In Maya, surfaces appear in a rendered image based on the shading materials you apply to them. The default shading material that gets assigned to surfaces provides basic attributes such as color, transparency, and incandescence.
Depending on your final image requirements, you can enhance the visual impact of an object by adding one or more texture maps to the assigned shading material. One basic texture map you can apply is a bitmap image also referred to as a file texture. In this lesson, you apply a texture map we’ve created for your use on the cracker box.
For more basic information on shading materials and texture maps see the Rendering chapter of this guide and the Maya Help.
To assign a shading material to the cracker box
This displays the cracker box with a default gray, smooth shading material, lit using default lighting. Turning on Smooth Shade All displays the assigned shading material you apply to the cracker box in the steps following.
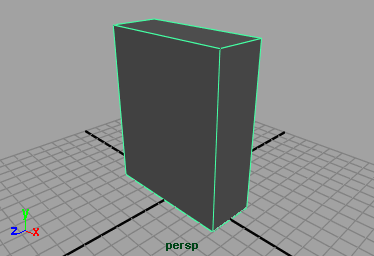
A new Lambert shading material is created and assigned to the cracker box. The Attribute Editor appears and displays the various attributes for the new Lambert shading material.
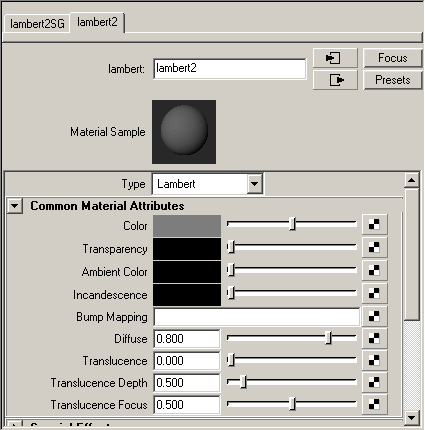
The new Lambert material is identical to the default gray material that was previously assigned to the cracker box. However, it’s always a good practice not to modify the default shading material in the scene and create a new shading material and modify it to suit your requirements.
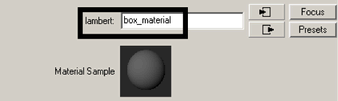
Renaming the shading material lets you easily identify it later on when you need to edit it. Naming items uniquely in Maya is a useful habit.
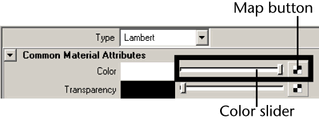
The shading material assigned to the box model also updates in the scene view so it appears in a brighter tone.
The Create Render Node window appears and lists the various texture options you can apply (or connect) to the color channel of the box material.
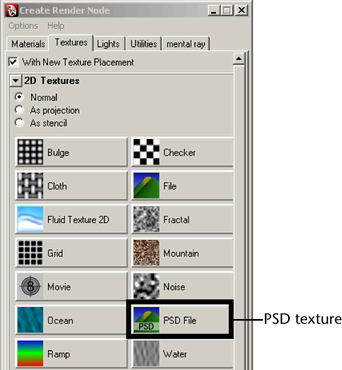
Choosing this option specifies that you want to apply an Adobe® Photoshop® format file as a texture. A PSD format file lets you keep the various components of your texture map on multiple layers. This is useful when you need the ability to edit a component of the texture during production.
The Attribute Editor updates to display the options for the PSD File texture.
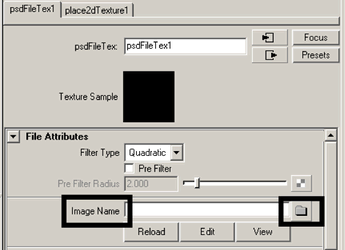
A browser window appears with the path set to the default project directory. By default, Maya looks for source images for texture maps in a sourceimages folder whenever the project folder is set. Maya can use file texture images from anywhere on your workstation or local network. For example, you can have images on a central disk drive that is shared among users in a production environment.
This file can be found in the GettingStarted directory that you set as your Maya project:
GettingStarted/UVMapping/sourceimages
The image contains 2D artwork for the front, back, top, bottom, and sides of the cracker box that was generated in Adobe® Photoshop®.

A small preview of the image appears in the Texture Sample box in the Attribute Editor.
When a texture is applied to a shading material its attributes get added to the existing attributes for shading material. That is, all of the existing shading attributes remain unchanged except for the attribute that gets modified by the texture. In this case, the grey color is substituted by the image of the cracker box artwork.

The texture map does not appear correctly on the cracker box model. The texture map was designed so that specific sides of the box receive specific regions of the image. Instead, the complete image is being placed on every side of the object.
To correct this problem you must modify the default UV texture coordinates for the model so they match the layout of the texture image. To do this, you use the UV Texture Editor.