Show in Contents

Add to Favorites

Home: Autodesk Maya Online Help

Preparing your model for the 3D Paint Tool
3D Paint Tool

Restrict the paint area on polygons
Paint textures on 3D objects
You can paint textures with the 3D
Paint Tool using two types of brushes: Artisan brushes
and Paint Effects brushes.
Artisan brushes use grayscale
images to define the brush profile (or shape). You can select from
40 predefined brush shapes, or you can create your own shapes using
any image format supported by Maya. You can paint, erase and clone
textures using Artisan brushes.
Paint Effects brushes are defined
by specific combinations of attribute settings and can be simple
(like pen, pastel, oil paint, and pencil brushes) or they can simulate
growth to get their look (like flowers, feathers, hair, and fire
brushes). You can select the default Paint, Smear,
or Blur brush to paint with, or
you can select any preset brush from Visor or
your shelves.
Warning
- Displaying
other surfaces significantly slows down painting. Display only the
surface you are painting using Isolate Select or
by hiding the other surfaces.
- On
textures larger than 512 (which have to be scaled down to appear
in the hardware render), sometimes darker pixels appear where there
are seams in the UV mesh. These do not show in
the software render.
- Changing
shader assignment while in 3D Paint Tool will
cause inconsistent display. Exit the 3D Paint Tool before
reassigning shaders to the selected surface.
- Switching
UV sets while in the 3D Paint tool gives unexpected
results. Exit
the tool before switching UV sets.
- When
using the 3D Paint Tool in High
Quality Rendering display mode, the display is not updated
until the end of the stroke. This is necessary to maintain interactive
painting performance.
To
paint on a 3D object
- Select
the surface(s) you want to paint on.
NotePolygonal and subdivision surfaces must
have non-overlapping UVs that fit within 0 to 1 in the texture space.
In general, Automatic Mapping produces
UVs that can be used for painting. For details, see the Polygonal Modeling and
the Subdivision Surface Modeling guides.
- Select
the 3D Paint Tool and open the Tool
Settings editor (Rendering menu
set,
Texturing > 3D Paint Tool >
 ). For
information on tool settings, see
3D Paint Tool.
). For
information on tool settings, see
3D Paint Tool.
- Click Reset
Tool to reset the tool settings. Resetting the tool is
a good practice to ensure you get expected results when you paint.
- Beside Attribute
to Paint (in the File Textures section
of the Tool Settings editor), select
the attribute you want to paint. The default is Color.
- If
you have not previously painted or assigned file textures to one
or more of the surfaces, the following warning appears on the Command
Feedback line:
Warning: Some surfaces
have no file texture assigned to the current attribute.
Also, the brush outline displays an X ( ) across
it when you move the brush over the surface to indicate that you
are unable to paint on the selected attribute texture.
) across
it when you move the brush over the surface to indicate that you
are unable to paint on the selected attribute texture.
- If
you have previously painted or assigned file textures, you do not
get the warning and the brush displays without the X, so you are
ready to paint. Skip to step #7.
NoteBe sure to assign a new shader before painting
your object, otherwise you will modify the default shader. If this
happens, the painted texture will be assigned to any new objects
you create in your scene.
- Click Assign/Edit
Textures. The Assign/Edit File Textures window
opens.
- Enter
a size for the texture in the Size X and Size
Y boxes, then select an Image Format and
click Assign/Edit Textures. The Keep
Aspect Ratio option ensures that the proportions of the
image are maintained. Turn this option off if you want the width
and the height of the texture to be different. The texture size
is currently limited to 2048 x 2048 and must be a power of 2 in
each dimension. Larger textures require more memory. Textures larger
than 512 will yield slower performance.
TipTo assign different-sized textures to different
surfaces, select each surface or group of surfaces separately and
assign textures to them. Once the textures have been assigned, you
can select any combination of surfaces to paint on.
- Set
a base color for the model and save the texture. This establishes
the texture you will erase back to. To do this, click the Color swatch
in the Flood section and select a
color from the Color Chooser. Set the Paint Operations to Artisan
Paint, click Flood Paint,
and then click the Save Textures button in the File
Textures section.
- Select
a brush to paint, erase, clone, smear or blur. For details, see
Select a brush.
- Modify
any other settings as required and drag on the model to paint. For information
on these settings, see
3D Paint Tool settings.
If you are painting Single Channel (grayscale)
attributes such as bump, or diffuse, the color you paint is automatically
converted to grayscale.
- Once
you have finished painting one attribute, you can paint another attribute
without leaving the tool by selecting the attribute beside Attribute
to Paint. The first time you paint an attribute, you
will have to assign a texture for it, unless a texture was already
assigned in Hypershade.
Select a brush
The
brush operation you select defines whether you are going to apply
paint to the texture, or whether you are going to erase, clone,
smear, or blur paint already applied to the surface.
You can apply paint to the texture using Artisan Paint
Brushes or Paint Effects Paint brushes.
To erase or clone you use Artisan brushes.
To smear or blur you use Paint Effects brushes.
To
select an Artisan brush to Paint, Erase,
or Clone
- In
the Paint Operations section, select Artisan, Paint, Erase,
or Clone.
Maya automatically selects the brush profile
selected when you last used the Artisan Paint
brush. (If the last profile was a custom brush, the operation
remembers only that it was a custom brush, not which custom brush. If
the custom brush was changed for either the Erase or Clone operations, it
changes for the Paint operation and for any
other operation with the custom brush profile selected.)
Use the Rotate To Stroke option
to change the orientation of brush profiles that are not uniformly
round. This option is not available for the Clone operation.
- If
you want to use a different brush profile, click the profile shape
beside Artisan in the Brush section,
or click Browse to select a custom profile. When
you select one of the custom profiles provided with Maya, the Last Image
File icon changes to show which image you selected.
- If
you selected Erase or Clone skip
to step #5.
- In
the Color section, select a Color.
If you are painting Single Channel (grayscale)
attributes such as bump, or diffuse, the color you paint is automatically
converted to grayscale.
- Select
an Opacity, if necessary.
- In
the Paint Operations section, select
a Blend Mode, if necessary.
- In
the Brush section, modify the brush Radius
(U) (Artisan), if necessary.
- If
the surface is very convoluted, you may prefer to turn Screen
Projection on.
To
select a Paint Effects brush to Paint, Smear,
or Blur
- Select
a Paint Effects brush using any
of the following methods:
- In
the Paint Operations section, select
a Paint Effects operation. If
you select:
Paint - The brush becomes the
last selected Paint Effects brush with a Brush
Type set to Paint. If
no Paint brush was previously
selected, the default Paint Effects paint
brush is used.
Smear - The brush becomes the
last selected Paint Effects brush with a Brush
Type set to Smear. If
no Smear brush was previously
selected, the default Paint Effects smear
brush is used.
Blur - The brush becomes the
last selected Paint Effects brush with a Brush Type set
to Blur. If no Blur brush
was previously selected the default Paint Effects blur
brush is used.
- Click the Get Brush icon
 and select
the brush from Visor. The paint operation
changes to Paint Effects Paint, Smear,
or Blur, depending on the Brush
Type defined for the brush preset. Paint
Effects Erase is not supported.
and select
the brush from Visor. The paint operation
changes to Paint Effects Paint, Smear,
or Blur, depending on the Brush
Type defined for the brush preset. Paint
Effects Erase is not supported.
- Click
a Paint Effects brush on a shelf.
The paint operation changes to Paint Effects Paint, Smear,
or Blur, depending on the Brush
Type defined for the brush preset.
- In
the Brush section, modify the brush Scale
(PFX) and Width (PFX) settings, if necessary.
- Click the Edit Template brush icon
 and make
the changes to the brush settings in the Paint Effects Brush
Settings window. Any changes you make to the settings
are remembered the next time you select the Paint
Effects Paint brush.
and make
the changes to the brush settings in the Paint Effects Brush
Settings window. Any changes you make to the settings
are remembered the next time you select the Paint
Effects Paint brush.
You can save these settings as a new preset
by following the instructions under
Create new brush presets,
starting at step #3. To create the icon for preset (step #8), go
into canvas mode, paint a stroke, grab the icon and return to the
scene view without leaving the 3D Paint Tool.
- Turn
on Screen Projection in the Stroke section
if the surface has seams, the UVs are cut up, you are painting across
multiple surfaces, or the surface has uneven parameterization.
To
select the last selected Paint Effects brush
- Click the Last brush icon
 and paint.
The Paint Operation changes to Paint
Effects Paint, Smear,
or Blur, depending on the Brush
Type defined for the last selected brush preset.
and paint.
The Paint Operation changes to Paint
Effects Paint, Smear,
or Blur, depending on the Brush
Type defined for the last selected brush preset.
Erase paint
You can erase
the strokes you paint by painting over them with the Artisan Erase brush.
When you erase, you remove the color from the painted pixels, revealing
the last saved texture.
To set the background texture to erase to, turn
off Update on Stroke and click the Save
Textures button. Flooding with the operation set to Erase restores the
texture to its last saved version. You cannot erase when Update on Stroke is
turned on, since the texture is constantly saved.
NotePaint Effects brushes
with a Brush Type of Erase are
not supported in the 3D Paint Tool.
Clone paint
You can clone an area of the texture (duplicate
it) and then paint that sample elsewhere on the texture or on other
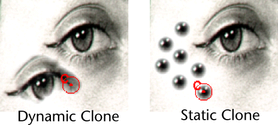
textures. There are two cloning approaches: dynamic and static.
With dynamic cloning, the clone source moves
as you paint. In the following Dynamic Clone example,
a small area of the top eye was set as the clone source. Painting
below the eye gradually reproduced the top eye. In the Static Clone example,
the pupil was cloned and stamped.
To
clone an area of the texture and paint with it
- In
the Paint Operations section, click Reset
Brushes to reset the brush settings. Resetting the tool
is good practice to ensure you get expected results when you paint.
- In
the Paint Operations section, select
the Artisan Clone option.
The brush outline displays an X across it when
you move the brush over the surface to indicate that you are unable
to paint on the selected attribute texture until you set a clone
source. 
Maya automatically selects the brush profile
selected when you last used the Clone operation.
However if the last profile was a custom brush, the operation remembers
only that it was a custom brush, not which custom brush. Changing
the custom brush for one operation changes it for any other operation
with the custom brush profile selected.
- Select
a Clone Brush Mode: Dynamic or Static.
By default, the Clone Brush Mode is
set to Dynamic. With dynamic cloning,
the cloned area changes as you paint, moving alongside your stroke and
maintaining a constant distance from the stroke path. This is an
effective way to copy areas from existing textures.
Select Static to
keep the clone source stationary.
- Click Set
Clone Source and click an area where you want to clone
the texture. A brush outline stays on the area where you clicked.
- If
the Clone Brush Mode is set to Dynamic,
click another area on the texture to define the offset between the
clone source and your paint stroke.
- Paint
on the model where you want the cloned texture to appear. As you paint,
the clone source moves alongside the stroke, maintaining the offset defined
by your second click.
If you paint over the clone source during a
stroke, the original paint sample is used for the rest of the stroke,
but the next stroke uses the updated clone source paint sample.
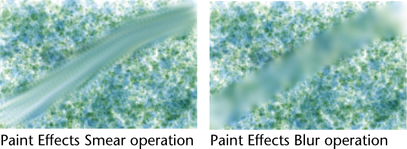
Smear and blur paint
Smearing with a Paint
Effects Smear brush blends adjacent
colors together along the stroke path.
Blurring with a Paint Effects Blur brush
softens the edges of adjacent colors by averaging their color values.
You can use the default Paint
Effects Smear or Blur brushes
or select any Paint Effects brush with a Brush
Type set to Smear or Blur.
To select the default Smear or Blur brushes,
click Reset Brushes and in the Paint
Operations section, select Paint Effects Smear or Blur,
as appropriate. Use the Blur Intensity option
to adjust the blur effect.
Set an image to erase back to
Using
the Set Erase Image button you
can set the current paint layer as what to erase back to.
Example
of using Set Erase Image
- Paint
a base layer, such as a layer of dirt.
- Click
the Set Erase Image button.
- Flood
the layer with a color, such as grey.
- Erase
patches and the dirt layer shows through.
Reset brushes
You
can reset the Artisan and Paint
Effects brushes to their default profiles and settings
by clicking the Reset Brushes button. The default
brushes will now be used the next time you select these operations.


 ). For
information on tool settings, see
3D Paint Tool.
). For
information on tool settings, see
3D Paint Tool.
 ) across
it when you move the brush over the surface to indicate that you
are unable to paint on the selected attribute texture.
) across
it when you move the brush over the surface to indicate that you
are unable to paint on the selected attribute texture.
 and make
the changes to the brush settings in the Paint Effects Brush
Settings window. Any changes you make to the settings
are remembered the next time you select the Paint
Effects Paint brush.
and make
the changes to the brush settings in the Paint Effects Brush
Settings window. Any changes you make to the settings
are remembered the next time you select the Paint
Effects Paint brush.