Curve and surface deformations use the U and V parameterizations of NURBS objects to twist the local space of a deformed object.
Deformation by curve distorts an object by remapping the Y axis to any curve you pick. You can animate the object in the deformed space defined by the curve and you can also animate the shape of the curve itself. This effect is sometimes called a flow path in other software.
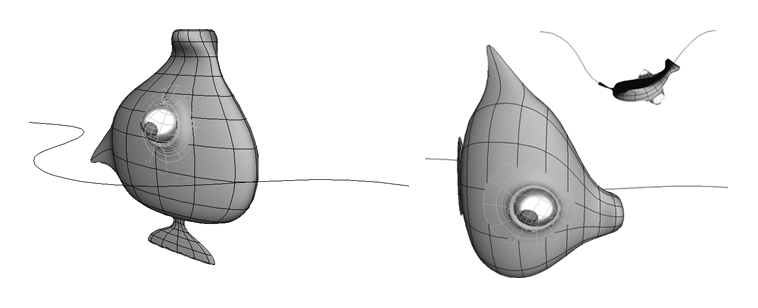
The object and curve before and after Deform by Curve is applied.
As an alternative to the Curve Deform operator, you can use the ICE-based Deform by Curve compound — see Deform by Curve [ICE Deformations].
Create a curve using any of the available tools. Note that if the curve contains extremely sharp bends, the object may become severely distorted. For information about curves in general, see Curves [Surface and Curve Modeling].
Select the object, branch, group, or model you want to deform.
Choose Deform  by Curve from the Model, Animate, or Simulate toolbar.
by Curve from the Model, Animate, or Simulate toolbar.
Pick the curve. The center of the deformed object snaps to the beginning of the curve and the Curve Deform Property Editor opens.
Use the Translation, Scaling, and Roll parameters to move the object in deformed space. You can still use the standard SRT commands to move the object in ordinary space.
If you moved either the curve or the object from the global scene center before applying the curve deformation, you can compensate with the options on the Constraint page:
Deformation by surface distorts an object by remapping the XZ plane to the UV space of a surface you pick. You can animate the object in the deformed space defined by the surface and you can also animate the deforming surface.
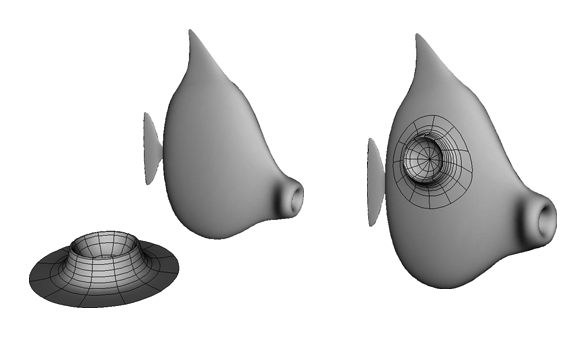
The object and surface before and after Deform by Surface is applied.
Create a surface of any shape using any of the surface or deformation tools.
Select the object, branch, group, or model you want to deform.
Choose Deform  by Surface from the Model, Animate, or Simulate toolbar.
by Surface from the Model, Animate, or Simulate toolbar.
Pick the surface. The object deforms and the Surface Deform Op Property Editor opens.
Use the Translation, Scaling, and Roll parameters to move the object in deformed space. In particular, if the object is severely distorted, try using the Scale parameters to shrink it.
You can still use the standard SRT commands to move the object in ordinary space.
If you moved either the surface or the object from the global scene center before applying the curve deformation, you can compensate with the options on the Constraint page:
Here are some tips and techniques related to deformations by curve or surface:
If you deform a clone or instance and then move points on the original object, the points of the instance move in the deformed space.
If you deform the parent of an object in branch, you can transform it in Parent mode instead of using the sliders in the property editor.
To keep the length of a curve approximately constant as you manipulate it, deform it by another curve and manipulate the second curve instead.
 Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License