kFloat);
aOutColor = nAttr.create( “outColor”, “oc”,
aOutColorR, aOutColorG, aOutColorB);
nAttr.setStorable(false);
nAttr.setHidden(false);
nAttr.setReadable(true);
nAttr.setWritable(false);
addAttribute(InputValue);
addAttribute(color1R);
addAttribute(color1G);
addAttribute(color1B);
addAttribute(color1);
addAttribute(color2R);
addAttribute(color2G);
addAttribute(color2B);
addAttribute(color2);
addAttribute(aNormalCameraX);
addAttribute(aNormalCameraY);
addAttribute(aNormalCameraZ);
addAttribute(aNormalCamera);
addAttribute(aPointCameraX);
addAttribute(aPointCameraY);
addAttribute(aPointCameraZ);
addAttribute(aPointCamera);
addAttribute(aOutColorR);
addAttribute(aOutColorG);
addAttribute(aOutColorB);
addAttribute(aOutColor);
attributeAffects (InputValue, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (color1R, color1);
attributeAffects (color1G, color1);
attributeAffects (color1B, color1);
attributeAffects (color1, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (color2R, color2);
attributeAffects (color2G, color2);
attributeAffects (color2B, color2);
attributeAffects (color2, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (aNormalCameraX, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (aNormalCameraY, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (aNormalCameraZ, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (aNormalCamera, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (aPointCameraX, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (aPointCameraY, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (aPointCameraZ, aOutColor);
attributeAffects (aPointCamera, aOutColor);
return MS::kSuccess;
}
MStatus InterpNode::compute( const MPlug& plug, MDataBlock&
block )
{int k=0;
float gamma,scalar;
k |= (plug == aOutColor);
k |= (plug == aOutColorR);
k |= (plug == aOutColorG);
k |= (plug == aOutColorB);
if (!k) return MS::kUnknownParameter;
MFloatVector resultColor(0.0,0.0,0.0);
MFloatVector& Side = block.inputValue( color1 ).
asFloatVector();
MFloatVector& Face = block.inputValue( color2 ).
asFloatVector();
MFloatVector& surfaceNormal = block.
inputValue( aNormalCamera ).
asFloatVector();
MFloatVector& viewVector = block.
inputValue( aPointCamera ).
asFloatVector();
float power = block.inputValue( InputValue ).asFloat();
// Normalize the view vector
double d = sqrt((viewVector[0] * viewVector[0]) +
(viewVector[1] * viewVector[1]) +
(viewVector[2] * viewVector[2]));
if (d != (double)0.0) {viewVector[0] /= d;
viewVector[1] /= d;
viewVector[2] /= d;
}
// find dot product
float scalarNormal = ((viewVector[0]*surfaceNormal[0])
+ (viewVector[1]*surfaceNormal[1])
+ (viewVector[2]*surfaceNormal[2]));
// take the absolute value
if (scalarNormal < 0.0) scalarNormal *= -1.0;
// Use InputValue to change interpolation
// power == 1.0 linear
// power >= 0.0 use gamma function
//
if (power > 0.0) {gamma = 1.0 / power;
scalar = pow(scalarNormal,gamma);
}
else { scalar = 0.0; }// Interpolate the colors
MFloatVector interp(0.0,0.0,0.0);
interp[0] = scalar * (Face[0] - Side[0]);
interp[1] = scalar * (Face[1] - Side[1]);
interp[2] = scalar * (Face[2] - Side[2]);
resultColor[0] = Side[0] + interp[0];
resultColor[1] = Side[1] + interp[1];
resultColor[2] = Side[2] + interp[2];
// set ouput color attribute
MDataHandle outColorHandle = block.
outputValue( aOutColor );
MFloatVector& outColor = outColorHandle.
asFloatVector();
outColor = resultColor;
outColorHandle.setClean();
return MS::kSuccess;
}