
This example includes two related examples:
Wireframe also draws edges, but it shows the true edges (before tesselation). Wireframe uses a UserDataBlob to pass edge information to a shader (which shows how to map Softimage user data into mental ray user data). A custom operator populates the UserDataBlob with the edge information. An operator is used rather than a custom command because whenever the geometry changes, Softimage re-evaluates the operator and re-renders the object. The operater and the shader are contained in the same DLL/SO, and this file is located in the Application\Plugins directory instead of the conventional shader directory (Application\bin\{CPU}) so that Softimage automatically loads it as a self-installed plugin. This approach is convenient for implementing both a shader and an operator together in an single dll, but it means that the normal ability to have multiple platform binaries on a single workgroup would not work. To support that configuration the example would be implemented as two separate dlls.
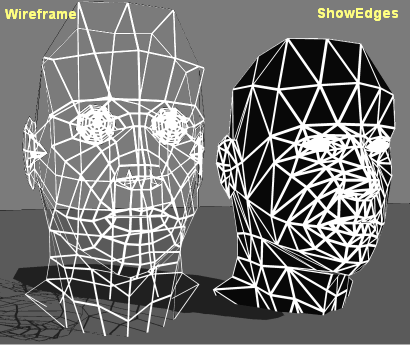
The difference between Wireframe and ShowEdges is illustrated in the figure below, which shows how the two examples render the same mesh.
Comparison of Wireframe and ShowEdges
| Location | |
| ShowEdges |
show_edges.spdl
show_edges.cpp
show_edges.h
show_edges_dll.cpp
show_edges.vcproj
GNUmakefile
|
| WireFrame Files |
WireframeOp.cpp
WireframeShader.cpp
WireframeShader.spdl
Wireframe.vcproj
GNUmakefile
|
To run the ShowEdges example
In a script editor, run this demo script:
// [ Jscript ] Demo script for ShowEdges
NewScene( null, false );
var oSphere = ActiveSceneRoot.AddGeometry( "Sphere", "MeshSurface" );
SelectObj( oSphere );
var oMaterial = oSphere.AddMaterial( "show_edges.Preset",false,"ShowEdges");
InspectObj( oMaterial.Parameters("Surface").Source );
To run the Wireframe example
In a script editor, run this demo script:
'[VBScript] Demo program for the Wireframe Softimage shader example
NewScene , false
' Create test sphere
set object = ActiveSceneRoot.AddGeometry( "Sphere", "MeshSurface" )
SetupObject object
'Shadow effect
set oGrid = ActiveSceneRoot.AddGeometry( "Grid", "MeshSurface" )
Translate oGrid, 0, -5, 0, siAbsolute, siParent, siObj, siY
oGrid.ulength = 100
oGrid.vlength = 100
SetValue "light.light.soft_light.shadow", True
sub SetupObject( in_obj )
' Add the UserDataBlob property and set it renderable
' The UserDataID must be set to the specific ID that
' the shader is expecting
set prop = in_obj.AddProperty( "UserDataBlob" )
prop.RenderData = True
prop.UserDataID = 6789
on error resume next
prop.AddCustomOp "WireframeOp",in_obj.ActivePrimitive
if ( err <> 0 ) then
MsgBox "Failed to create WriteframeOp Custom Operator" & vbCrLf & _
"Please make sure the example is fully installed"
exit sub
end if
on error goto 0
' Add wireframe shader to an empty material
set material = in_obj.AddMaterial
set oSurfParam = material.Parameters( "surface" )
set oSpriteShader = oSurfParam.connectfrompreset( "Sprite", siMaterialShaderFamily )
material.Parameters("Shadow").Connect( oSpriteShader )
set inputParam = oSpriteShader.Parameters( "input" )
on error resume next
set oWireShader = inputParam.connectfrompreset( "WireframeShader", siTextureShaderFamily )
if ( err <> 0 ) then
MsgBox "Failed to create WriteframeShader " & vbCrLf & _
"Please make sure the example is fully installed"
exit sub
end if
oWireShader.Parameters("wire_width").value = 0.1
oWireShader.Parameters("base_color").Parameters("red").value = 1
oWireShader.Parameters("base_color").Parameters("green").value = 1
oWireShader.Parameters("base_color").Parameters("blue").value = 1
oWireShader.Parameters("base_color").Parameters("alpha").value = 0
InspectObj oWireShader
end sub
The Softimage SDK includes a compiled version of ShowEdges. If you want to modify the code, you can rebuild the shader by following these instructions.
To build ShowEdges on Windows
Open an Softimage command prompt, and type devenv to start Visual Studio .NET.
Starting Visual Studio .NET from an Softimage command prompt ensures that environment variables such as XSISDK_ROOT are set (otherwise you'll get build and link errors).
Tip To load the show_edges project from the command line, type:
devenv cppsrc_ShowEdges\show_edges.vcproj
To build Wireframe on Windows
Open an Softimage command prompt, and type devenv to start Visual Studio .NET.
Starting Visual Studio .NET from an Softimage command prompt ensures that environment variables such as XSISDK_ROOT are set (otherwise you'll get build and link errors).
Tip To load the Wireframe project from the command line, type:
devenv cppsrc_Wireframe\Wireframe.vcproj
To build the example on Linux
In a shell (tcsh) window, type:
source $XSI_HOME/.xsi_<xsi_version>
Change directories to
cppsrc_ShowEdges
To remove all intermediate files before building the example, run this command:
gmake clean
To compile the example, run this command:
gmake
This example uses the following keywords:
mental ray, shader, tessellated, geometry, edges, polygon, C++ example, operator, Update, InputPort, OutputPort, UserData, UserDataBlob, GetUserData, user data, segments, CSegmentRefArray, GetSegments, CPointRefArray, MATH, CVector3, miQ_FUNC_USERPTR, miQ_INST_DATA, miQ_DATA_LABEL, miQ_DATA_PARAM