Show in Contents
Add to Favorites

Home: Autodesk Maya Online Help
Surface shading
Shading
Swatch rendering for any renderer
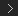
Surface texture
In
visual arts, a texture is any kind of surface detail, both visual
and tactile. In Maya, you create surface detail with textures connected
to the material of objects as texture maps. (Materials define a
the basic substance of an object; see
Surface shading for
more details.)
For more information
on texture maps, see
Texture mapping.
Factors beyond basic
color, transparency, and shine (see below) that determine the appearance
of an object’s surface include:
You can also bake illumination
and color to a texture that you can later apply to objects in a
scene. See
Baking illumination and color.
Color
You can work with color in Maya in so many different
ways. Here are some of the most common:
- Change the basic color of an object by
adjusting the color attribute of a material applied to the object.
To find out more about material node attributes, see
Render node attributes.
- Apply a texture as a color map to the
material’s color attribute.
- Use a Ramp Shader for
extra control over the way color changes with light and view angle.
You can simulate a variety of exotic materials and tweak traditional
shading in subtle ways. For a description of the Ramp
Shader, see
Ramp Shader.
- Expand, enhance, or manipulate colors
in applied textures using the Color utilities.
For example, you can blend colors, adjust contrast, and convert HSV
to RGB. For a description of each of the color utilities and what
you can use them for, see
About Color Utilities.
Transparency
You can work with the transparency
of an object in the following ways:
- Change the transparency level of an object
adjusting the transparency attribute of a material applied to the
object. To find out more about material node attributes, see
Render node attributes.
- Apply a texture as a transparency map
to the material’s transparency attribute to designate which areas
of an object are opaque, transparent or semi-transparent.
Specular highlight (shine)
You can work with the
shininess of objects in your scene in the following ways:
- Change the intensity and size of the
specular highlights of an object by adjusting the Specular
Shading attributes of a material applied to the object.
To find out more about material node attributes, see
Render node attributes and
Common surface material Specular Shading attributes.
- Apply a texture as a specularity map
to the material’s Specular Color attribute to
designate which areas of an object shine (and the color of the highlights).
- For more information about texture mapping,
see
Texture mapping.
- To map a 2D or 3D texture, see
Texture mapping.
NoteOnly materials with
specular attributes (
Anisotropic,
Blinn,
Phong, and
PhongE)
have surface highlights. The
specular highlight is
the white shiny glow on the material.
What are specular highlights?
Some surfaces are shinier
than others (for example a wet fish has a shinier surface than a
dry leaf). Depending on how shiny a surface is, it reflects light in
different ways.
Shiny objects reflect
light directly; matte objects diffuse light. Specular highlights
show the places on the object where the light sources are reflected
at consistent angles; reflections on an object show, among other
things, light bounced from surrounding objects.
Specular highlights depend
directly on the view (camera), not the position of the light, like
diffuse shading does.
TipThe Blinn material
is recommended for shiny surfaces in animations. Highlights on other
specular materials, like Phong and PhongE,
may flicker when animated.
Highlights
The size of a specular
highlight on a surface makes the surface look either flat or shiny.
Highlight color
You
can control the color of highlights on surfaces.
Reflections
You
can control the degree of reflectivity as well as other surface
properties like refracted color.