Show in Contents

Add to Favorites

Home: Autodesk Maya Online Help

poleVectorConstraint
Constraint nodes

Character nodes
pairBlend
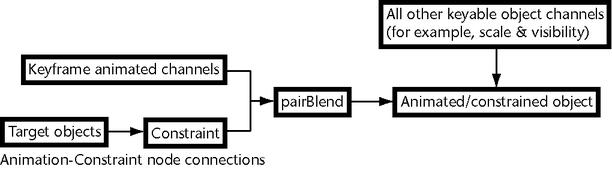
The pairBlend node
is automatically generated when both keyframe animation and a constraint
are applied to an object. Once the animation and constraint are
linked to the pairBlend node,
you can modify the weight of the Animation-Constraint blend to generate
various effects. See
Blend Weights in the Channel Box.
- In
the dependency graph (DG), the pairBlend node
functions as a link between constraints, keyframe animation, and
the object to which both are applied. The pairBlend node
connections resemble the following: all target objects connect to
the constraint node, the constraint node and keyframe animation
connect to the pairBlend node,
and the pairBlend node
connects to the object.
When multiple constraints are applied to the
same object, a separate pairBlend node
is created for each constraint and the keyframe animation channels
of the constrained object connect to the same pairBlend node
as their related constraints.
pairBlend Attributes
Translate X Mode
Select one of the following options:
- Blend Inputs
-
The blended X translation of Input 1 and Input 2
controls the driven object’s X translation.
- Input 1 only
-
The X translation of Input 1 controls the X translation
of the driven object.
- Input 2 only
-
The X translation of Input 2 controls the X translation
of the driven object.
Translate Y Mode
Select one of the following options:
- Blend Inputs
-
The blended Y translation of Input 1 and Input 2
controls the driven object’s Y translation.
- Input 1 only
-
The Y translation of Input 1 controls the Y translation
of the driven object.
- Input 2 only
-
The Y translation of Input 2 controls the Y translation
of the driven object.
Translate Z Mode
Select one of the following options:
- Blend Inputs
-
The blended Z translation of Input 1 and Input 2
controls the driven object’s Z translation.
- Input 1 only
-
The Z translation of Input 1 controls the Z translation
of the driven object.
- Input 2 only
-
The Z translation of Input 2 controls the Z translation
of the driven object.
Rotate Mode
Rotation is calculated by blending the rotation of
the specified inputs along all axes.
- Blend Inputs
-
The blended X, Y, and Z rotation of Input 1
and Input 2 controls the driven object’s rotation along all axes.
- Input 1 only
-
The X, Y, and Z rotation of Input 1 controls
the driven object’s rotation along all axes.
- Input 2 only
-
The X, Y, and Z rotation of Input 2 controls
the driven object’s rotation along all axes.
Rot Interpolation
For more information, see
Animated rotation in Maya.
- Euler Angles
-
Use Euler Angles when
the pairBlend weight value is between
0 (driven by keyframes) and 1 (driven by the constraint). Euler
Angles is the default rotation interpolation.
NoteEuler angles may cause flipping when used to
interpolate between keyframes and constraints. If this occurs, we
recommend that you switch to quaternion rotation.
- Quaternions
-
Quaternions smoothly interpolate the keyframe-constraint
blend without producing anomalies (such as flipping). Use Quaternion when
the pairBlend weight value is 1
or 0.
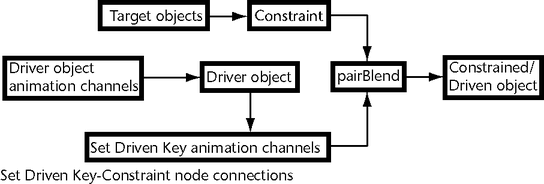
Current Driver
Sets what is currently driving the selected object.
- Weight
-
Displays a blend value that determines the amount
of influence that the constraint and keyframe animation have on
the constrained object. This field is read-only. See
Blend Constraintn.
- In Translate
-
The In Translate fields
display the X, Y, and Z translation values for Input 1 and Input
2. n represents the input number.
- In Rotate
-
The In Rotate fields
display the X, Y, and Z rotation values for Input 1 and Input 2.
n represents the input number.
- Caching
-
Unlike other cache data in Maya (for example, caches
in Dynamics, Maya® nCloth™, Maya® Classic Cloth™, and Maya® Fluid Effects™), the cache data for pairBlend is
also an animation curve. See
Caching.
- Node State
-
Blend Weights in the Channel
Box
NoteWhen the driven object is selected, all
its target and blend weight values can be viewed in the Channel
Box under SHAPES > objectn_typeConstraintn or INPUTS
> pairBlendn.
- Blend Constraintn
-
The keyframe animation-constraint blend value determines
the amount of influence that the constraint and keyframe animation
have on the constrained object. If the value is 0, the keyframe
animation has total control over the constrained object’s transformations.
If the value is 1, the constraint has total control over the constrained
object’s transformations.
If there are more than one of the same type
of constraint applied to the object, n stands for the constraint
number. This value appears in the pairBlend node’s
attributes as Weight.