: Choose from the Simulate toolbar, from the other toolbars, or from the Hair toolbar.
: Select the fan object and press Enter.
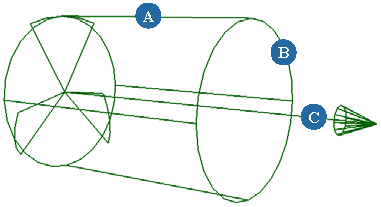
A Fan force simulates the effect of a "local" wind blowing via a cylinder on other objects. The wind's direction follows with
cylinder's axis, while wind's intensity falls off from the center to the cylinder's border, moving from bottom to top.
Fan has no effect on Soft body simulations.
For more information on forces in general, see Forces [ Simulation].
To use this force in an ICE tree, see Creating and Applying ICE Forces to ICE Simulations [ICE Fundamentals].
See the parameters in the table below that match the letters in this image.
|
|
The name of the force.
|
|
|
Toggles on/off the force effect.
|
|
|
Speed of the fan's force.
|
|
|
The amount of resistance the simulated objects have to the fan's force. A fan force with low viscosity values makes the simulated
objects resist motion more strongly, thereby slowing down their flow.
|
|
|
Uses size of the simulated objects in the fan force's calculations.
|
|
|
Radius of the fan's cylinder.
|
|
|
Length of the fan's cylinder.
|
Decay
|
|
Falloff (decay) along the fan's starting from its center and moving to its outer edges.
-
A value of 0 is no decay so a simulated object would have the same amount of influence on it throughout the radius of the
cylinder.
-
A value of 1 is a linear decay so the fan would have full influence at its center and less influence as the simulated object
gets closer to the radius edge where its influence is 0.
-
A value of 2 is the same as 1 except that it produces a quadratic, smooth falloff.
|
|
|
Falloff along the fan's cylinder axis starting from the point of its origin and moving to its end ().
-
A value of 0 is no decay so a simulated object would have the same amount of influence on it throughout the length of the
cylinder.
-
A value of 1 is a linear decay so the fan would have full influence at its origin and less influence as the simulated object
gets closer to the end of the cylinder where its influence is 0.
-
A value of 2 is the same as 1 except that it produces a quadratic, smooth falloff.
|
 Force
Force  Fan from the Simulate toolbar, Get
Fan from the Simulate toolbar, Get  Primitive
Primitive  Control Object
Control Object  Fan from the other toolbars, or Create
Fan from the other toolbars, or Create  Force
Force  Fan from the Hair toolbar.
Fan from the Hair toolbar.