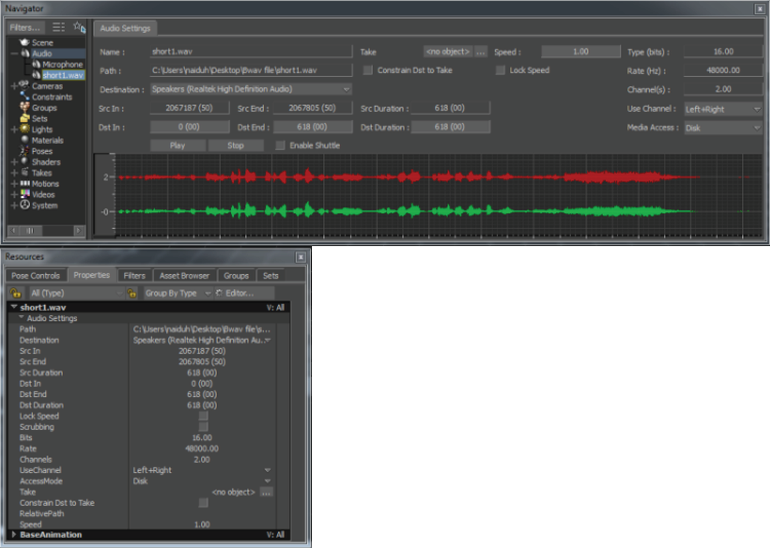
The audio settings help to adjust the speed of the audio, select left, right, or both channels, and so on. The audio settings
appear in the window and in the window tab.
From the in the window, click:
- — to hear audio content
- — to end the audio
The following table explains the audio settings in the tab.
NoteThe setting name mentioned within brackets is the corresponding name that appears in the pane of the Navigator window.
| Audio Setting |
Description |
| Path |
Path from where the audio file is imported |
| Destination |
Destination device to play the audio file. Choose the destination device from the list of all the connected audio devices.
|
| Src In Point |
The count of audio samples recorded in the source audio sequence, and the starting frame of the audio file. This information
is stored as a time stamp, only in the BWAV header files and not in the WAV files.
|
| Src End Point |
The last frame of the source audio file. |
| Src Duration |
The total number of frames included in the source audio file.
NoteThe Src In Point, Src End Point, and Src Duration are the existed parameters when the source audio files was recorded. So you cannot alter the data in these fields.
|
| Dst In |
The frame from which the audio plays in the selected destination (output device such as speakers). |
| Dst End |
The last frame of the audio file. |
| Dst Duration |
The total duration of the audio file.
NoteAlter the , , and values to specify the start and end time to play the audio file.
|
| Scrubbing (Enable Shuttle) |
Enables the shuttle mode. You can shuttle the audio, back and forth, between the start and end frames in the time line. To shuttle the audio, back and forth, press J and the left mouse button simultaneously and move the mouse to the left or right
on the . This option helps to hear the audio by increasing and decreasing the speed without manually changing the value of .
|
| Type (Bits) |
Specifies the number of bits of information recorded for each audio sample. The depth of bit (8, 16, or 24) directly corresponds
to the resolution and quality of an audio sample.
|
| Rate (Hz) |
Specifies the audio sample count per second.
NoteType and Rate values are part of the header information of the audio file.
|
| Channels |
Specifies whether the source audio is a mono (1.0) or stereo (2.0) file. |
| Use Channel |
The Left or Right (mono) and Left+Right (dual) channels are supported. If you select only the Right or Left channel, then
the graphical representation of the unselected channel appears faded in the window.
|
| Access Mode (Media Access) |
Specifies from which location to pick and play the audio file. You can choose or as the location to pick the audio file.
|
| Take |
Specifies the current take to which the audio file is assigned to. You can change the value, if there are many audio files and want to assign each audio file to different Takes.
|
| Constrain Dst to Take |
Restricts from modifying the value.
NoteTurning on this option, automatically turns on the option.
|
| Relative Path |
The location of the audio file. |
| Speed |
The velocity at which sound travels in a given medium under specified conditions. Increase or decrease the audio speed according
to the slow or fast movements in your animation scene. Using this option, you can adjust the audio speed from 0.01 to 10. This means, you can play the audio 100 times slower or
10 times faster than the original speed (1.0).
|
See the Audio settings topic for more information.
To get the relative path of the audio file:
- From the menu, select .
The window appears.
- Specify a name for the file, and click .
The path where you saved the file with audio content appears in the field. You can use the relative path, later, to open the file with the audio content.