There are several types of geometric objects that you can add to your scenes. The set of points belonging to an object is called its geometry, while the number of points and how they are connected is called its topology. In addition, geometric objects have attributes like centers and normals.
Softimage offers several types of geometry: polygon meshes, subdivision surfaces, curves, surfaces, and surface meshes.
Polygon meshes are quilts of polygons joined at their edges and vertices. Because their geometry is mathematically simple and quick to calculate, they are particularly useful when modeling for games and other real-time environments where speed is important. You can subdivide specific polygons in areas where you need more detail, and remove them where you require less detail.

For more information, see Modeling Polygons & Polygon Meshes [Polygon Modeling].
Subdivision surfaces, also known as subdees or subdivs, are low-resolution polygon mesh hulls that control a higher-resolution polygon mesh object. They provide many of the benefits of polygon meshes, plus the ability to approximate smooth surfaces without the need for heavy geometry in the control hull.
You can animate and texture the control hull for greater speed and interaction while you work, and then let the hull drive the high-resolution version for your final output.
Subdivision surfaces are described in more detail in Subdivision Surfaces [Polygon Modeling].
A subdivision surface created from a cube.
Curves are one-dimensional NURBS (non-uniform rational B-splines) of linear or higher degree. They have points but they are not renderable because they have no thickness. Curves serve as the basis for constructing surfaces, paths for objects to move along, controlling deformations like deform by curve and deform by spine, and so on.
For more information, see Curves [Surface and Curve Modeling].
Surfaces are two-dimensional NURBS patches defined by intersecting curves in the U and V directions. In a cubic NURBS surface, the surface is interpolated between the control points, resulting in an accurately smooth shape. Surfaces are always four-sided, and unlike polygon meshes, they do not support different textures on different areas of the object.
For more information, see Surfaces [Surface and Curve Modeling].
Surface meshes are quilts of NURBS subsurfaces acting as a single object. They overcome the limitation that surfaces must be four-sided: with surface meshes, you can create complex objects and characters with holes, legs, and so on. You can control the continuity at the junctions between subsurfaces to create complex yet seamless objects.
For more information, see Surface Meshes [Surface and Curve Modeling].
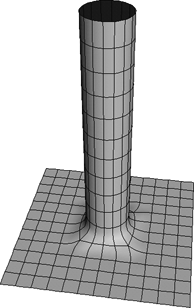
A smooth surface mesh composed of several surfaces.
Point clouds are composed of disconnected points and can be used to create particle and other effects controlled by ICE trees. You can use them to simulate things such as fire, rain, smoke, and more.
For more information, see ICE Particle Simulations.
Hair objects let you use guide hairs to control a full head of render hairs. You can style the hairs manually as well as apply a dynamic simulation.
For more information, see Hair.
