The Mapping constraint lets you map one Parent/Child relation to another Parent/Child relation. It is mainly used to scale movement between limbs or other structures of different sizes.

Mapping constraint
For example, in the following figure, a Mapping constraint is created using four cubes. When the constraint is activated, the constrained object moves when the reference, source object, or the Source reference is translated or rotated.
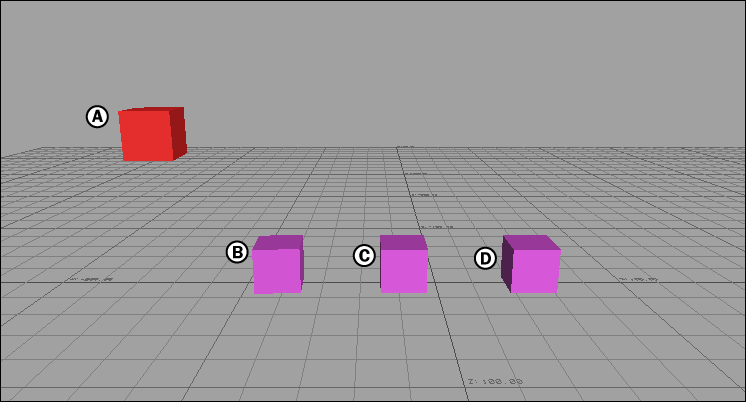
Mapping constraint A. Constrained object (child) B. Reference (parent) C. Source Object (child) D. Source Reference Parent)

Mapping constraint activated: rotating or translating B, C, and/or D creates motion in A.